Difference Between 32-Bit and 64-Bit Operating Systems
Computer architecture uses 32-bit integers, memory addresses, and data units. 64-bit computing uses processors that specify different data path widths, integer sizes, and memory addresses with a width of 64-bits. They are the central processing unit for any computer. It also specifies the driver and software program which utilizes the particular architecture. Different software supports both these architectures, and choosing does make a difference if the two were programmed for other systems. People often refer to 32-bit hardware and software as x86 or x86-32. The 64-bit hardware and software are referred to as x64 or x86-64. Let’s look at other differences between the 32-Bit vs 64-Bit operating systems in detail.

What is 32-bit?
In computer systems, 32-bit refers to the fraction of bits that can be transmitted or processed in parallel. In other words, 32 bits is the number of bits that constitute a data element. A 32-bit register can store 232 various values. The integer representation determines the range of integer values that can be saved in 32 bits. With the two most famous representations, the range is 0 through 4,294,967,295 (232 − 1) for representation as an (unsigned) binary number and −2,147,483,648 (−231) through 2,147,483,647 (231 − 1) for representation as two’s complement.
One significant consequence is that a processor with 32-bit memory addresses can immediately access 4 GiB of byte-addressable memory at most. Prominent 32-bit instruction set designs used in general-purpose computing include the IBM System/360 and IBM System/370 (which had 24-bit addressing) also the System/370-XA, ESA/370, and ESA/390 (which had 31-bit addressing), the DEC VAX, the NS320xx, the Motorola 68000 family (the initial two models of which had 24-bit addressing), the Intel IA-32 32-bit version of the x86 structure, and the 32-bit versions of the ARM, SPARC, MIPS, PowerPC, and PA-RISC designs. 32-bit instruction set architectures used for embedded computing involve the 68000 family and Cold Fire, x86, ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, and Infineon TriCore designs. 32-bit usually refers to the state where data is saved, read, and processed.
When associated with operating systems and processors, this implies how many 1s and 0s are being managed to represent your data. The more bits the system can process, the more data it can work at once.
What is 64-bit?
64-bit is the number of bits that can be processed or transmitted in parallel or the number of bits used for individual elements in data formats. It also refers to word sizes that describe a particular class of computer architecture, buses, memory, and CPU. In computer design, the 64-bit indicates those 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units that are at most 64-bit or eight octets wide. In microprocessors, 64 bits means the width of a register. A 64-bit microprocessor can process memory addresses plus data represented by 64 bits. A 64-bit register stores 264 = 18 446 744 073 709 551 616 separate values. The name can also indicate the size of low-level data types, such as 64-bit floating-point numbers.
Head To Head Comparison (Infographics)
Below are the top 4 differences between 32-bit and 64-bit Operating Systems
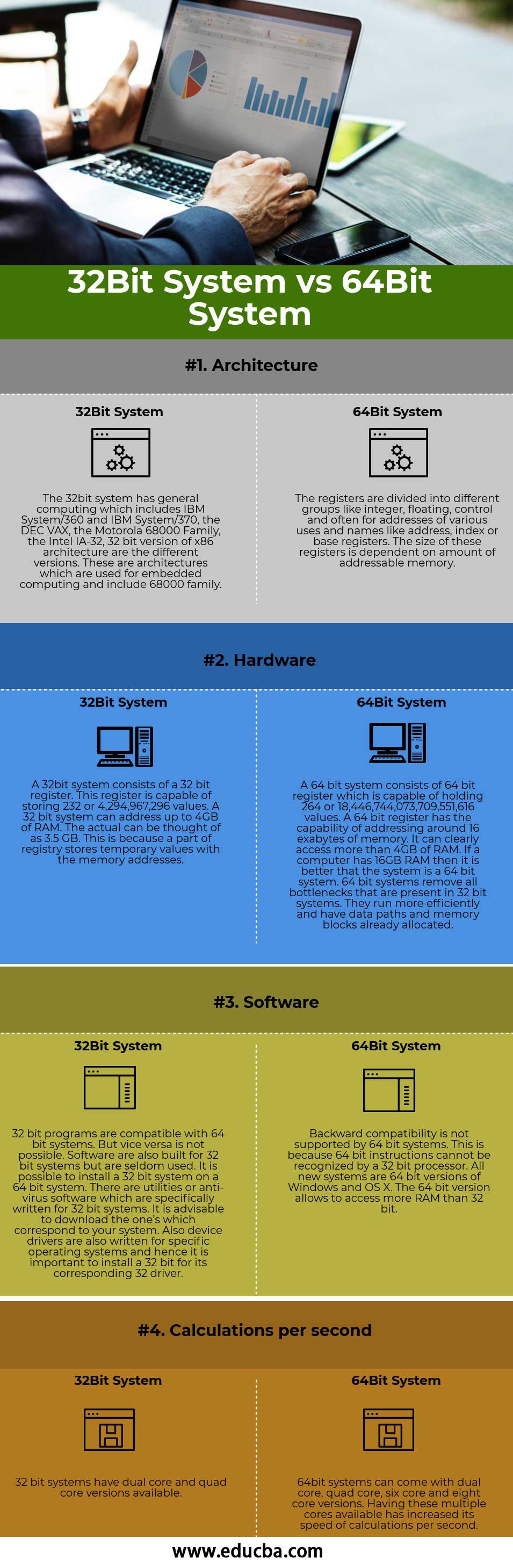
Key Differences Between 32-Bit vs 64-Bit Operating Systems
Both 32-Bit vs 64-Bit operating systems are popular choices in the market. Let us discuss some of the significant Differences:
- To begin with the comparison, we can say that a 64-bit processor is more capable than a 32-bit one. It can handle more data at once. In addition, it can store more data and more computational values, including memory addresses, which helps access approximately four billion times the physical memory that a 32-bit processor can access.
- A 32-bit processor can easily handle a limited amount of RAM. This can be considered as 4GB. 64-bit systems, on the other hand, can access much more. It is essential to have this as the operating system should be designed in a way by which it can access more memory. The basic version of operating systems has its limitations on RAM, which applications can utilize. $GB is the maximum that a 32-bit system can use. The latest versions of the 64-bit system can increase the processor’s capabilities. Video games and other high-performance applications require high memory, making 64-bit systems superior in these cases.
- If you were a Windows user, you would have noticed two folders in Program Files: Program Files and Program Files (x86). The 32-bit architecture though old, has been there for a long time. Many applications host and utilize 32-bit architecture. The new systems, which have 64-bit systems, can run 32-bit and 64-bit software together. Hence they have two different directories for both. When encountered, the system moves a 32-bit application to the x86 folder and a 64-bit application to the other folder.
- By using a 64-bit system, a lot of multitasking is possible. The user can easily switch between the different applications without any glitches. The games demand high performance, and the applications that consume a lot of memory can run efficiently on a 64-bit processor.
- 32-bit processors are proficient in managing a limited amount of RAM (in Windows, 4GB or less), and 64-bit processors can use much higher.
- The least amount of RAM needed for a 64-bit Windows OS is 2 GB, in contrast to 32-bit Windows, which requires 1 GB RAM. It’s slightly evident because, with large-sized registers, more memory will be required.
- A significant difference between 32-bit and 64-bit processors is the number of calculations per second they can function, influencing the speed at which they can complete tasks. 64-bit processors can proceed in dual-core, quad-core, six-core, and eight-core versions for home computing. Multiple cores improve the number of calculations per second a computer can perform, which enhances processing power and makes the computer run faster. Software programs that need many calculations to function smoothly can operate quicker and more efficiently on multi-core 64-bit processors, for the most part.
- One point to remark is that 3D graphics programs and games do not benefit much from shifting to a 64-bit computer unless the program is a 64-bit program. A 32-bit processor is adequate for any program addressed for a 32-bit processor. In the case of computer games, you’ll get much more performance by upgrading the video card rather than getting a 64-bit processor.
- In the end, 64-bit processors are becoming more and more common in home computers. Most manufacturers develop computers with 64-bit processors due to lower costs and because more users use 64-bit operating systems and programs. Computer components retailers are offering fewer and fewer 32-bit processors and soon may not offer any at all.
Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between 32-Bit vs 64-Bit operating systems:
| The Basis Of Comparison |
32-Bit System |
64-Bit system |
| Architecture | The 32-bit system has general computing, including IBM System/360 and IBM System/370, the DEC VAX, the Motorola 68000 Family, the Intel IA-32, and the 32-bit version of x86 architecture the different versions. Embedded computing architectures include 68000 families. | We categorize registers into integer, floating, and control groups and assign them names such as address, index, or base registers based on their uses and addresses. The size of these registers is dependent on the amount of addressable memory. |
| Hardware | A 32-bit system consists of a 32-bit register. This register is capable of storing 232 or 4,294,967,296 values. A 32-bit system can address up to 4GB of RAM. The actual can be thought of as 3.5 GB. This is because a part of the registry stores temporary values with the memory addresses. | A 64-bit system consists of the 64-bit register, which can hold 264 or 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 values. A 64-bit register has the capability of addressing around 16 exabytes of memory. It can access more than 4GB of RAM. If a computer has 16GB RAM, then it is better than the system is a 64-bit system. 64-bit systems remove all bottlenecks that are present in 32-bit systems. They run more efficiently and have data paths and memory blocks already allocated. |
| Software | 32-bit programs are compatible with 64-bit systems. But vice versa is not possible. Although the software is built for 32-bit systems, it is seldom used. It is possible to install a 32-bit system on a 64-bit system. Software developers specifically write utilities or anti-virus software for 32-bit systems. It is advisable to download the ones which correspond to your system. Also, device drivers are written for specific operating systems, so installing a 32-bit for its corresponding 32 drivers is essential. | 64-bit systems do not support backward compatibility. A 32-bit processor cannot recognize 64-bit instructions. All new systems are 64-bit versions of Windows and OS X. The 64-bit version allows accessing more RAM than 32-bit. |
| Calculations per second | 32-bit systems have dual-core and quad-core versions available. | 64bit systems can come with dual-core, quad-core, six-core, and eight-core versions. Having these multiple cores available has increased the speed of calculations per second. |
Conclusion
If you install any operating system, you must know your computer’s processor type and ensure you install the right one. With this, it is also necessary to see your computer’s operating system. Most modern-day systems have 64-bit processors that provide better performance in many aspects. They offer better memory utilization and speedy system functioning. They also have more significant memory utilization when compared to 32-bit processors. But sometimes, there will not be 64-bit drivers, which is when a 32-bit system can rescue you. It is the best option to buy a 64-bit operating system with 64-bit applications that help in providing the best performance.
In short, the principal contrast between the 32-bit and 64-bit is that 64-bit can process much greater designs. Due to the amount of data volume processed and produced by 64-bit, the approach to the resulting system has changed. Nevertheless, if you plan on having less than 3Gb of RAM, have an older computer, or have a 32-bit processor, you usually recommend a 32-bit system.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between the 32-bit vs 64-bit operating systems. Here we also discuss the key differences between infographics and comparison tables. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

