Updated March 28, 2023
Definition of XPath Position
The position is the most predefined method in XPath language which is used to set or trace the element node at the correct position of the given node type. It is used to execute the integer that represents the ordinal position of the context. Here the position initiates at one which is set as the first node from the given node-set and increased till it reaches the value of the last function. In this article, the definition of XPath position, usage, and examples are discussed in brief.
What is XPath’s position?
If there are number n child tags that are present under the parent tag which is used to place the child tag in the appropriate position with the other child tag, to implement this position() function is used in XPath. It is used in a function that executes the integer that fixes the node-set of context. The position initiates the node-set for the first context and increases to the value that has the last function.
How to use the XPath position function?
The root element of an XML document and a simple XPath position and syntax is discussed below.
The supermarket which is the root element has five-element nodes which are applied in the entire descendant:: the axis.
(supermarket: counter, supermarket: kids, Supermarket: groceries, supermarket: veggies, supermarket: clothes)
In the location path, it is defined as follows,
/supermarket : supermarket / descendant :: *
This function sets the node-set values which is composed of five element nodes that helps to locate by adding the predicate like below syntax,
/supermarket : supermarket / descendant :: * [position () = 3]
It helps to select the third node present in the local node set.
Now the value is passed with the help of the position () function which is applied in both reverse and forward directions from the axis. In the axes, to travel forward type like the prior example, descendant:: the nodes are selected in the given order from the document. If the user tries to access the axis in reverse, he should provide the appropriate negative values to fetch the element from the node. So to frame a location path, the syntax should start at the clothes node and then locate the prior supermarket: counter node.
Here the location path is framed like below,
// clothes/ prior:: * [position ( ) = 3]
To work in the reverse order, the syntax should be represented as prior #1 which fetches the result from the supermarket : clothes and for prior or ancestor #2, it fetches the data from the supermarket: veggies
The position () function is more mandatory for two valid reasons, one is it can be mentioned in any step from the location and the value can be fetched easily and it is not mandatory to travel along with the entire XML document.
// clothes/ prior:: * [position ( ) = 3]
Or // clothes/ prior:: * [3]
The other reason is in many XSLT functions, it is performed for all the nth values present in a few kinds of nodes and then the source tree is transformed.
If the user wants to choose every even row of the table in the document, then all the odd rows should be removed. In other terms, all the alternate rows can be selected. It can be easily achieved using the function position () in the XPath and it works well with numeric operator mod.
XPath position Selenium Locators
The below steps are used in selenium to locate the position () in the function of XPath,
The basic link of selenium should be opened in the default chrome browser where the application chropath should be installed prior. The link to the application is found on the standard selenium website.
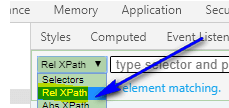
In the chrome browser, choose chropath, and there select Rel XPath
Then Relative expression of XPath should be selected using the //p in the chropath option and the given details are observed from the selected location.
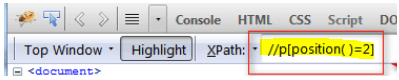
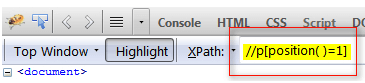
The user can locate the details by using the position () from the function of XPath in the relative expression available in XPath. It can be defined as Relative XPath expression :: // p [position ( ) = 3]
Then as per the syntax, the relative expression in chropath is executed.
Then to locate the next option the same syntax is used but the position values should be changed.
Relative XPath expression :: // p [position ( ) = 2]
The relative XPath expression is fed in chropath and all the option which is given should be executed.
If already the application chropath is installed and the chrome browser is updated, then the process can be initiated in prompt. The initial input tag is used by applying the relative XPath expression
(// input) [position =1].
If the number of input tags is used with position () with relative XPath expression.
Then it should be given as relative XPath expression : ( // input ) [position = n]
Execute the above syntax and give the correct tag in place of n to fetch the required data.
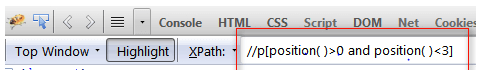
In XPath relative expression with greater or lesser than symbol is used when the value between two elements should be compared and fetched. The syntax is below,
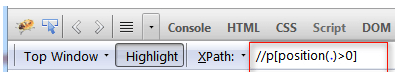
// p [ position () > O ]. Here all the p tags are chosen in the HTML and observe that the suitable values are fetched.
If the user wants to trace all the elements from the local node-set, which is placed between greater than 0 and lesser than 2, it can be executed by defining the function with position ( ) and it can be compared with position () > 2. The syntax to fetch the between values of 0 and 2 are
// p [ position ( ) > 0 and position ( ) < 2 ].
Conclusion
Hence the selenium locators and usage of XPath position in the document are discussed and the user can be implied to fetch the data easily from the higher dimensional document.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XPath Position. Here we discuss the Definition, What is XPath’s position, How to use the XPath position function, and examples with code implementation respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –