Updated March 27, 2023
What is Impala?
IMPALA is an open-source parallel processing query engine designed on top of clustered systems(HDFS for an example) written in C++ and java for processing of large volume of data with SQL interactions. It has interactive SQL like queries where we can fetch and work on data as needed.
Why Impala?
So we had hive that is capable enough to process these big data queries, so what made the existence of impala we will try to find the answer for this. hive basically used the concept of map-reduce for processing that evenly sometimes takes time for the query to be processed. to overcome this slowness of hive queries we decided to come over with impala. it offers high performance, low –latency SQL queries. so it is basically faster than hive. not built on map-reduce, impala has its own execution engine and stores the results in-memory making it very fast for execution. it gives results in real-time so it best fits for data processing tools like tableau and all. it also integrates well with hive meta store to share databases and tables between hive and impala.
The Default File Format used by IMPALA is PARQUET, parquet being a columnar data storage model store data vertically in a data warehouse. This has a huge performance impact in the queries as aggregation function on numeric fields reads the only column split part file rather than the entire data set.
Architecture of Impala
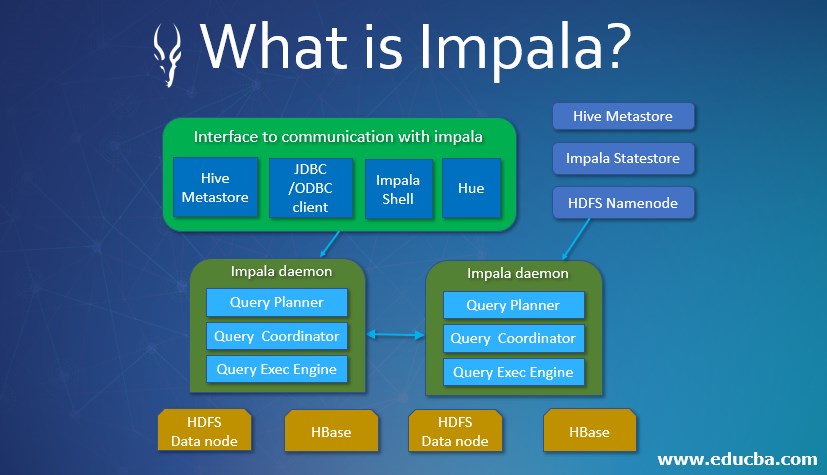
Now let us have a look over the architecture:

1. Client
We can have many entities to interact with IMPALA such as JDBC/ODBC Client, impala-shell, Hue, these are the client for IMPALA.
2. Hive Meta Store
To store information about the data available we use Hive MetaStore. It just lets impala know about the databases available and the structure for these databases.
3. Daemons
It is the core part of IMPALA that runs on each node of a cluster. So basically daemons are installed on every data node. Daemons read data from HDFS / HBASE and accept queries from Hue or any Data Analytics tools via the connection. Once that is done it distributes work across the cluster and parallelizes the query.
The job launching node is called as the Coordinator Node. The daemons submit the results to these coordinator nodes only and further, the result is prepared. A query plan is made that parses the Query, a single plan is made first that is further distributed afterward. Then the Coordinator is responsible for executing the entire Query.
4. StateStore Daemons
So for keeping track of the daemons that are running and to report the point of failure (if any), these Daemons are used. Basically they are responsible for keeping track of the active daemons available. Only one node in the cluster needs to have this installed and working. The impala daemons continuously communicate with the State Store Daemons to confirm their health and accept the new work.
5. Catalog Daemons
Catalog Daemons basically distributes the metadata information to the impala daemons and checks communicate any changes over Metadata that come over from the queries to the Impala Daemons. So there are some changes we need to refresh or invalidate the catalog daemons using the “INVALIDATE METADATA “ command. It is suggested to have State Store and Catalog Daemons over the host because any change request will be known to both the Daemons.
6. HBASE and HDFS
These are basically the storage level for the data. So basically whenever a query after planning and optimization is run over impala they come over here for data handling.
Data Types Supported by Impala
It supports all the datatypes be it numeric, character, date.
- Tinyint
- Smallint
- Int
- Bigint
- Float
- Boolean
- String
- Varchar
- Char
- Double
- Real
- Decimal
Features of Impala
There are several features of Impala that make its usage easy and reliable now let us have a look over some of the features.
- Faster Access: It is comparatively much faster for SQL Queries and data processing.
- Storage System: Has the capability to access HDFS and HBASE as its storage system.
- In-Memory Processing: the data are present in memory that makes the query optimization faster and easy.
- Secured: It offers Kerberos Authentication making it secure.
- Multi API Supports: Its supports multiple API that helps it for the connection with the data sources.
- Easily Connected: It is easy to connect over many data visualization engines such as TABLEAU, etc.
- Built-in Functions: Impala comes over with several built-in Functions with which we can go over with the results we need. Some of the built-in function IMPALA supports are abs,concat, power, adddate, date_add, dayofweek, nvl, zeroifnull.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- All the basic features we look over as high speed, in-memory computation all comes over as an advantage that focuses the benefits of having IMPALA.
We will check for some disadvantages that IMPALA is having making it a scope for further development:
- Refreshing every time on the metadata change. On every change in metadata or tables, we have to refresh the content that makes the changes visible in the hive.
- We can only read a text file in impala there is no scope for reading the binary files.
- We cannot update or delete individual records in impala.
There are also lots of other things that can be needed as a scope of improvement for IMPALA.
Conclusion
From the above article, we see the properties of how IMPALA is used and what are the various features that make IMPALA a unique and more convenient one. The In-Memory Computation makes it faster for data access and other SQL operations.
We also checked the internal working on how the Daemons are worked and how they plan for execution is made. We checked all the built-in functions supported by IMPALA too. So from the above article, we can have a clear picture of the working of IMPALA and how good it is to use for Big Data Applications.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is Impala. Here we discuss the Introduction and the Architecture of Impala along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


