Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Virtual Keyword in C++
A virtual keyword in C++ is used to create a virtual function in C++. The virtual function is the parent class function which we want to redefine in the child class. The virtual function is declared by using the keyword virtual. When we define the virtual function the keyword virtual is to be proceeding in the declaration of the function. The virtual keyword tells the compiler to perform late binding or dynamic linkage on the function.
The single pointer is required to refer to all objects of different classes. Therefore, the pointer is created on the superclass to refer all the objects of the derived class and then the superclass pointer contains the address of the object of the derived class always run the superclass function. So, to resolve this we use the virtual function. So, when the virtual function is created in the superclass then the C++ compiler identifies which function is to be executed at run time and the identification of the function takes based on the type of object the superclass pointer pointing.
Virtual Function
The virtual functions of the syntax are given below:
Syntax
class name_class
{
public :
virtual return fun(arg1, arg2, ..)
{
//code inside the function
}
}As in the syntax, the fun() declares by the virtual keyword, which means the child class can redefine the same methods.
Examples of Virtual Keyword in C++
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void disp()
{
cout << " Message from the class A\n ";
}
};
class B :public A
{
public:
void disp()
{
cout << "Message from the class B\n";
}
};
int main()
{
A* obj1; // super class pointer
B obj2; // child class object
obj1 = &obj2;
obj1-> disp(); // Late Binding Occurs
}Output:
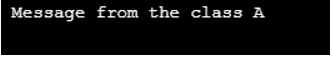
In the above program the superclass A having the function disp( ), which is a rewrite in the derived class B. In the main function the disp( ) method is calling on the obj1 object (which is a dynamic binding or late binding. Dynamic binding is a process in which, which specific function to execute is decide at the run time) and disp( ) function of class A is executed.
Example #2
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
virtual void disp()
{
cout << " Message from the class A \n ";
}
};
class B :public A
{
public:
void disp()
{
cout << "Message from the class B\n";
}
};
int main()
{
A* obj1; // super class pointer
B obj2; // child class object
obj1 = &obj2;
obj1-> disp(); // Dynamic Binding Ocuurs
}Output:
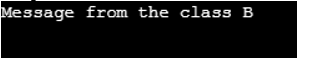
The above program code is the alteration of the program 1, the disp() function is defined with the keyword virtual and now when the obj1 calling the disp() function, the disp() function of the child class B is executed.
Example #3
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
virtual void disp()
{
cout << " Message from the class A\n ";
}
};
class B :public A
{
public:
virtual void disp()
{
cout << "Message from the class B\n";
}
};
int main()
{
A* obj1; // super class pointer
B obj2; // child class object
obj1 = &obj2;
obj1-> disp(); // Dynamic Binding Ocuurs
}Output:
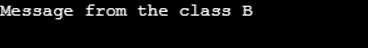
The above program code is the alteration of the program 2, the disp() function which is also redefining with the keyword virtual in class B and now when the obj1 calling the disp() function, the disp() function of the child class B is executed.
Next, we write the program for the pure virtual function. The pure virtual function is a function for which don did not have implementations. The pure virtual function also called an abstract virtual function. The pure virtual function declaration assigns 0, as shown in the below code –
Example #4
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
virtual void disp()=0;
};
class B :public A
{
public:
void disp()
{
cout << "Message from the class B\n";
}
};
int main()
{
A* obj1; // super class pointer
B obj2; // child class object
obj1 = &obj2;
obj1-> disp(); // Dynamic Binding Ocuurs
}Output:
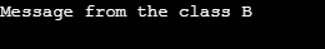
Advantages of Virtual Keyword in C++
- Virtual functions are used to achieve runtime polymorphism.
- If a class is derived from a class having a virtual function, then the function definition can be redefined in the derived class.
Rules of Virtual Keyword in C++
- The Virtual keyword in C++ use in the function declaration.
- Virtual functions must be class members.
- The virtual function accessed through object pointers.
- The virtual function cannot be declared as static.
- The virtual function can be friends from another class.
- If the virtual function is not used in the superclass then also we can define it in the superclass.
- The signature of a virtual function of the superclass and the child classes should be the same, so-called as function overriding, else if the two functions with the same name but different signature, it is considered as the overloaded functions in C++.
- We can have a virtual destructor but not have a virtual constructor.
Conclusion
- A virtual keyword in C++ is used to create a virtual function in C++.
- The virtual function is the parent class function which we want to redefine in the child class.
- The single pointer is required to refer to all objects of different classes.
- The superclass pointer contains the address of the object of the derived class always run the superclass function.
- The Virtual functions must be class members, must be class members, cannot be declared as static, accessed through object pointers.
- The signature of a virtual function of the superclass and the child classes should be the same, so-called as function overriding, else if the two functions with the same name but different signature, it is considered as the overloaded functions in C++.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Virtual keyword in C++. Here we discuss the Introduction and the Advantages of Virtual keyword in C++ along with its Syntax of the virtual function. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


