What are the VBA Operators?
Before we move to learn what the operators in VBA are, we must clear our basics first. In general, what is an operator? Operators are the symbols in any computer language or mathematical calculation which is used to compute or compare some given expression. For example, we have mathematical operators like Addition (+), Subtraction (-), Multiplication (*), Division (/) and exponential (^). There are logical operators And Or and Not. Then there are comparison operators, which is Equals To and others. In VBA, we have similar operators to work with our day to day code.
In VBA, we mostly use the comparison operators in most of the line of our code. Let us look at the comparison operators at first. What are they?
- Equals To ( = ): This operator is used to find out whether two given values are exactly similar or not.
- Greater Than ( >): This operator is used to find out whether a given value is greater than the other given value or not.
- Less Than (<): This operator is used to find out whether a given value is smaller than the other value or not.
- Greater than or Equals to (>=): This operator is like a combination of Equals to and greater than an operator. It returns true if the certain value is greater than or equals to the other value.
- Less Than or Equals To (<=): This operator is like a combination of Equals to and smaller than an operator. It returns true if the certain value is smaller than or equals to the other value.
The value returned by these comparison operators are either true or false.
Now, apart from the comparison operators in excel, there is another type of operator which is also used mostly in VBA, and they are logical operators. They are as follows:
- And Operator: This operator returns the value true if both of the given conditions are true in the given conditions. Even if a single condition is false, the value returned is false.
- Or operator: This operator returns true if any one of the given conditions is true.
- Not operator: This is also called a Negation Operator. It returns the opposite value of the given condition.
How to Use Operators Function in Excel VBA?
Below are the different examples to use Operators Function in Excel using VBA code.
Now let us test these basic operators through some examples and learn how they work.
VBA Operators Function – Example #1
Let us first test how the equals to operator work.
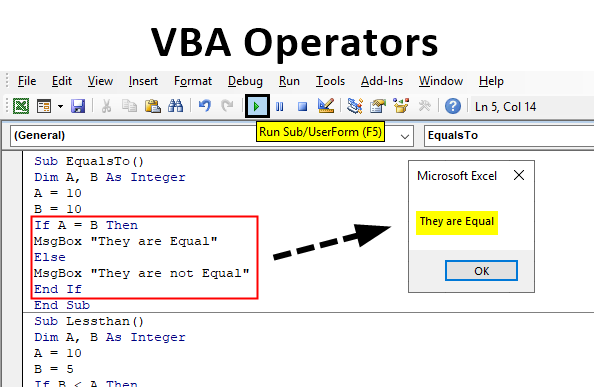
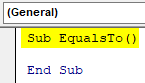
Step 1: Insert a module in the VB Editor and start the subprocedure as follows:
Code:
Sub EqualsTo() End Sub
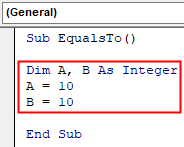
Step 2: Define two variables as Integer and assign them some random value as shown below,
Code:
Sub EqualsTo() Dim A, B As Integer A = 10 B = 10 End Sub
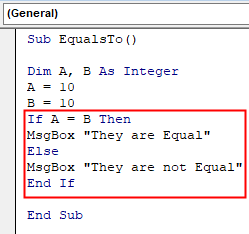
Step 3: Now, let us test whether the two values in A and B are the same or not using the Equals To Operator.
Code:
Sub EqualsTo() Dim A, B As Integer A = 10 B = 10 If A = B Then MsgBox "They are Equal" Else MsgBox "They are not Equal" End If End Sub
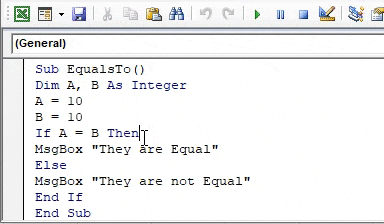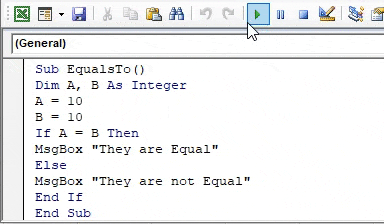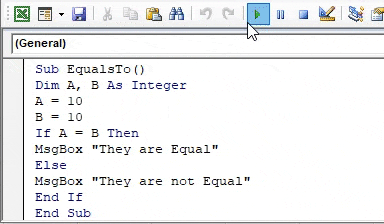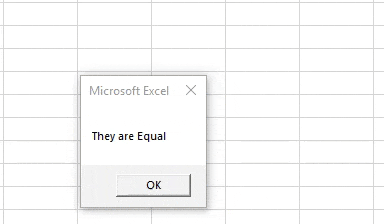
Step 4: We can see that both the given values are equal as they both have the same value. Execute the above code and find the result as below,
VBA Operators Function – Example #2
Now let us test the less than operator as follows,
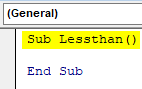
Step 1: Start another subprocedure as follows,
Code:
Sub Lessthan() End Sub
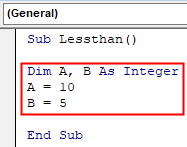
Step 2: Let us start again by declaring two variables as integers and assign them some random variables as follows,
Code:
Sub Lessthan() Dim A, B As Integer A = 10 B = 5 End Sub
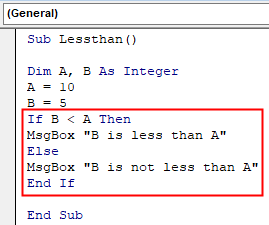
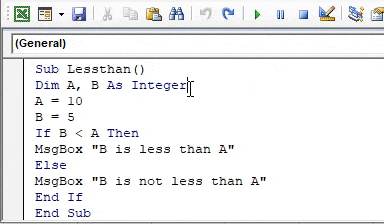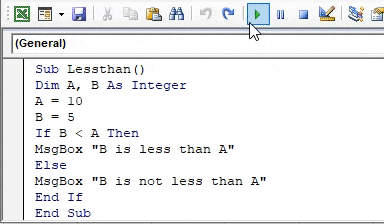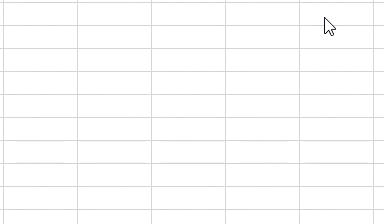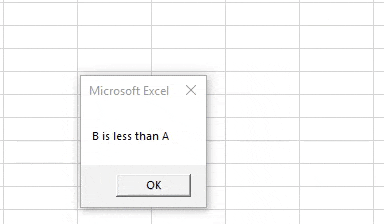
Step 3: Now let us test that if B is smaller than A or not using the IF statement as Less than operator as follows,
Code:
Sub Lessthan() Dim A, B As Integer A = 10 B = 5 If B < A Then MsgBox "B is less than A" Else MsgBox "B is not less than A" End If End Sub
Step 4: We can see that B is certainly less than A, but let us execute the code and find out the result as follows,
VBA Operators Function – Example #3
Now let us use the greater than or Equals to an operator in another example as follows,
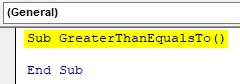
Step 1: In the same module, declare another subprocedure as shown below,
Code:
Sub GreaterThanEqualsTo() End Sub
Step 2: Now define another two sets of variable and assign them some random values as follows,
Code:
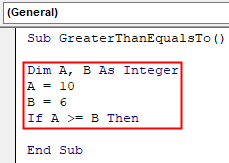
Sub GreaterThanEqualsTo() Dim A, B As Integer A = 10 B = 6 If A >= B Then End Sub
Step 3: Now, let us use the IF statement to use Greater than or equals to an operator to find out whether A is greater than or equals to B or not as follows,
Code:
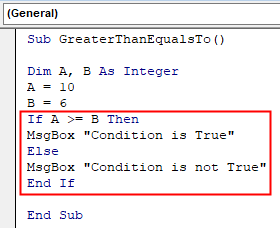
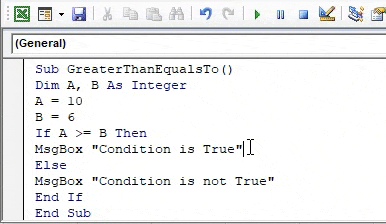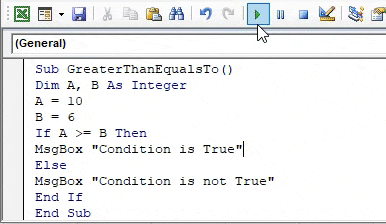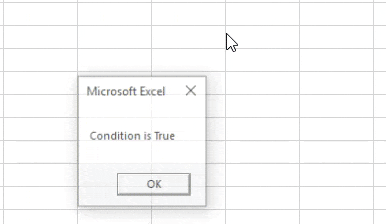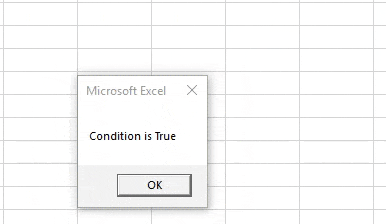
Sub GreaterThanEqualsTo() Dim A, B As Integer A = 10 B = 6 If A >= B Then MsgBox "Conditions is True" Else MsgBox "Condition is not True" End If End Sub
Step 4: Now execute the above code and find out the following result,
VBA Operators Function – Example #4
Now, let us use the logical operators in our example. First, we will use the And Operator.
Step 1: Let us define another subprocedure for this fourth example as follows,
Code:
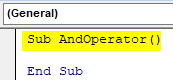
Sub AndOperator() End Sub
Step 2: To use And Operator, we need two conditions, so to make such, we need to declare four variables this time and assign them some random values as shown below,
Code:
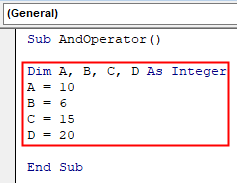
Sub AndOperator() Dim A, B, C, D As Integer A = 10 B = 6 C = 15 D = 20 End Sub
Step 3: Now, let us use the IF statement with the AND operator as follows,
Code:
Sub AndOperator() Dim A, B, C, D As Integer A = 10 B = 6 C = 15 D = 20 If A > B And C > D Then MsgBox "True" Else MsgBox "False" End If End Sub
Step 4: Now we have two conditions together, we know that both conditions are true by looking at the values, so when we execute the code, we should get the following result,
Step 5: For demonstration purpose, let us reverse one condition as C>D and run the code again to get the following result.
VBA Operators Function – Example #5
Similar to And Operator, let us use the OR operator in another example. As we know, if any of the condition is true, we will get True as a result. Let us test it.
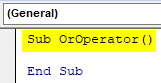
Step 1: Declare a subprocedure for this example,
Code:
Sub OrOperator() End Sub
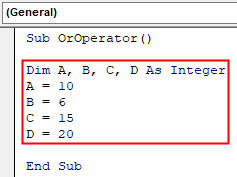
Step 2: Since we need two conditions again, let us define four variables and assign them random values as shown below,
Code:
Sub OrOperator() Dim A, B, C, D As Integer A = 10 B = 6 C = 15 D = 20 End Sub
Step 3: Let us use the OR operator with the IF statement, and as a previous example, we will have one condition as true and another as false as shown below,
Code:
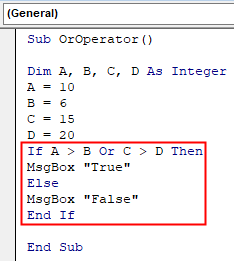
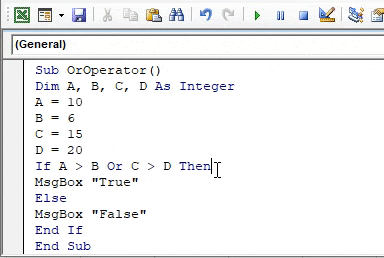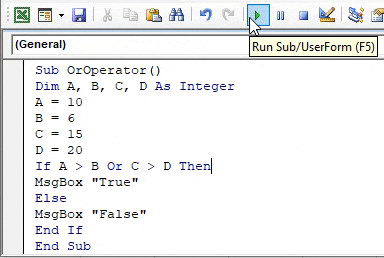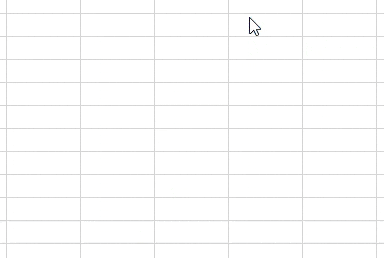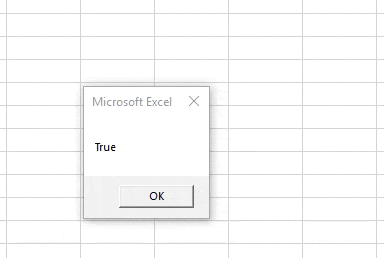
Sub OrOperator() Dim A, B, C, D As Integer A = 10 B = 6 C = 15 D = 20 If A > B Or C > D Then MsgBox "True" Else MsgBox "False" End If End Sub
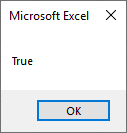
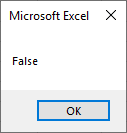
Step 4: Let us execute the above code and find out the following below result as follows,
Even if we reverse the conditions, we will get the same result as long as one condition returns true.
Things to Remember
- Operators are symbols in VBA which are used in our calculations or comparisons.
- The value returned by operators is either true or false.
- The Equals to an operator (=) is an operator for equality. It does not assign any values.
- Though operators behave like functions, they are not functions. They are used with other functional statements, such as the If statement in the above examples.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Operators Function. Here we discuss how to use Operators Function in Excel VBA along with some practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –