Excel VBA Error Handling
Error Handling is a very useful & significant mechanism for programming languages like VBA. Error control or prevention is an aspect of Error handling which means taking effective & significant measures inside a VBA script to avoid the occurrence of an error pop up message.
Different Types of Errors in VBA
- Syntax Error or Parsing error
- Compile or Compilation Error
- Runtime Error
- Logical Error
The above errors can be rectified with the help of below mentioned debug & different ‘On Error’ Statements inserted in between a code.
On Error Resume Next
On Error Goto 0
On Error Goto <Label>
On Error Goto -1
VBA Error Handling with the help of Different ‘ON ERROR’ Statements
Example #1 – VBA Compile Errors
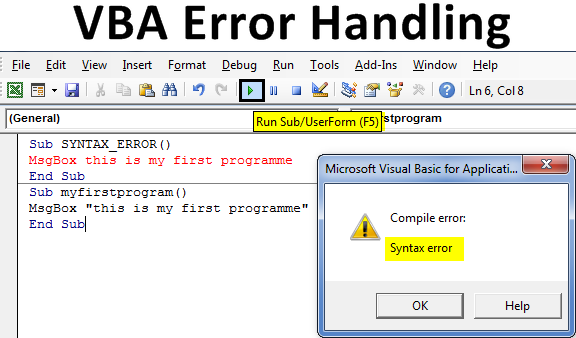
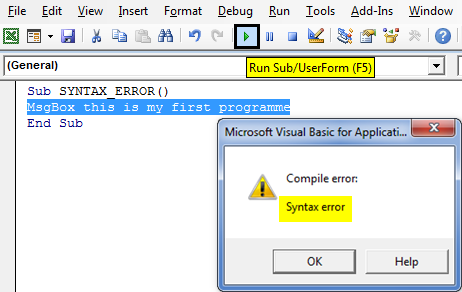
When there is an error in a statement or syntax of VBA code, when you mistype a code by mistake, it will be highlighted in red color depending on the setting options in tools (If you have selected Auto syntax check).
A popup message box of compile error will appear when you run the code with incorrect syntax.
Code:
Sub SYNTAX_ERROR() MsgBox this is my first program End Sub
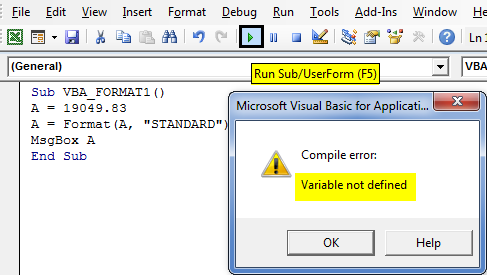
“COMPILE ERROR: VARIABLE NOT DEFINED” is the most common error which appears as a popup message. when the referencing variable is not defined, this error occurs.
Code:
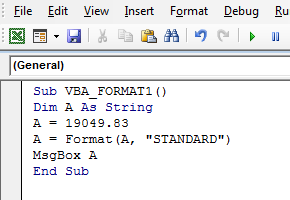
Sub VBA_FORMAT1() A = 19049.83 A = Format(A, "STANDARD") MsgBox A End Sub
I have not declared the variable type as String; therefore, this error occurs. So, I need to declare a variable as Dim A As String.
Code:
Sub VBA_FORMAT1() Dim A As String A = 19049.83 A = Format(A, "STANDARD") MsgBox A End Sub
Example #2 – VBA Runtime Error
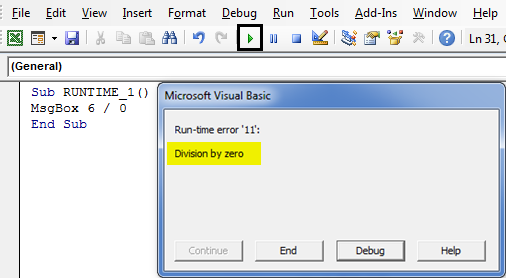
When impossible mathematical statements or terms present in a statement, then this runtime error occurs.
Code:
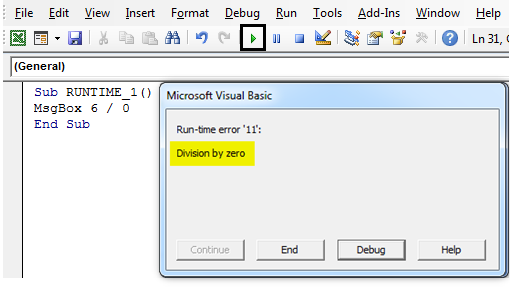
Sub RUNTIME_1() MsgBox 6 / 0 End Sub
Example #3 – VBA Logical Errors or Bugs
These errors are very difficult to track; neither will get highlighted nor a pop-up error message appears. it will result in unexpected actions & incorrect results.
Example: When two variables are present in code, it may contain an incorrect one. In this case, a logical error occurs.
How to Prevent Errors in VBA?
Let’s check out How to Prevent the above Different Types of Errors in VBA Excel.
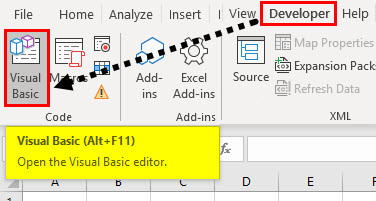
Step 1: To open a VB Editor window, Select or click on Visual Basic in the Code group on the Developer tab or you can directly click on Alt + F11 shortcut key.
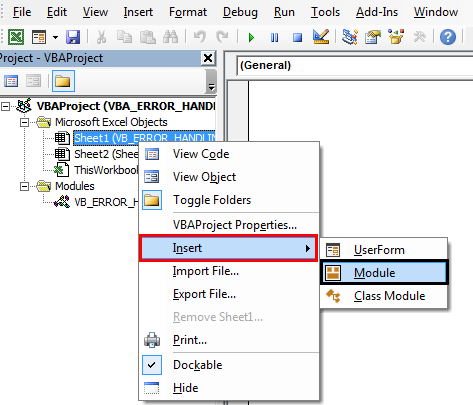
Step 2: To create a blank module, under the Microsoft excel objects, right-click on sheet 1(VB_ERROR HANDLING) & Insert Module to create a new blank module.
VBA Error Handling With Debug Option
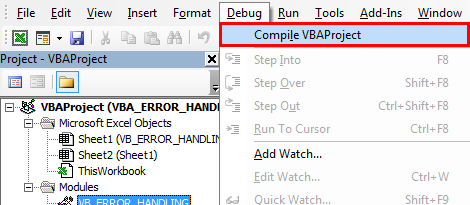
It’s better to compile code before we run it. To follow the compilation, the below steps need to be followed. Under the Debug option, we need to select a compile VBA project in the VB menu toolbar. When you click on it, it checks the code step by step; once it finds the error, it will highlight it & a popup message appears, thereby you need to correct it. once it is corrected, you need to compile it to find the next error in the code.
VBA Error Handling with the help of Different ‘ON ERROR’ Statements
1. On Error Resume Next
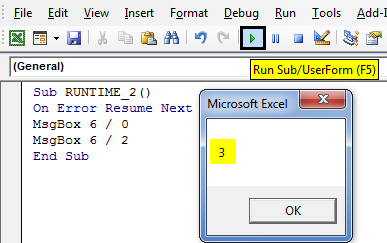
Here, the error will be ignored, and code will move on.
In the below-mentioned example, 6 can’t be divided by zero; if you run it without entering the On Error Resume Next statement, then below mentioned runtime error occurs.
Code:
Sub RUNTIME_1() MsgBox 6 / 0 End Sub
If On Error Resume Next is entered at the top of code after Sub statement, it ignores runtime error and moves on to the next statement, which results in the output of 6/2, i.e. 3 (Popup message box with result of it).
Code:
Sub RUNTIME_2() On Error Resume Next MsgBox 6 / 0 MsgBox 6 / 2 End Sub
2. On Error GoTo 0 and Error GoTo -1
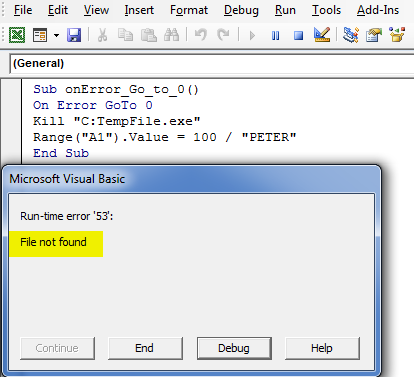
‘On Error GoTo 0’ will stop the code on the specific line that causes the error and shows a message box that describes or indicates the error.
Code:
Sub onError_Go_to_0() On Error GoTo 0 Kill "C:TempFile.exe" Range("A1").Value = 100 / "PETER" End Sub
Usually, it showcases default error checking behavior; it is significant when it is used along with ‘On Error Resume Next.
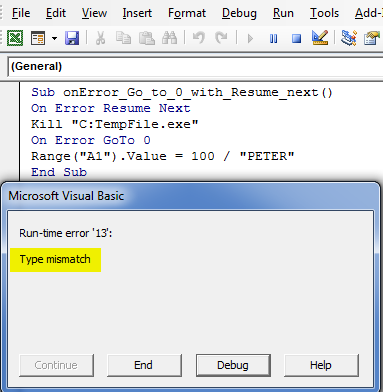
Usually, you can observe the Runtime Error Message box, which contains ‘Continue’, ‘End’, ‘Debug’ and ‘Help’ options. let’s check out the uses of each of them.
- The continue option will ignore the exception and continue the code if it is possible.
- The end option terminates the program.
- Debug option will highlight the statement where the error has occurred, which helps you to debug or correct the code.
- The help option will take you to open the Microsoft MSDN help page.
On Error GoTo 0 with On Error Resume Next
Code:
Sub onError_Go_to_0_with_Resume_next() On Error Resume Next Kill "C:TempFile.exe" On Error GoTo 0 Range("A1").Value = 100 / "PETER" End Sub
In the above code, it will ignore errors until it reaches the On Error GoTo 0 statement. After the On Error GoTo 0 statement, the code goes back or proceed to normal error checking and triggers the expected error ahead. when I run the above code, it will showcase the division error, i.e. type mismatch (numeric value can’t be divided by text).
On Error GoTo 0 disables any error trapping currently present in the VBA code, i.e. turn off the error handling in the main code, whereas On Error GoTo -1 clears the error handling and sets it to nothing, which helps or allows you to create another error trap.
3. On Error GoTo < LABEL
VBA to transfer the program control to the line followed by the label if any runtime errors are encountered, i.e. code jumps to the specified label. Here, the code statements between the exception line and the label will not be executed.
This method is more suitable & significant for exiting the program gracefully if any major fatal error occurs during the execution.
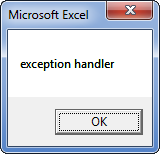
In the below mentioned VBA code, as soon as the error occurs at line 3, the program transfers the control to Line 6, i.e. label (Popup message appears as “Exception handler”).
Code:
Sub OnError_Go_to_Label() On Error GoTo Error_handler: MsgBox 9 / 0 MsgBox "This line will not be executed" Exit Sub Error_handler: MsgBox "exception handler" End Sub
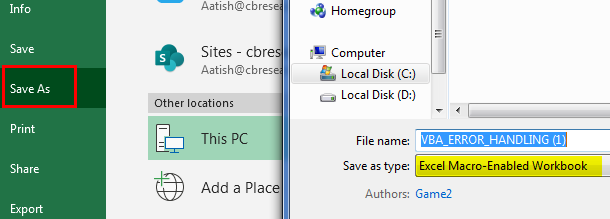
Here you can notice that ‘Exit Sub’ should be used just before the ‘Error_handler:’ label, this is done to ensure that the Error handler block of code should stop or doesn’t execute if there is no error. Now, you can save your workbook as an “Excel macro-enabled workbook”. By click on save as at the left corner of the worksheet.
Once again if you open a file, you can click on shortcut key i.e. Fn + Alt +f8, “Macro” dialog box appears, where you can run a saved macro code of your choice or you can click on Fn + Alt + F11 for a full macro window.
Things to Remember
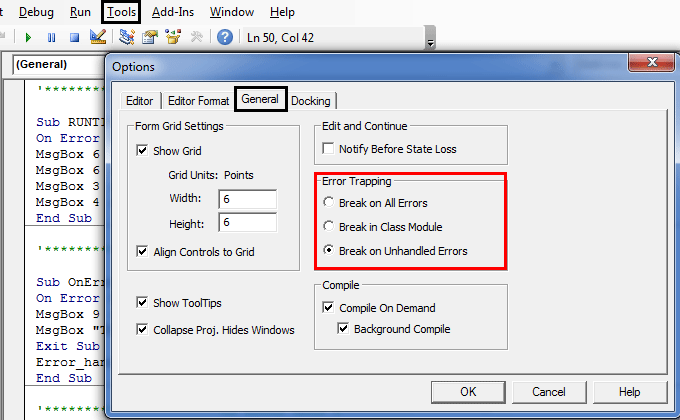
- Before you write code, you have to ensure that, break on unhandled errors is checked or selected in error. trapping option under general in the tool’s options of the VBA toolbar.
- It’s a default setting that helps out to stop your code for errors that are not handled.
- Break on All Errors: It will stop your code on all types of errors.
- Break-in Class Module: In case an object such as user form is used in the code, it will highlight that the exact line causing the error.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Error Handling. Here we discuss how to use VBA Error Handling in Excel along with some practical examples and a downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –