What is Excel VBA CDBL?
CDBL is a VBA function that uses to convert the expressions into a double data type. VBA consists of a number of data conversion functions. This help to change the data type of a variable or value from one to another. In different calculations, the conversion is a necessary process to get the proper result. CDBL is one of the data conversion function included in the Type conversion functions in VBA. CDBL stands for ‘Convert to double’. While processing data you may come across situations to change the integer numbers to double. To print the accurate result this function will help you. VBA CDBL function only accepts numbers. Any expression apart from numbers will produce a type mismatch error.
Format of CDBL function in Excel VBA
CDBL is a simple function which requires a single expression to operate in VBA. The expression should be a number.
- Expression: Is the number you want to convert into a floating number.
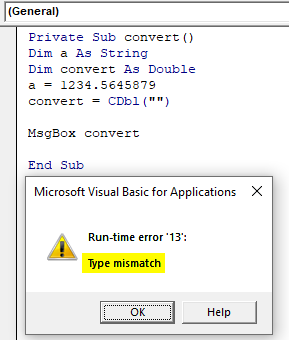
If the expression is anything apart from a number, the function will return a mismatch error. See the below example, where a non-number expression is passed to the function CDBL and it produced an error type mismatch.
Use of CDBL Function in VBA
Let’s check how the VBA CDBL function helps us on data processing. To get a clear view and understand the practical use of changing the data type see the below example. You can see the difference according to the data type used on the same variable.
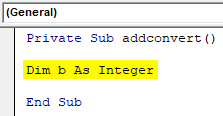
- Declare a variable as integer data type and assign a floating value to it. While printing the value see how it’s going to show the value.
Code:
Private Sub addconvert() Dim b As Integer End Sub
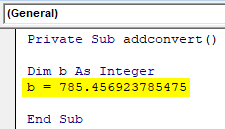
- A floating value is assigned to the declared integer variable. 785.456923785475 is assigned to variable b which is an integer variable.
Code:
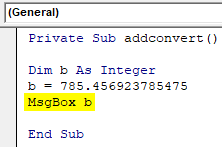
Private Sub addconvert() Dim b As Integer b = 785.456923785475 End Sub
- Using a message box, print the assigned value.
Code:
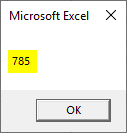
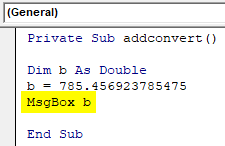
Private Sub addconvert() Dim b As Integer b = 785.456923785475 MsgBox b End Sub
See how the results show difference while printing the value.
You have assigned a number with floating values but the output shows only the integer part of the given number. Here the variable ‘b’ is declared as integer number so it will not accept a floating value. The integer part of the decimal value is taken and the decimal part is avoided. Since the variable is declared as an integer the number will be rounded to the nearest integer.
To print the data as it is, changing the variable data type into double Instead of the integer data type.
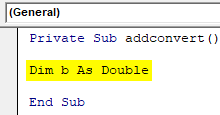
- By making a simple change in the same code you can print the given number as it is. Declare the variable as a double datatype.
Code:
Private Sub addconvert() Dim b As Double End Sub
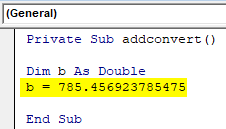
- A number as double is assigned to the declared double variable. 785.456923785475 is assigned to variable b which is double in datatype.
Code:
Private Sub addconvert() Dim b As Double b = 785.456923785475 End Sub
- Using a message box print the assigned value.
Code:
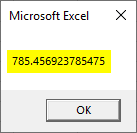
Private Sub addconvert() Dim b As Double b = 785.456923785475 MsgBox b End Sub
See how the results show difference while printing the value. You have assigned a number with floating values.
Compare both outputs you can see the difference. Even the data and variable are the same the change in data type changed the entire output. From this, you will get the importance of datatype and how it influences the entire program. This is the reason for using a different type of conversion functions with VBA.
Examples of CDBL Function in Excel VBA
Below are the different examples of VBA convert to double.
Example #1: Convert string data type to double
Let’s see how the data conversion is performing, and what are the changes that you can make with the help of data conversion functions. The string is a datatype which accepts all datatypes. A variable is defined as a string and assigns a number to it.
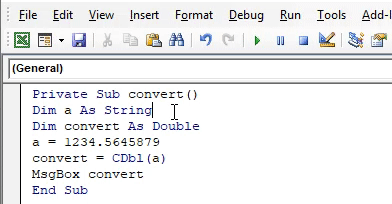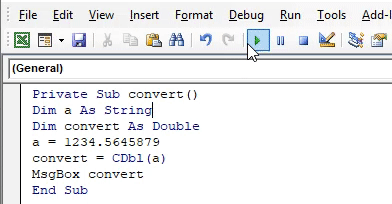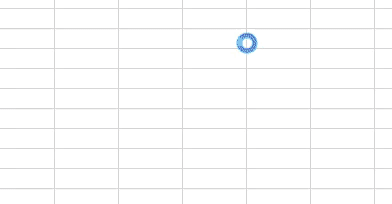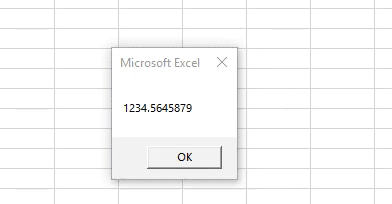
- Use a private function to check the changes in different datatype, create a function convert as private the declare the variable ‘a’ as a string.
Code:
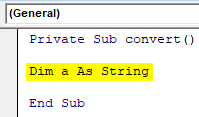
Private Sub convert() Dim a As String End Sub
- To perform the conversion, you need a variable. Since the variable is converting into double data type declare it as a double datatype. After data conversion, the value will be assigned to this variable.
Code:
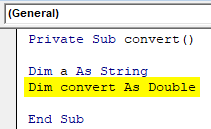
Private Sub convert() Dim a As String Dim convert As Double End Sub
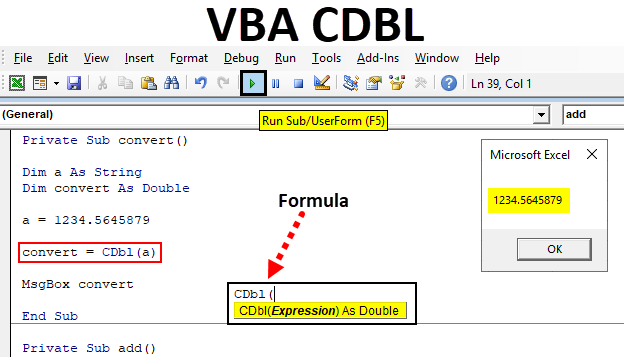
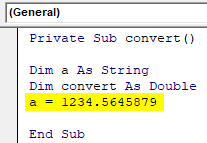
- Assign a floating number 1234.5645879 to the string variable. The string datatype will accept the numbers with floating values.
Code:
Private Sub convert() Dim a As String Dim convert As Double a = 1234.5645879 End Sub
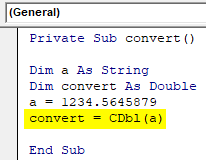
- Now use the VBA CDBL function to convert the value to double. You can use the ‘convert’ variable which is declared as a double datatype. Pass the variable ‘a’ as an expression to CDBL function.
Code:
Private Sub convert() Dim a As String Dim convert As Double a = 1234.5645879 convert = CDbl(a) End Sub
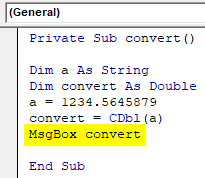
- To view the output value, you can print using a message box.
Code:
Private Sub convert() Dim a As String Dim convert As Double a = 1234.5645879 convert = CDbl(a) MsgBox convert End Sub
- Run this code by hitting F5 directly or manually hitting the Run button on the upper left panel.
- The value assigned to variable ‘a’ will be printed as same with floating points and an integer value. The value is converted into double data type and the same is printed as below.
Example #2 – Converting and Adding Two Numbers
You have two variables to add and find the sum as part of your calculation. Both are floating numbers with decimal values. But one variable is declared as integer and another as double.
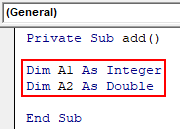
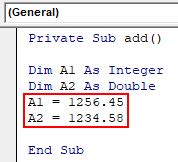
- Create a function add to find the sum of two numbers. Two variables A1 and A2 are declared as integer and double respectively.
Code:
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double End Sub
- Assign the two numbers to the respective variables. Both are two floating numbers with decimal values.
Code:
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double A1 = 1256.45 A2 = 1234.58 End Sub
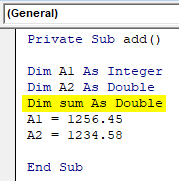
- Declare a third variable sum as double data type since the result will be a double value.
Code:
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double Dim sum As Double A1 = 1256.45 A2 = 1234.58 End Sub
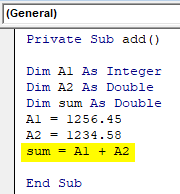
- Add the given two numbers and put the result in the variable sum.
Code:
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double Dim sum As Double A1 = 1256.45 A2 = 1234.58 sum = A1 + A2 End Sub
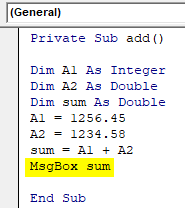
- Using a message box lets print the output.
Code:
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double Dim sum As Double A1 = 1256.45 A2 = 1234.58 sum = A1 + A2 MsgBox sum End Sub
- Run this code by hitting F5 directly or manually hitting the Run button on the upper left panel.
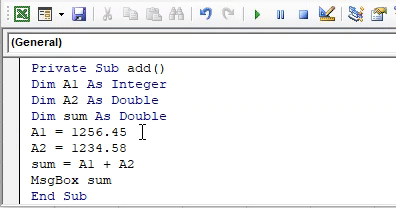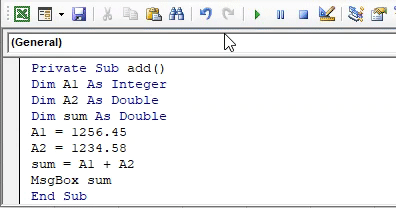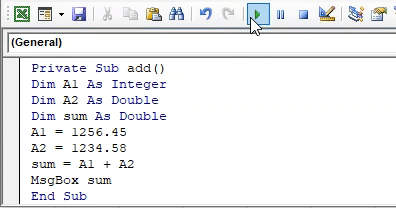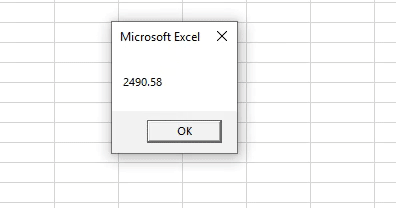
The expected result is 2491.03 and while checking the output you can see some difference in the result. The mismatch in result occurred due to the value taken by variable A1. Since this is an integer variable this will not accept the decimal part of the number only the integer part is taken while processing the sum.
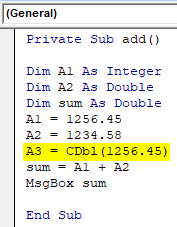
- To avoid this, convert the number A1 to double and assign the converted number to another variable A3.
Code:
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double Dim sum As Double A1 = 1256.45 A2 = 1234.58 A3 = CDbl(1256.45) sum = A1 + A2 MsgBox sum End Sub
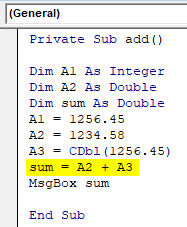
- Now add the converted variable with A2 instead of A1. Since the number is converted to double datatype the value with floating numbers will be accepted and added with A2.
Code:
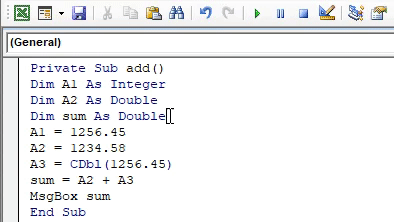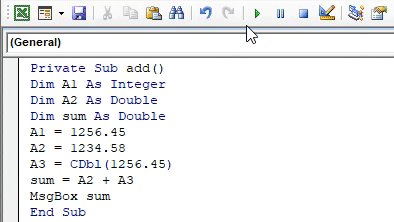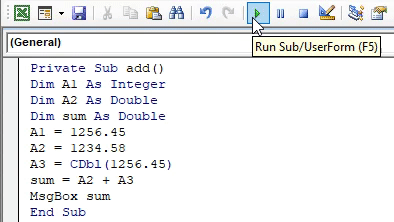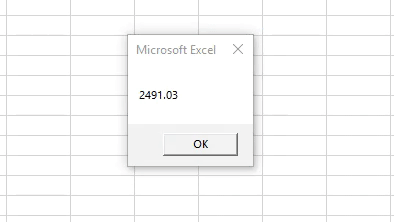
Private Sub add() Dim A1 As Integer Dim A2 As Double Dim sum As Double A1 = 1256.45 A2 = 1234.58 A3 = CDbl(1256.45) sum = A2 + A3 MsgBox sum End Sub
- Run this code by hitting F5 directly or manually hitting the Run button on the upper left panel.
The sum value has been corrected and produced the expected result.
Things to Remember
- VBA CDBL function will not accept values rather than a number.
- A type mismatch error will be produced if a text value is given to the VBA CDBL function.
- Double data type displays a 13 digit decimal values.
- VBA CDBL function helps you to get a proper result while processing the numbers in Excel.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA CDBL Function. Here we discuss how to use VBA CDBL function to convert the value to Double data type in Excel along with some practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –