What is a Value Chain?
A value chain is a set of steps that a company uses to deliver a product or service to the market. It begins with raw material sourcing and concludes with final delivery to the customer. Each step in the chain adds value, whether through production, design, marketing, or customer support.
In Simple Terms:
A value chain maps how each stage of production adds value, from input to final output.
Michael Porter introduced the concept in his 1985 book, Competitive Advantage. According to Porter, companies can gain an edge over competitors by optimizing it, either through cost leadership or product differentiation.
Table of Contents
- What is a Value Chain?
- Components of the Value Chain
- How to Perform a Value Chain Analysis?
- Real-World Examples
- How to Analyze Your Own Value Chain?
- Digital Transformation
- Benefits of an Optimized Value Chain
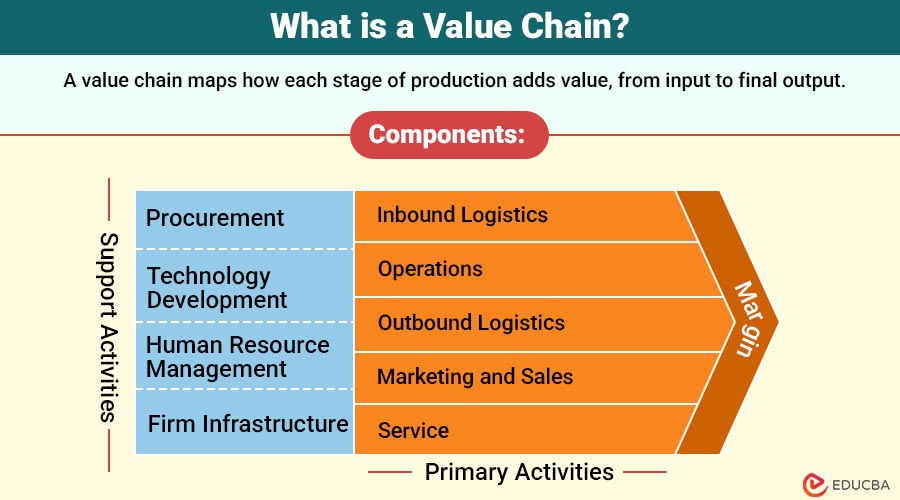
Components of the Value Chain
Porter divided the chain into two main categories:
1. Primary Activities
These directly relate to the creation and sale of a product or service. They include:
- Inbound Logistics: The process of receiving, storing, and distributing raw materials (e.g., suppliers delivering components to a factory).
- Operations: Transforming inputs into the final product (e.g., assembly lines in manufacturing).
- Outbound Logistics: Delivering the product to customers (e.g., shipping, warehousing).
- Marketing and Sales: Promotional activities and sales tactics (advertising, pricing strategies).
- Service: Post-sale support (customer support, warranty services).
2. Support Activities
These help the primary activities function effectively:
- Procurement: Purchasing raw materials and other inputs.
- Technology Development: Research and development, innovation, process automation.
- Human Resource Management: Recruiting, training, and retaining employees.
- Firm Infrastructure: Company systems, finance, legal, management.
How to Perform a Value Chain Analysis?
Follow these steps to perform your value chain analysis:
Step 1: Map Out Activities
List all the activities involved in your business, from raw materials to after-sales service.
Step 2: Identify Value Drivers
Look for where value is being added or lost. Organizations can achieve this through innovation, better customer experiences, faster delivery, or improved cost efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Costs and Benefits
Compare the cost of each activity with the value it delivers. Is there waste? Can it be outsourced or automated?
Step 4: Optimize
Take actions to enhance strengths and improve weaknesses—this could mean streamlining logistics, improving customer service, or investing in tech.
Real-World Examples
Let us explore how companies use the value chain in practice:
Example 1: Starbucks
- Inbound Logistics: Starbucks sources high-quality coffee beans directly from farmers worldwide.
- Operations: Beans are roasted at centralized plants and then shipped globally.
- Outbound Logistics: The company delivers products to over 30,000 stores in more than 80 countries.
- Marketing and Sales: Strong branding with seasonal drinks, loyalty programs, and mobile ordering.
- Services: Starbucks offers app-based rewards and customer service, enhancing the experience.
Example 2: Apple Inc.
- Inbound Logistics: Apple sources components from suppliers like Foxconn and TSMC.
- Operations: Assembly mostly occurs in China and India.
- Outbound Logistics: Apple distributes its products through Apple Stores and online channels.
- Marketing and Sales: Iconic ad campaigns, product launches, and premium pricing.
- Services: AppleCare, software updates, and 24/7 support add long-term value.
How to Analyze Your Own Value Chain?
Here is a step-by-step method:
- List all activities your business does, from acquiring materials to after-sales support.
- Categorize each as a primary or support activity.
- Evaluate how much value each activity adds and its cost.
- Identify bottlenecks or areas with low value or high cost.
- Look for opportunities to optimize or outsource.
Digital Transformation
Modern businesses are integrating AI, IoT, and Big Data into their value chains.
- AI-powered chatbots reduce service response time by 70%
- IoT-enabled logistics help track shipments in real time
- Predictive analytics assist in forecasting demand and optimizing inventory
Example:
Walmart utilizes predictive analytics to optimize inventory and pricing, resulting in billions of dollars saved in logistics and warehousing costs.
Benefits of an Optimized Value Chain
Here are some tangible advantages:
- Cost Savings: Automation of manual tasks can lead to substantial cost reductions.
- Faster Delivery: Streamlined logistics ensure quicker turnaround.
- Customer Satisfaction: Providing better service and support fosters loyalty.
- Innovation: Focus on R&D enhances competitiveness.
- Increased Profit Margins: By cutting waste and enhancing productivity.
Final Thoughts
The value chain is a powerful framework for businesses to understand their operations in depth and identify ways to increase value and profitability. Companies like Apple and Starbucks demonstrate how well-managed value chains can lead to strong competitive advantages and impressive financial performance. By regularly analyzing and optimizing your value chain, your business can enhance efficiency, lower costs, and deliver a superior customer experience — all essential factors for success in the dynamic markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What’s the difference between a value chain and a supply chain?
Answer:
- A value chain focuses on value creation across all business activities.
- A supply chain manages the movement of goods and services from suppliers to end customers.
Q2. Can service-based businesses use value chains?
Answer: Yes! Even in services such as healthcare, education, or consulting, it helps streamline internal operations and enhance the customer experience.
Q3. What tools can help with value chain analysis?
Answer: SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, and ERP software, such as SAP or Oracle, help analyze and manage the value chain effectively.
Q4. Is value chain analysis only for large companies?
Answer: No, businesses of all sizes can benefit by identifying efficiencies and improving customer value.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on understanding the value chain helps you identify key areas to add value and improve business efficiency. Explore these recommended articles for more insights into optimizing operations and gaining a competitive advantage.

