Updated April 15, 2023

Introduction to Unsigned Int in C
In C programming language, there are different varieties of data types, which are used to declare variables before they are used as they are data storage for a particular variable to perform particular tasks like int data types for integers, float for floating real numbers, etc. In C, unsigned is also one data type in which is a variable type of int this data type can hold zero and positive numbers. There is also a signed int data type in which it is a variable type of int data type that can hold negative, zero, and positive numbers. This unsigned int is data type cannot represent a negative number.
Syntax
In C programming language, unsigned data type is one of the type modifiers which are used for altering the data storage of a data type. In C, usually, we have integer (int) data type by default are signed where it can store values both negative and positive values. Let us see how to declare it in the C programs.
unsigned int variable_name;Example:
unsigned int a;Explanation: In the above example, the variable “a” can hold the values only zero and positive values. We know that the data type “int” has the size of 4 bytes where it can hold values from -231 to 231 – 1, but in this, we have declared “x” as unsigned int so it can hold values from 0 to 232 – 1. The unsigned int can contain storage size either 2 or 4 bytes where values ranging from [0 to 65,535] or [0 to 4,294,967,295]. The format specifier used for an unsigned int data type in C is “ %u ”.
Examples to Implement Unsigned Int in C
Let us see some examples:
Example #1
Let us see a small C program that uses unsigned int:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("Unsigned int values range: %u\n", (unsigned int) UINT_MAX);
return 0;
}Output:
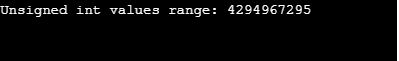
Explanation: So in general, in C we have signed and unsigned integer data types to declare in the program. Let us see if the variable is declared signed int and we want it to convert it into unsigned int which is a bit confusing in C programming. In C, the compiler performs implicit casting but sometimes it gives a warning so most of the time they are manually cast explicitly which is done using the data type you want to convert it in the parenthesis to another data type.
Example #2
Let us see the C program that converts the signed variable to an unsigned variable:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a = 57;
unsigned int b = (unsigned int)a;
printf("The value of signed variable is: %u\n",a);
printf("The value of unsigned variable is: %u\n",b);
return 0;
}Output:
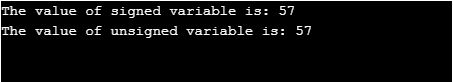
Explanation: In the above program, we have declared variable “a” as integer data type which is by default is signed int data type, and then we are converting variable “a” to unsigned int data type using casting for converting the variable from signed to unsigned by using “(unsigned)” before the variable “a” for converting. According to C99 standard the integer value when converted to another type then the value will not be changed, so in the above program also the value of the variable “a” is 57 so when it is changed to unsigned int the value for the new variable “b” which stores the value of variable “a” which is converted to unsigned has the same value which was declared in the starting as “57”.
In C, the int data type is by default is signed data type which can store even negative values also other than positive values. So to convert negative values to unsigned int also is possible in C programming language. If the variable is having negative value and if we are converting it into unsigned then the value of that variable is repeatedly converted by adding or subtracting one or more than a maximum value until the value is in the range of the new type.
Example #3
Let us see the example for converting negative signed int variable to unsigned int variable:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int a = -57;
unsigned int b = (unsigned int)a;
printf("The unsigned value of negative signed value 0x%x\n",a);
return 0;
}Output:
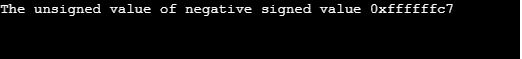
Explanation: In the above program, the hexadecimal representation of value -57 is 0xffffffc7 where this value is in the range of unsigned int so after the casting of this value there is no specific change in the bits of the value.
In C programming language, the overflow of unsigned int is well defined than signed int. Unsigned int is much better than signed int as the range for unsigned int is larger than signed int and the modulus operation is defined for unsigned int and not for signed int. The unsigned int can reduce some conditional statements and also it is mostly used in embedded systems, registers, etc so only unsigned int is more preferable than signed int. Unsigned int can also be declared in the function argument.
Unsigned int is usually used when we are dealing with bit values that means when we are performing bitwise operations like bit masking orbit shifting. As bit shifting in negative integers is undefined or implementation-defined outputs.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed unsigned int in C programming language. Unsigned int is a data type that can store the data values from zero to positive numbers whereas signed int can store negative values also. It is usually more preferable than signed int as unsigned int is larger than signed int. Unsigned int uses “ %u ” as a format specifier. This data type is used when we are dealing with bit values like bit masking or bit shifting, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Unsigned Int in C. Here we discuss introduction to Unsigned Int in C, syntax, examples with code, output, and explanation. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


