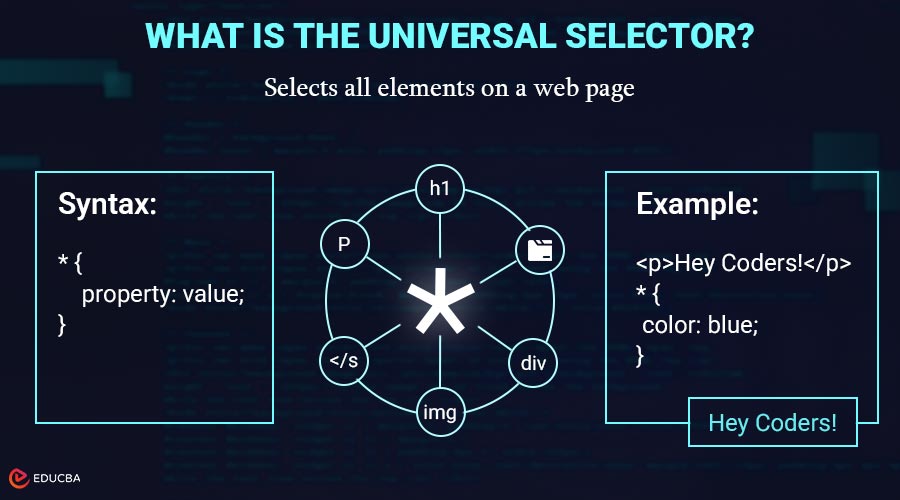
What is the Universal Selector in CSS?
The universal selector in CSS is represented by the asterisk (*). It selects all elements on a web page and applies styles universally. This means that any CSS property applied using the universal selector will affect every element in the HTML document, unless a more specific selector specifically overrides it.
Syntax:
* {
property: value;
}Explanation:
- * → selects all elements.
- Inside {}, you write the CSS properties to apply to every element.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Basic Example
- Reference HTML Code
- Practical Use Cases
- Combining with Other Selectors
- Why Use the Universal Selector?
- Limitations
- Best Practices
Basic Example of Universal Selector
Html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Universal Selector Example</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to CSS Universal Selector</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<div>This is a div element.</div>
</body>
</html>CSS:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}Output:
- All elements have no margin or padding.
- Using box-sizing: border-box ensures that the element’s total width includes its padding and border, thereby preventing unexpected sizing issues.
This is the classic CSS reset approach using the universal selector.
Reference HTML Code for Testing Universal Selector
Here is a simple HTML structure you can use to test universal selector styles:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Universal Selector Demo</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>Welcome to Universal Selector Demo</h1>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<section>
<h2>About Universal Selector</h2>
<p>The universal selector targets all elements on a page.</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>Example List</h2>
<ul>
<li>Item One</li>
<li>Item Two</li>
<li>Item Three</li>
</ul>
</section>
</main>
<footer>
<p>© 2025 Universal Selector Tutorial</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>Practical Use Cases
Here are some practical ways to use the Universal Selector effectively in real-world web design:
1. Resetting Default Styles
Different browsers have their own default margins and paddings for elements. Using the Universal Selector to reset these ensures uniformity.
Code:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}Output:
This snippet is often one of the first lines in a CSS file. It eliminates unexpected spacing and layout issues caused by default browser styles.
2. Setting Global Font Styles
To maintain consistency in typography across all elements:
Code:
* {
font-family: 'Helvetica Neue', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
font-size: 16px;
color: #222;
}Output:
Every element, from headings to paragraphs, inherits the same base font and color.
3. Debugging and Development
During development, it can be used to temporarily apply border outlines or background colors to visualize element boundaries.
Code:
* {
border: 1px solid red;
}Output:
This technique helps debug layout issues quickly.
Combining the Universal Selector with Other Selectors
You can enhance the power of the universal selector by combining it with different selectors.
1. Child Combinator
Code:
div * {
color: blue;
}Output:
Here, every element inside a <div> will have a blue color.
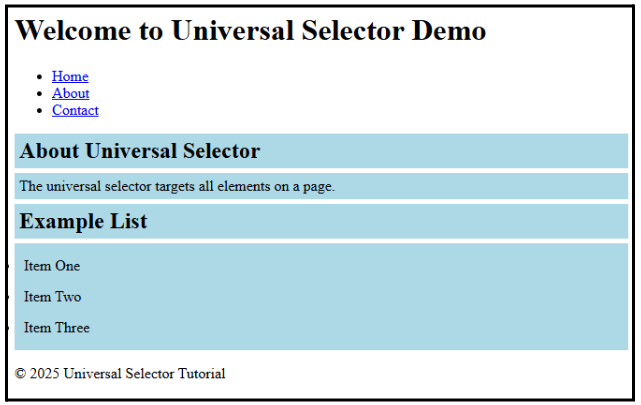
2. Descendant Selector
Code:
section * {
background-color: lightblue;
padding: 5px;
margin: 5px 0;
}Output:
Every element inside a <section> in your HTML will get a light blue background, along with some padding and spacing for visibility.
3. Pseudo-classes
You can also use pseudo-classes with the universal selector for more advanced styling:
Code:
*:hover {
background-color: brown;
color: white;
}Output:
Every element on the page will change its background color to brown and text color to white when hovered over.
Why Use the Universal Selector?
The selector is incredibly useful in several scenarios:
- CSS Reset: Browsers apply default styles to HTML elements, which can vary. Using the universal selector, developers can reset these styles to create a consistent baseline.
- Global Styles: If you want a specific style to affect all elements—like a font family or a background color—the universal selector saves you from writing repetitive code.
- Quick Prototyping: When creating a quick layout prototype, applying general styles to all elements at once can speed up development.
- Box-Sizing Control: Modern web development often uses the universal selector to set box-sizing: border-box globally, making layout calculations easier.
Limitations
It comes with a few limitations:
- Performance Impact: Applying styles to all elements can slow down the rendering performance, especially on pages with many elements. It is important to use it judiciously.
- Specificity Issues: Since the Universal Selector has low specificity, other selectors like class (.classname) or ID (#id) selectors can easily override it.
- Unintended Styling: Using this selector carelessly can lead to unwanted changes, such as affecting form elements, tables, or images unintentionally.
- Cannot Select Certain Pseudo-Classes Directly: While it can affect pseudo-elements (::before, ::after), it cannot directly target pseudo-classes like :hover without additional specification.
Best Practices
To make the most out of this selector without compromising performance or control, follow these key best practices below:
- Use for Global Resets: Apply margin, padding, and box-sizing resets globally to create a consistent base.
- Avoid Excessive Styling: Do not use this selector to style every visual property (like colors or fonts) if it is not necessary. Focus on properties that truly need global consistency.
- Combine with Specific Selectors: Use it alongside class and ID selectors to maintain both global and element-specific styles without conflicts.
- Consider Performance: On large-scale applications with complex DOM structures, test the performance impact of applying the universal selector.
- Be Mindful of Accessibility: Avoid removing essential default styles that affect usability, such as focus indicators for form inputs.
Conclusion
The universal selector is a foundational tool in CSS that can dramatically simplify your styling workflow. From resetting default browser styles to applying consistent fonts and layouts, it provides developers with a powerful way to maintain uniformity across a website. However, it is important to use it judiciously to avoid performance issues and unintended style overrides. By combining the universal selector with best practices, you can create clean, efficient, and visually consistent web designs. Mastering the universal selector is essential for becoming a more effective front-end developer. Whether for resets, global fonts, or box-sizing control, this simple * symbol holds a world of styling possibilities.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive guide to the Universal Selector in CSS helps you enhance your web design skills. Check out these recommended articles for more insights and strategies to improve your CSS mastery and build responsive, modern websites.