Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to UNION in PostgreSQL
Union in PostgreSQL is used to combine the result of two or more select queries without returning duplicate values, union is most important in PostgreSQL. To use this function, each select statement must have the same number of columns selected and the same number of column expressions but don’t need the same length. Union in PostgreSQL will remove duplicate values from the table and give output to the user. We can combine one or more queries in the result set.
Syntax:
Below is the syntax, which is as follows.
Select Column_name1, Column_name2, …, Column_nameN from table1
UNION
Select Column_name1, Column_name2, …, Column_nameN from table2Select expression1, expression2, …, expressionN from table1
UNION
Select expression 1, expression 2, …, expressionN from table2Select * from table1
UNION
Select * from table2Below is the parameter description of the above syntax, which follows.
- Select: Select statement is used to select no of the column from tables.
- Column1 to ColumnN: Column used in the select statement to fetch results using union in
PostgreSQL. - Expression1 to ExpressionN: Column used in the select statement to fetch result.
- Table1 and Table2: Table used to retrieve data using the Union operator in PostgreSQL.
- UNION: UNION operator combines the results of two or more queries.
- From: Keyword to define table from which we have fetching data.
- Asterisk (*): Retrieve all columns in a result set from the specified table.
How does UNION Clause work in PostgreSQL?
- Combining results using the UNION clause means both queries must have the same row count to retrieve the output.
- Also, in both, the columns need to have compatible data types.
- Union operator is used to combine results from one or multiple tables.
- We have used a union clause or operator to combine data from a similar table that was not perfectly normalized. Such tables were found in database warehouse applications.
- The union operator in PostgreSQL places the rows in the first query after, between, or before the second used query.
- We also use order by clause to sort the result in ascending or descending order.
- A union clause removes or eliminates duplicate records from the table.
Examples to Implement
We have used employee_test1 and employee_test2 tables to describe.
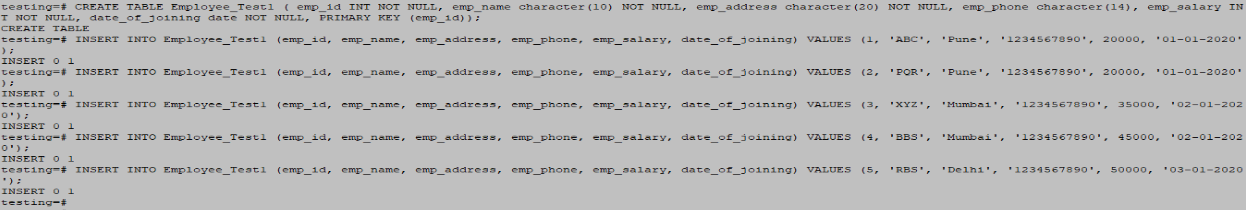
Example #1 – Employee_Test1
Code:
CREATE TABLE Employee_Test1 ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (4, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test1 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (5, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, '03-01-2020');Output:
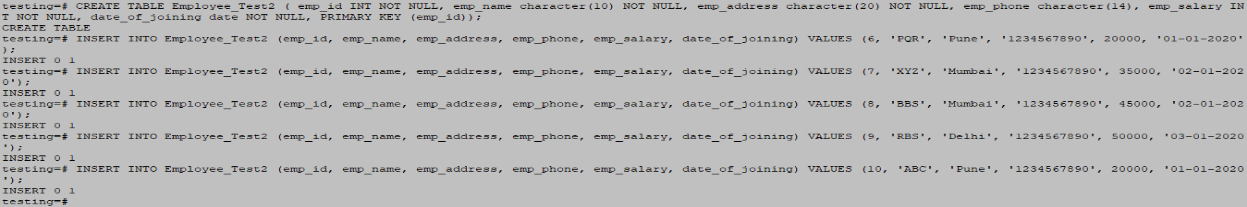
Example #2 – Employee_Test2
Code:
CREATE TABLE Employee_Test2 ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (6, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (7, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (8, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (9, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, '03-01-2020');
INSERT INTO Employee_Test2 (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (10, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');Output:
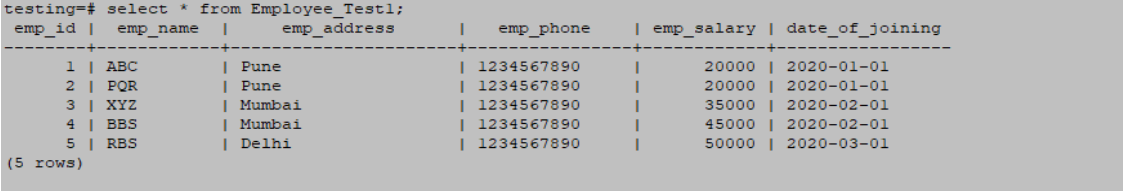
select * from Employee_Test1;Output:
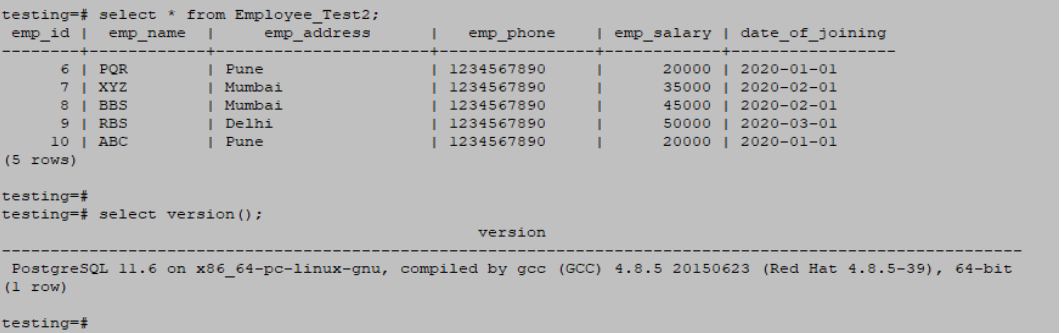
select * from Employee_Test2;Output:
Please find below an example of a UNION operator in PostgreSQL.
Union operator using all columns from both the table.
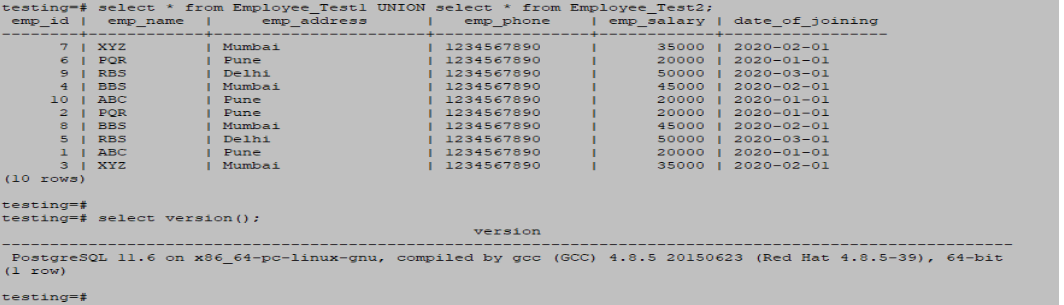
- The below example, we have retrieved data from all the columns. In such a case, all data is combined with the employee_test1 and employee_test2 tables.
- In this scenario, all records will be retrieved from both tables because, in some columns, the data is different.
testing=# select * from Employee_Test1 UNION select * from Employee_Test2;Output:
Union operator using a specific column from both the table.
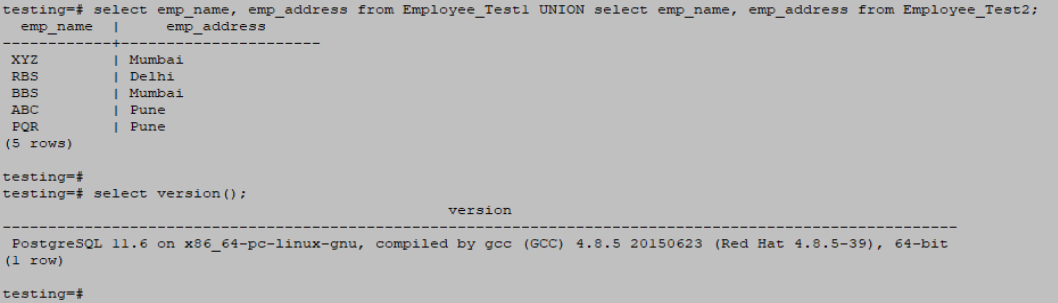
- In the below example, we have retrieved data from specific columns. In such a case, only distinct records from both tables are fetched.
- The elimination or removal of duplicate records from both tables takes place.
- In this scenario, the retrieval of only distinct records from both tables occurs due to the presence of duplicated data in specific columns.
testing=# select emp_name, emp_address from Employee_Test1 UNION select emp_name, emp_address from Employee_Test2;Output:
Union clause using ORDER BY clause in PostgreSQL.
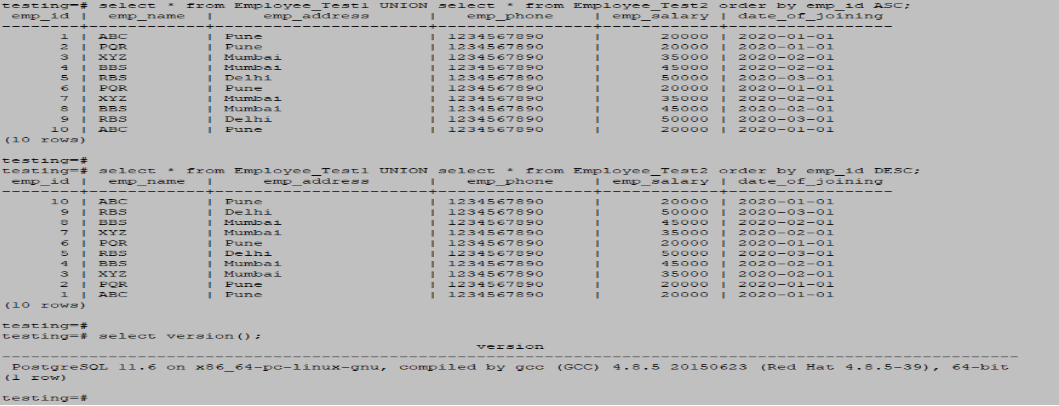
- To sort results combined from both queries, we used to order by clause in PostgreSQL.
- We sort the result data using order by clause with ascending and descending order.
- The below example shows a union clause using order by clause in PostgreSQL.
testing=# select * from Employee_Test1 UNION select * from Employee_Test2 order by emp_id ASC;
testing=# select * from Employee_Test1 UNION select * from Employee_Test2 order by emp_id DESC;Output:
Rules for Using UNION in PostgreSQL
- Below are the rules and regulations while using the union clause in PostgreSQL.
- We need the same column in both tables while using UNION to combine the results of one or more queries.
- Also, we need the same data type in the table column list while combining the result.
- The UNION clause or operator is beneficial and essential in PostgreSQL to combine the result of one or more queries.
- We must select the same column from both tables to combine the result.
- We use order by clause in the UNION operator to sort results by ascending and descending order.
Conclusion
The UNION clause is beneficial and important in PostgreSQL to combine the result of one or more queries. We have sorted the data in ascending and descending order. Using order by clause in the UNION operator. We need the same column to combine the result of one or more queries.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “UNION in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.