Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to Uniform Cost Search
Uniform Cost Search is an algorithm used to move around a directed weighted search space to go from a start node to one of the ending nodes with a minimum cumulative cost. This search is an uninformed search algorithm since it operates in a brute-force manner, i.e. it does not take the state of the node or search space into consideration. It is used to find the path with the lowest cumulative cost in a weighted graph where nodes are expanded according to their cost of traversal from the root node. This is implemented using a priority queue where lower the cost higher is its priority.
Algorithm of Uniform Cost Search
Below is the algorithm to implement Uniform Cost Search in Artificial Intelligence:-
centre;”>Algorithm for USC
- Insert RootNode into the queue.
- Repeat till queue is not empty:
- Remove the next element with the highest priority from the queue.
- If the node is a destination node, then print the cost and the path and exit
else insert all the children of removed elements into the queue with their cumulative cost as their priorities.
Here rootNode is the starting node for the path, and a priority queue is being maintained to maintain the path with the least cost to be chosen for the next traversal. In case 2 paths have the same cost of traversal, nodes are considered alphabetically.
Example of Uniform Cost Search
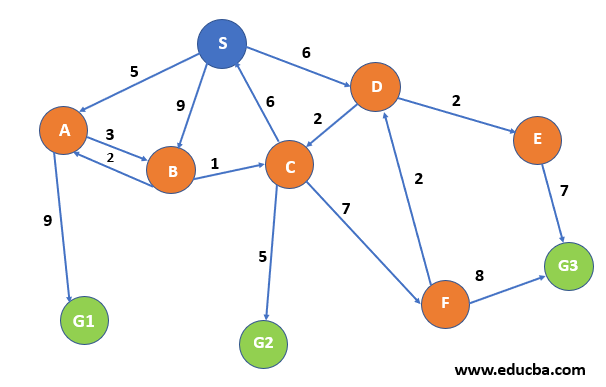
Consider the below example, where we need to reach any one of the destination node{G1, G2, G3} starting from node S. Node{A, B, C, D, E and F} are the intermediate nodes. Our motive is to find the path from S to any of the destination state with the least cumulative cost. Each directed edge represents the direction of movement allowed through that path, and its labelling represents the cost is one travels through that path. Thus Overall cost of the path is a sum of all the paths.
For e.g. – a path from S to G1- {S->A -> G1} whose cost is SA +AG1 = 5 + 9 = 14
Here we will maintain a priority queue the same as BFS with the cost of the path as its priority, lower the cost higher is the priority.
We are going to use a tree to show all the paths possible and also maintain a visited list to keep track of all the visited nodes as we need not visit any node twice.
| Explanation | Flow | Visited List |
| Step 1-
We will start with start node and check if we have reached any of the destination nodes, i.e. No thus continue.
|
 |
|
| Step 2– We reach all the nodes that can be reached from S I .eA, B, D. And Since node S has been visited thus added to the visited List. Now we select the cheapest path first for further expansion, i.e. A | 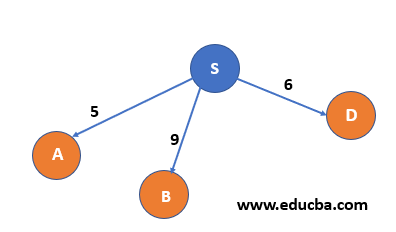 |
S |
| Step 3 – Node B and G1 can be reached from A and since node A is visited thus move to the visited list.
Since G1 is reached but for the optimal solution, we need to consider every possible case; thus, we will expand the next cheapest path, i.e. S->D. |
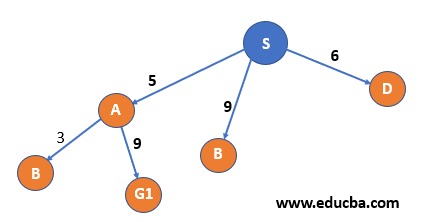 |
S, A |
| Step 4– Now node D has been visited thus it goes to visited list and now since we have three paths with the same cost, we will choose alphabetically thus will expand node B | 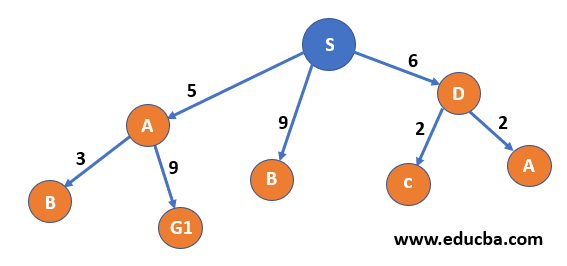 |
S,A,D |
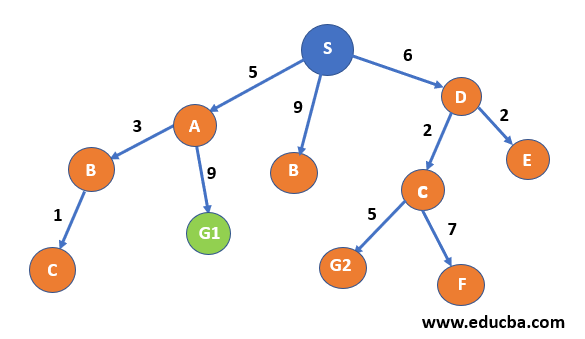
| Step 5-: From B, we can only reach node C. Now the path with minimum weight is S->D->C, i.e. 8. Thus expand C. And B has now visited node. | 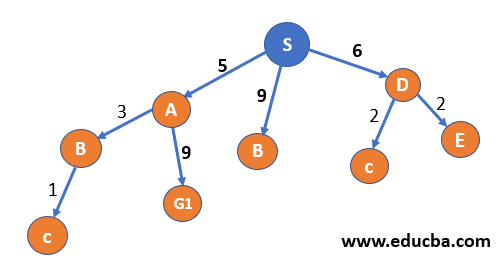 |
S,A,D,B |
| Step 6:- From C we can reach G2 and F node with 5 and 7 weights respectively.
Since S is present in the visited list thus, we are not considering the C->S path. Now C will enter the visited list. Now the next node with the minimum total path is S->D->E, i.e. 8. Thus we will expand E. |
 |
S,A,D,B,C |
| Step 7:- From E we can reach only G3. E will move to the visited list. | 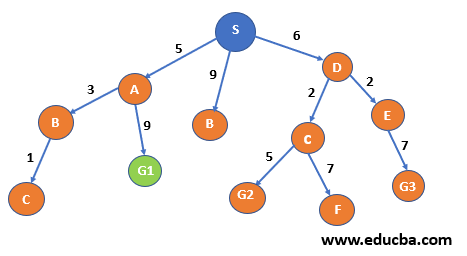 |
S,A,D,B,C,E |
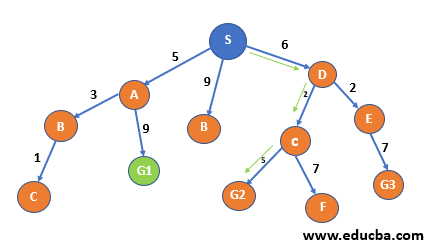
| Step 8 – In the last, we have 6 active paths
. S->B – B is in the visited list; thus will be marked as a dead end. b.Same for S->A->B->C – C has already been visited thus is considered a dead end. Out of the remaining S->A->G1 S->D->C->G2 S->D->C->F S->D->E->G3 Minimum is S->D->C->G2 And also, G2 is one of the destination nodes. Thus, we found our path.
|
 |
S,A,D,B,C,E |
In this way we can find the path with the minimum cumulative cost from a start node to ending node – S->D->C->G2 with cost total cost as 13(marked with green colour).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Uniform Cost Search
Below are the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- It helps to find the path with the lowest cumulative cost inside a weighted graph having a different cost associated with each of its edge from the root node to the destination node.
- It is considered to be an optimal solution since, at each state, the least path is considered to be followed.
Disadvantage
- The open list is required to be kept sorted as priorities in priority queue needs to be maintained.
- The storage required is exponentially large.
- The algorithm may be stuck in an infinite loop as it considers every possible path going from the root node to the destination node.
Conclusion
Uniform Cost Search is a type of uninformed search algorithm and an optimal solution to find the path from root node to destination node with the lowest cumulative cost in a weighted search space where each node has a different cost of traversal. It is similar to Heuristic Search, but no Heuristic information is being stored, which means h=0.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Uniform Cost Search. Here we discuss the introduction to Uniform Cost Search, algorithm, examples, advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –