
Introduction to typedef in C
typedef is a predefined keyword in the C language. This typedef keyword tells the C compiler that “please assign a user given keyword to the already existing type”. It Means typedef gives an alternative user-friendly keyword for existing C language data types like unsigned int, long, int, char, float, etc. This concept is very useful when the existing data types are a little bit handy to use; then, we will use this typedef concept.
Real-Time Example: Let’s take if we want to declare some variables like unsigned int, then we have to write unsigned int always throughout the program is a very lengthy process. So, instead of that, we can assign a new name to the already existing data type, then it is easy to use in the code. For this, we can use the typedef keyword.
How does typedef Work in C Language?
This keyword works with typedef followed by existing data type, and the user wanted a name to the data type. Then the compiler will assume the existing keyword name becomes user givenname for the entire application.
Syntax:
typedef<existing data type or keyword in C><user required name for the data type or keyword>;Examples of typedef in C
Below given are the practical examples of typedef:
Example #1 – Typdef unsigned int ui
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries
#include <string.h>//Add the String library to perform string actions
//typedef for give struct keyword to user wanted keyword as like below (Courses)
typedef struct Courses {
char courseName[60];//declare character variable
float CourseFee;//declare float variable
char companyName[100];//declare character variable
int loginID;//declare integer variable
} Courses; //To make work user defined keyword we have call the keyword from here
//main method to execute application code
int main( ) {
//Taken Courses name as course( alias name)
Courses course;
//Copying character values into varaible
strcpy(course.courseName, "C Programming");
strcpy(course.companyName, "EDUCBA");
//Initailize float values into varaible
course.CourseFee = 5000.00;
//Initailize integer values into varaible
course.loginID=2452;
//display the output of all the declared variable below
printf( "Course Name : %s\n", course.courseName);
printf( "Company Name : %s\n", course.companyName);
printf( "Course Fee : %f\n", course.CourseFee);
printf( "Login ID : %d\n", course.loginID);
return 0;
}Output:
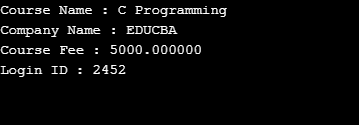
Example #2 – Typedef union keyword
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries
#include <string.h>//Add the String library to perform string actions
//typedef for give struct keyword to user wanted keyword as like below (Employee)
typedef union Employee
{
inteID;//declare integer variable
float salary;//declare float variable
char company[30];//declare character variable
}Employee;//To make work user defined keyword we have call the keyword from here
//main method to execute application code
int main()
{
//Taken Courses name as course( alias name)
Employee e1, e2, e3, e4;
//Initailize float values into varaible
e1.salary = 18314912111343777091682304.000000 ;
//Initailize integer values into varaible
e1.eID=1769104726;
//Copying character values into varaible
strcpy(e1.company,"Verinon Technologies Private Limited");
//displaying employee details
printf("Details of First Employee\n");
printf("Employee ID : %d\n", e1.eID);
printf("Employee Salary : %f\n", e1.salary);
printf("Company Name : %s\n", e1.company);
//Initailize integer values into varaible
e2.eID = 1667330639 ;
//Initailize float values into varaible
e2.salary = 4158754218828133040128.000000;
//Copying character values into varaible
strcpy(e2.company,"Oracle Technologies Private Limited");
//displaying employee details
printf("Details of Second Employee\n");
printf("Employee ID : %d\n", e2.eID);
printf("Employee Salary : %f\n", e2.salary);
printf("Company Name : %s\n", e2.company);
//Initailize integer values into varaible
e3.eID = 1919117645;
//Initailize float values into varaible
e3.salary = 4504345476014339048099257778176.000000;
//Copying character values into varaible
strcpy(e3.company,"Microsoft Technologies Private Limited");
//displaying employee details
printf("Details of Third Employee\n");
printf("Employee ID : %d\n", e3.eID);
printf("Employee Salary : %f\n", e3.salary);
printf("Company Name : %s\n", e3.company);
//Initailize integer values into varaible
e4.eID = 1735356231 ;
//Initailize float values into varaible
e4.salary = 1130698294087203659186176.000000;
//Copying character values into varaible
strcpy(e4.company,"Google Technologies Private Limited");
//displaying employee details
printf("Details of Fourth Employee\n");
printf("Employee ID : %d\n", e4.eID);
printf("Employee Salary : %f\n", e4.salary);
printf("Company Name : %s\n", e4.company);
return 0;
}
course.loginID=2452;
//display the output of all the declared variable below
printf( "Course Name : %s\n", course.courseName);
printf( "Company Name : %s\n", course.companyName);
printf( "Course Fee : %f\n", course.CourseFee);
printf( "Login ID : %d\n", course.loginID);
return 0;
}Output:
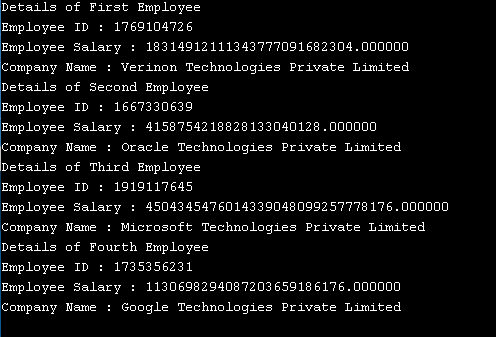
Example #3 – Typedef unsigned char
Code:
#include <stdio.h>//Add all the basic C language libraries
int main()
{
//typedef for give struct keyword to user wanted keyword as like below
typedef unsigned char uchar;
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar alphabet = 'a';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar a='P';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar b='b';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar c = 'C';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar d='d';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar e = 'E';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar f='f';
//declare character variable with user defined keyword
uchar g='g';
//Displaying output of the user
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", alphabet);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", a);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", b);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", c);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", d);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", e);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", f);
printf("alphabet inside main() : %c\n", g);
return 0;
}Output:
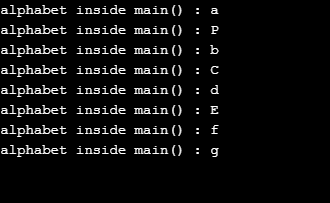
Conclusion
Typedef is used to declare predefined C data types or keywords with user-defined names. It reduces the repetition same data type again and again. We can conclude by this we can change any c data type name with any user wanted name.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to typedef in C. Here we also discuss the Introduction and how does typedef works, along with examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


