Updated July 21, 2023
Definition of Turnover Ratios
The term “Turnover Ratios” refers to the set of financial ratios that indicate how efficiently a company is leveraging its assets and managing its liabilities.
The formula (Receivables, Payables, and Inventory) is expressed as,
Types of Turnover Ratios
In this article we will discuss three of the major ratios:
- Receivable Turnover Ratio (RTR) is an asset side turnover ratio that assesses the ability of a company to collect the receivables from the customers due to credit sales during a given period.
- Payables Turnover Ratio (PTR) is a liability side turnover ratio that determines how well a company can manage and extend the payments that are to be made to the suppliers during a given period.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio (PTR) is another asset side turnover ratio that indicates how effectively a company manages raw material, WIP and finished goods stock during a given period.
Examples
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
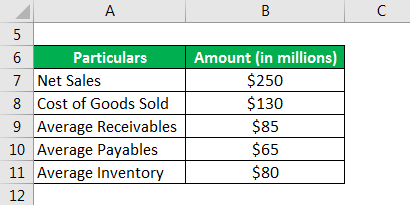
Let us take the example of a company to illustrate the calculation of turnover ratios. According to the company’s annual report for the year 2019, it booked net sales of $250 million and incurred the cost of goods sold of $130 million. Further, average receivables, average payables and average inventory for the period were $85 million, $65 million and $80 million respectively. Based on the given information, calculate the following: Receivables, Payables, and Inventory Turnover Ratio.
Solution:
RTR is calculated using the formula given below
Receivables Turnover Ratio = Net Sales / Average Receivables
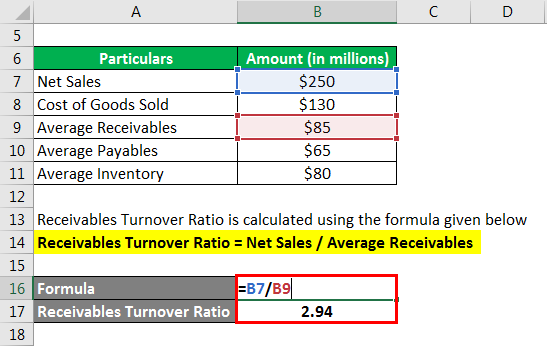
- RTR = $250 million / $85 million = 2.94x
Payables Turnover Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
PTR = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Payables
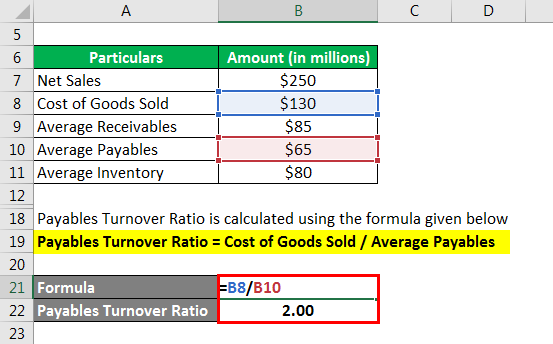
- PTR = $130 million / $65 million = 2.00x
Inventory Turnover Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory
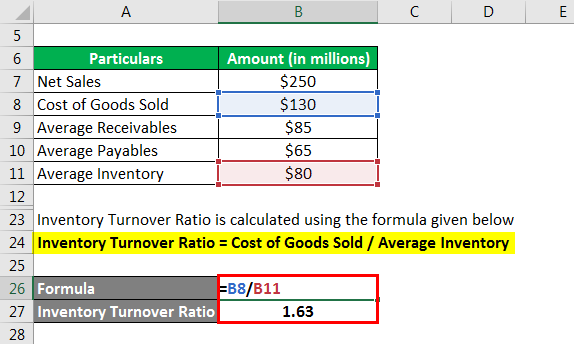
- ITR = $130 million / $80 million = 1.63x
Therefore, the company’s receivables, payables, and inventory ratio during 2019 were 2.94x, 2.00x and 1.63x respectively.
Example #2
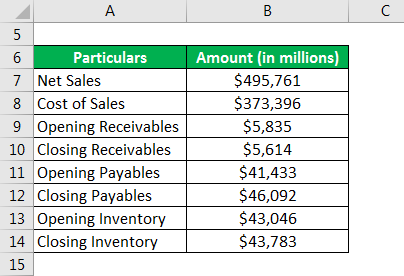
Let us now calculate the turnover ratios using the example of Walmart Inc. As per its income statement for 2018, it booked net sales of $495,761 million and incurred the cost of sales of $373,396 million. Further, its balance sheet shows that receivables, payables, and inventory at the start of 2018 were $5,835 million, $41,433 million and $43,046 million respectively and at the end of the year were $5,614 million, $46,092 million and $43,783 million respectively. Calculate Walmart Inc.’s Receivable, Payables and Inventory ratio for 2018.
Solution:
Receivables Turnover Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
RTR = 2 * Net Sales / (Opening Receivables + Closing Receivables)
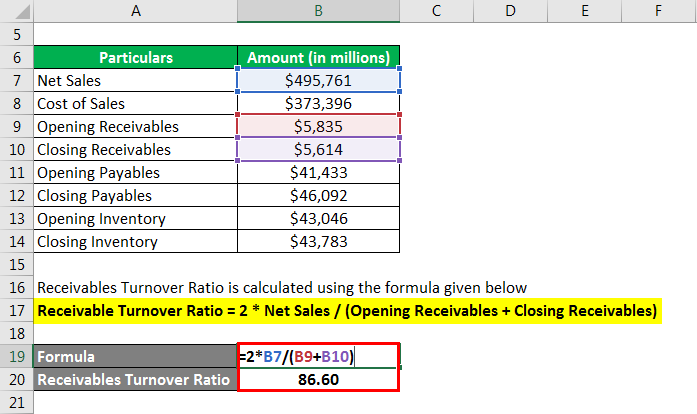
- RTR = 2 * $495,761 million / ($5,835 million + $5,614 million) = 86.60x
Payables Turnover Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
PTR = 2 * Cost of Sales / (Opening Payables + Closing Payables)
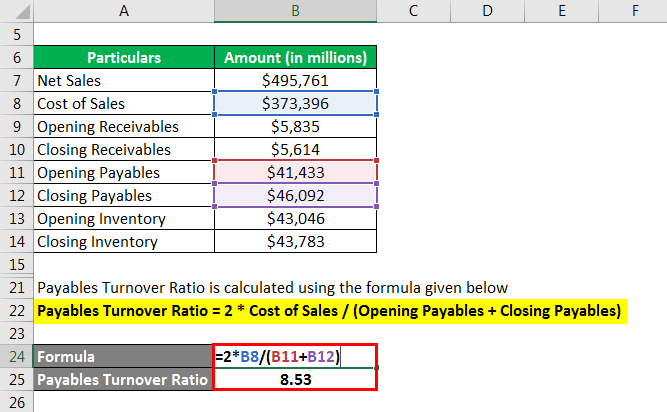
- PTR = 2 * $373,396 million / ($41,433 million + $46,092 million) = 8.53x
Inventory Turnover Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
ITR = 2 * Cost of Sales / (Opening Inventory + Closing Inventory)
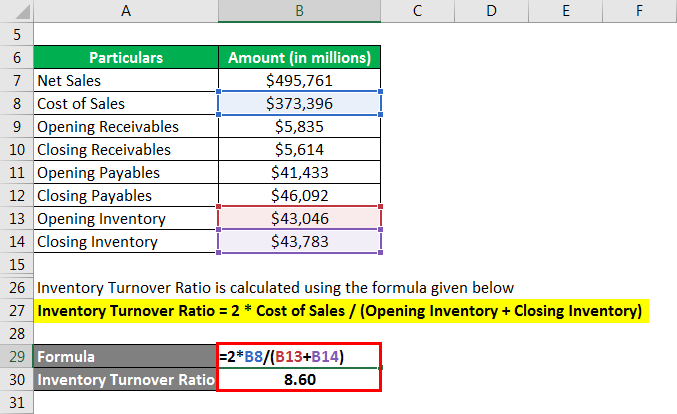
- ITR = 2 * $373,396 million / ($43,046 million + $43,783 million) = 8.60x
Therefore, Walmart Inc.’s receivable, payables and inventory turnover ratio during 2018 were 86.60x, 8.53x and 8.60x respectively.
Explanation of Turnover Ratios
The formula can be calculated by using the following points:
Step 1: Firstly, determine the net sales registered by the company during the given period.
Step 2: Next, determine the average receivables during the period based on the receivables at the start (opening) and at the end (closing) of the period.
Average Receivables = (Opening Receivables + Closing Receivables) / 2
Step 3: Finally, the formula for the receivables can be expressed as net sales (step 1) divided by average receivables (step 2) as shown below.
RTR = Net Sales / Average Receivables
The formula for payables can be derived by using the following steps:
Step 4: Firstly, determine the cost of goods sold or cost of sales incurred by the company during the given period, which is the aggregate of all directly assignable costs of production.
Step 5: Next, determine the average payables during the period based on the payables at the start (opening) and at the end (closing) of the period.
Average Payables = (Opening Payables + Closing Payables) / 2
Step 6: Finally, the formula for the payables can be expressed as the cost of goods sold (step 4) divided by average payables (step 5) as shown below.
PTR = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Payables
The formula for inventory can be derived by using the following steps:
Step 7: Same as step 4.
Step 8: Next, determine the average inventory during the period based on the inventory held at the start (opening) and at the end (closing) of the period.
Average Inventory = (Opening Inventory + Closing Inventory) / 2
Step 9: Finally, the formula for inventory turnover ratio can be expressed as the cost of goods sold divided by average inventory.
Importance
These ratios basically indicate the working capital requirement of a business. Typically, a higher value of receivable and inventory coupled indicates that receivables are collected quickly and inventory is well utilized resulting in the lower amount of working capital is engaged in the business, while a lower value of payables means that the company is able to stretch the supplier payment which again reduces working capital requirement.
Conclusion
So, it can be easily said that the turnover ratios are very important for a company as it indicates its short-term liquidity position and working capital cycle during a given period.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Turnover Ratios. Here we discuss how to calculate along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


