What is Transfer Learning?
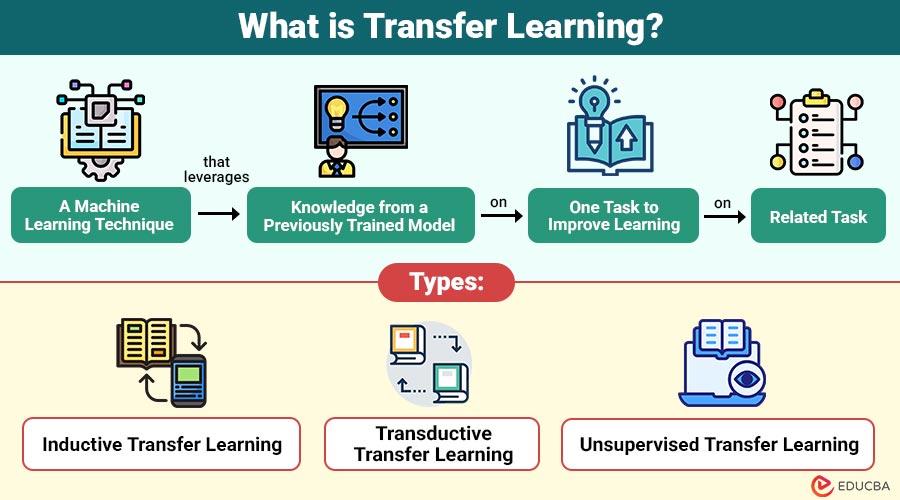
Transfer learning is machine learning technique that leverages knowledge from a previously trained model on one task to improve learning on related task.
Transfer learning uses pre-trained weights on a related dataset to train a model instead of starting from scratch. This greatly reduces training time and improves performance, particularly when the new dataset is small.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Transfer learning leverages knowledge from pre-trained models to improve performance and lower training time for new tasks.
- Fine-tuning enables models to adapt to domain-specific datasets, even when labeled data are limited.
- It enables rapid prototyping and cost-efficient AI solutions across computer vision, NLP, speech, and robotics.
- Transfer learning enhances generalization by reusing learned features from related tasks, improving accuracy on target problems.
How Does Transfer Learning Work?
Transfer learning typically follows these steps:
1. Select a Pre-trained Model
Choose a model trained on a large, relevant dataset (e.g., ImageNet, Wikipedia, Common Crawl).
2. Freeze or Fine-Tune Layers
- Freeze early layers that capture general features
- Fine-tune later layers for task-specific learning
3. Adapt to Target Task
Replace the output layer to match the new task’s requirements.
4. Train on Target Dataset
Train the modified model using a smaller dataset.
Types of Transfer Learning
It can be categorized based on the relationship between source and target tasks:
1. Inductive Transfer Learning
The domains are distinct (e.g., different datasets), but the source and goal tasks are the same.
2. Transductive Transfer Learning
Although the domains (e.g., distinct datasets) differ, the source and target tasks are the same.
3. Unsupervised Transfer Learning
Both source and target tasks are unsupervised learning problems, such as clustering or dimensionality reduction.
Advantages of Transfer Learning
Here are the key advantages of transfer learning
1. Reduces Training Time
Pre-trained models significantly reduce the time required to train complex neural networks from scratch.
2. Requires Less Labeled Data
Fine-tuning pre-trained models is effective even with small datasets, addressing data scarcity.
3. Improves Model Performance
Models leverage previously learned patterns, often achieving better accuracy and generalization than training from scratch.
4. Cost Efficiency
Transfer learning lowers computational and storage expenses by reusing existing models rather than building new ones.
5. Facilitates Rapid Prototyping
Developers can quickly experiment and iterate on models, which is ideal for research projects or startup environments.
Real-World Applications of Transfer Learning
Transfer learning has become a cornerstone in modern AI across multiple domains:
1. Computer Vision
Image classification, object detection, and medical imaging rely heavily on transfer learning.
2. Natural Language Processing
It has revolutionized NLP, enabling models such as BERT, GPT, and RoBERTa.
3. Speech Recognition
Models trained on large voice datasets can be adapted to recognize regional accents or specific languages.
4. Recommender Systems
Pre-trained embeddings can improve personalization in recommendation engines for e-commerce or streaming platforms.
5. Robotics
Transfer learning allows robots to apply skills learned in simulations to real-world tasks.
Key Differences Between Transfer Learning and Traditional Machine Learning
Here is a comparison highlighting their key differences:
| Feature | Transfer Learning | Traditional Machine Learning |
| Training Requirement | Can work with smaller datasets | Requires a large labeled dataset |
| Time and Resources | Reduced training time and costs | High computational cost |
| Generalization | Leverages knowledge from source tasks | Limited to trained domain |
| Use Cases | Multiple related tasks across domains | Domain-specific, isolated tasks |
| Model Development | Fine-tuning existing models | From scratch |
Challenges in Transfer Learning
Despite its advantages, transfer learning has some challenges:
1. Negative Transfer
Transferred knowledge may reduce performance when the source and target tasks are too dissimilar.
2. Domain Shift
Differences between source and target datasets may require careful adaptation to avoid biases.
3. Overfitting Small Datasets
Fine-tuning on very small datasets can lead to overfitting unless regularization techniques are applied.
4. Model Complexity
Pre-trained models can be large and resource-intensive, posing deployment challenges on low-power devices.
5. Data Privacy and Licensing
Using publicly available pre-trained models may raise concerns regarding data ownership and compliance.
Best Practices for Implementing Transfer Learning
Here are some essential best practices to ensure effective knowledge transfer, improved performance, and efficient model training.
1. Choose a Relevant Pre-trained Model
Select a source model trained on a dataset closely related to your target domain for better feature transfer.
2. Freeze Initial Layers First
Keep early layers frozen initially, as they capture general features like edges, textures, or linguistic patterns.
3. Use a Lower Learning Rate for Fine-Tuning
Apply a smaller learning rate to prevent destroying previously learned weights during fine-tuning.
4. Gradually Unfreeze Layers
Unfreeze layers progressively to allow controlled adaptation while minimizing the risk of overfitting.
5. Monitor Validation Metrics Carefully
Track validation loss and accuracy to detect negative transfer, overfitting, or domain mismatch early.
Final Thoughts
Transfer learning revolutionizes machine learning by reusing pre-trained models to reduce training time, costs, and data requirements. It improves accuracy and accelerates model development across domains like computer vision, NLP, robotics, and speech recognition. As AI evolves, transfer learning remains essential for scalable, efficient, and accessible AI innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can transfer learning be applied to small datasets?
Answer: Yes, transfer learning is particularly effective with small datasets because pre-trained models provide a strong starting point.
Q2. What is negative transfer?
Answer: Negative transfer occurs when the source task knowledge hinders performance on the target task due to task dissimilarity.
Q3. Which models are commonly used for transfer learning in NLP?
Answer: Models like BERT, GPT, RoBERTa, and XLNet are widely used for NLP transfer learning applications.
Q4. Is transfer learning suitable for real-time applications?
Answer: Yes, especially with lightweight models and fine-tuned networks optimized for inference speed.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Transfer Learning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
