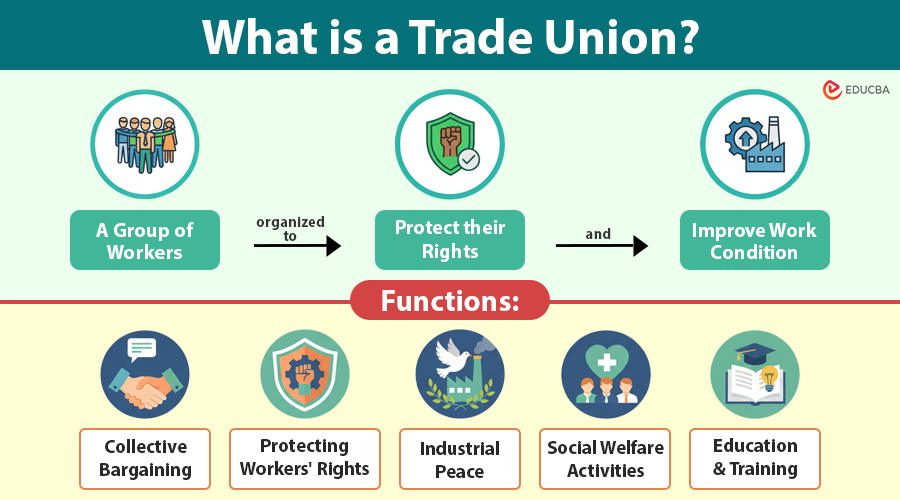
Meaning of Trade Union
Wage earners form a trade union to maintain and improve their working conditions. The International Labour Organization (ILO) defines a trade union as a group of workers formed to safeguard and enhance their economic and social interests.
Key elements of trade unions include:
- Membership: Composed of workers from a particular industry, sector, or profession.
- Collective purpose: Protecting members’ rights through negotiation and collective bargaining.
- Voluntary association: Workers voluntarily join unions to pursue common interests and goals.
- Legal recognition: Many countries regulate through labor laws, granting them rights and responsibilities.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Historical Development
- Objectives
- Functions
- Importance
- Types
- Structure and Organization
- Role in Industrial Relations
- Challenges
- How Does it Work Today?
- Trade Unions in India
- International Role
- Future
Historical Development
Trade unions originated in the 18th and 19th centuries during the Industrial Revolution. Workers faced unsafe environments, long hours, and inadequate pay, leading to the formation of early worker associations.
Early Origins
- Guilds in Medieval Europe: Craftsmen’s guilds in the Middle Ages functioned as early forms of labor organizations, regulating standards and protecting members.
- Industrial Revolution (18th–19th Century): With the rise of mass factory employment, exploitation increased. Workers began organizing strikes and protests, which led to the emergence of modern unions.
19th Century Movements
- Britain: The Combination Acts initially banned worker organizations, but after repeal, unions gained legal recognition in 1824.
- United States: The Knights of Labor (1869) and the American Federation of Labor (1886) were two of the earliest labor unions.
- India: The first formal trade union was the Madras Labour Union, founded in 1918. In 1920, workers established the All India Trade Union Congress (AITUC).
20th Century and Beyond
- During the 20th century, labor unions expanded globally, advocating for fair wages, shorter workdays, paid leave, and improved workplace safety.
- In modern times, unions continue to advocate for workers’ rights in the face of globalization, privatization, and technological advancements.
Objectives of Trade Unions
Trade unions broadly pursue objectives in three main areas: economic, social, and political. Each objective focuses on improving the lives of workers and ensuring fairness in the workplace.
1. Economic Objectives
It aims to protect the financial and professional interests of its members. Key economic objectives include:
- Secure fair wages and compensation: Unions negotiate with employers to ensure workers receive salaries that reflect their skills, experience, and contributions, including allowances and bonuses.
- Reduce working hours and improve working conditions: By advocating for reasonable work hours, proper breaks, and safe work environments, unions help prevent exploitation and improve productivity.
- Ensure job security and prevent unfair dismissals: Unions provide a safety net by defending workers against arbitrary layoffs, ensuring employment stability.
2. Social Objectives
It also focuses on improving the quality of life and promoting solidarity among workers. Social objectives include:
- Promote solidarity and unity among workers: Unions encourage teamwork, cooperation, and a collective voice to address common concerns.
- Enhance the social and cultural welfare of members: Unions often organize cultural events, sports activities, and social programs to strengthen community bonds among workers.
- Provide educational, medical, and recreational facilities: Many unions offer scholarships, healthcare programs, and recreational facilities to support members and their families.
3. Political Objectives
It plays a vital role in shaping labor policies and advocating for workers’ rights at the national level. Political objectives include:
- Influence government policies in favor of workers: Unions lobby for labor-friendly laws, minimum wage standards, and social security schemes.
- Participate in the democratic process to safeguard labor rights: Unions ensure that workers’ voices are heard in governance by participating in policy discussions and forming alliances with political parties.
- Advocate for labor-friendly laws and social justice: Unions fight for legislation that promotes equality, protects workers from discrimination, and ensures justice in the workplace.
Functions of Trade Unions
There are a variety of functions to protect and promote the welfare of workers.
1. Collective Bargaining
Unions negotiate with employers on behalf of workers to agree on pay, benefits, and working conditions. This process balances the power between employers and employees.
2. Protecting Workers’ Rights
Unions defend workers against exploitation, discrimination, and unfair treatment. They adhere to labor laws and provide workers with legal support when needed.
3. Industrial Peace
By mediating disputes between employers and workers, unions contribute to industrial peace. Their involvement helps prevent frequent strikes and lockouts.
4. Social Welfare Activities
Many unions offer financial aid, scholarships, housing, and healthcare benefits to their members and their families.
5. Education and Training
Unions often conduct training programs to enhance workers’ skills, thereby increasing their employability and career growth.
6. Political Participation
It influences government policies to protect labor rights at the national level.
Importance of Trade Unions
It plays a crucial role in maintaining a fair and balanced labor market.
- Empowerment of workers: By uniting, workers gain collective bargaining power that strengthens their position against employers.
- Fair wages and benefits: Unions ensure that employees receive just wages, pensions, and other benefits.
- Workplace safety: Unions advocate for better health and safety measures to reduce accidents and hazards.
- Job security: They protect members from arbitrary layoffs or unfair dismissals.
- Reduction of inequality: Unions play a crucial role in reducing income disparities by advocating for fair wages and equitable pay.
- Improved industrial relations: Unions promote dialogue between workers and employers, reducing conflicts and strikes.
- Social justice: They contribute to social reforms, labor welfare, and workplace equality.
Types of Trade Unions
Trade unions can be classified based on their structure and membership.
- Craft Unions: Composed of workers with a particular skill or trade (e.g., electricians, carpenters).
- Industrial Unions: Represent all workers in a specific industry, regardless of skill level (e.g., automobile or textile industry unions).
- General Unions: Open to workers across different trades and industries.
- White-Collar Unions: Represent office staff, professionals, and service sector employees.
- Federations and Confederations: Umbrella organizations coordinating multiple unions (e.g., International Trade Union Confederation).
Structure and Organization of Trade Unions
The structure varies, but they typically include:
- Local unions: Grassroots organizations at the factory or enterprise level.
- Regional/state unions: Groups of local unions under one state or region.
- National federations: Central organizations representing unions at the national level.
- International unions: Global federations promoting international solidarity (e.g., the International Labour Organization collaborates with unions).
Role of Trade Unions in Industrial Relations
Trade unions act as a bridge between employers and employees, ensuring cooperation and understanding. They play a critical role in:
- Negotiating collective agreements.
- Preventing and resolving industrial disputes.
- Encouraging participatory management.
- Promoting fair labor practices.
Challenges Faced by Trade Unions
Despite their importance, they face several challenges in the modern era.
- Declining membership: In many countries, union membership has decreased due to the rise of informal employment, the gig economy, and changing work patterns.
- Employer resistance: Some employers discourage unionization, using strategies to weaken collective action.
- Globalization: Outsourcing and relocation of industries weaken unions’ bargaining power.
- Technological changes: Automation and AI are creating new employment challenges that unions must address.
- Political interference: In some nations, unions are heavily politicized, affecting their independence.
- Fragmentation: Rivalries among multiple unions in the same industry weaken collective strength.
How Trade Unions Work Today?
In the globalized economy, trade unions have expanded their role beyond traditional labor issues.
- Advocating for gig and platform workers in companies like Uber, Swiggy, and Amazon.
- Addressing issues of gender equality and workplace diversity.
- Promoting environmentally sustainable practices in industries.
- Engaging in international solidarity movements to protect migrant workers’ rights.
Trade Unions in India
In India, it is governed by the Trade Unions Act of 1926. The main national federations are:
- All India Trade Union Congress (AITUC): Founded in 1920, it is one of India’s oldest trade unions.
- Indian National Trade Union Congress (INTUC): Affiliated with the Indian National Congress.
- Bharatiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS): Affiliated with the RSS, it is one of the largest unions by membership.
- Centre of Indian Trade Unions (CITU): Associated with leftist political ideologies.
It has played a significant role in achieving labor-friendly laws, such as the Factories Act, the Minimum Wages Act, and the Payment of Bonus Act.
International Role of Trade Unions
Globally, unions have influenced international labor standards through organizations like:
- International Labour Organization (ILO)
- International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC)
- World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU).
They ensure workers’ rights across borders, particularly in multinational corporations and global supply chains.
Future of Trade Unions
The future of trade unions depends on how well they adapt to changes in the workplace.
- Digital platforms: Using technology to connect and organize workers.
- Inclusive membership: Representing gig workers, women, and marginalized groups.
- Policy advocacy: Focusing on global labor issues such as migration, climate change, and automation.
- International collaboration: Building stronger global networks to influence multinational corporations.
Final Thoughts
Trade unions remain an essential pillar of industrial relations, social justice, and workers’ rights. From their origins in the Industrial Revolution to their evolving role in the digital and global economy, unions have consistently fought for fair wages, safe workplaces, and equitable treatment. While they face challenges such as declining membership, globalization, and technological disruption, their continued relevance lies in their ability to adapt, innovate, and expand their role in protecting all categories of workers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a trade union and a professional association?
Answer: A trade union primarily focuses on protecting workers’ rights, wages, and working conditions, while a professional association promotes the interests, skills, and professional development of its members.
Q2. Can self-employed or gig workers join a trade union?
Answer: Yes, many modern trade unions are expanding their membership to include self-employed, freelance, and gig economy workers in order to protect their rights and improve working conditions.
Q3. Are trade unions allowed in all countries?
Answer: No, the legal recognition and rights of trade unions vary by country. Some nations have strict labor laws supporting unions, while others restrict or limit union activity.
Q4. How do trade unions raise funds?
Answer: Unions typically collect membership fees, donations, and contributions from members. Some also run cooperative services, training programs, or social welfare initiatives to generate funds.
Q5. Do trade unions have political affiliations?
Answer: Many trade unions align with political parties or movements, while some operate independently. However, the degree of political involvement varies, and some unions remain non-partisan, focusing solely on worker welfare.
Recommended Articles
We hope this comprehensive guide on Trade Unions helped you understand their role in protecting workers and shaping labor policies. Explore our related articles on:

