Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Ternary Operator in SQL
In this article, we will see how to use ternary Operator which is unfortunately not supported in SQL so then we are going to see an alternative of a conditional operator to work with SQL. A ternary operator with conditional expression performs real-life scenario like for different conditions different actions are performed. Ternary Operator in SQL also be termed as Conditional Operator can be defined as a unique decision-making operator found in many programming languages. Case Expression can be expanded as a generalization of Ternary Operator. In other words, I can say that it is a shorthand way of using If-Else and nested if-else statement in a query. It is called ternary as it takes three elements (condition, true statement and false statement) which takes one condition and produces two results true or False and it takes up any data type as a value. It comes with Select statement along with Where, Group By, Order By clause.
Syntax
The basic Syntax of Ternary operator is given below:
(condition)? (First statement): (Second Statement);Where condition implies the expression when the condition is evaluated if the statement is true first statement will be executed.
How does Ternary Operator works in SQL?
As Ternary Operator Alternative is CASE Statement and IF (), Let’s Go with that. Let’s see this topic in detail in the following Section. There are two different cases where ternary operator logic can be implemented. Some versions would use case, if, when, then. Based on the value of the respective condition is selected.
The cases are:
- Using CASE statement
- Using IF function
IF(Statement expression, Result for true , result)Case Expression: It is a simple statement with at least using One WHERE and THEN statements in the query and should end finally with END Statement. Default component is SELECT in which CASE goes pretty well. This expression checks with each row in the table to meet the conditions true. Nevertheless, the Ternary operator of SQL has a similar Case expression which is very flexible. And below displays the generic form of Syntax. This is the syntax for a single case when statement.
CASE WHEN expression statement THEN <true statement result> ELSE <false statement _result> ENDThe above syntax compares the given expression statement to value of WHEN clause and displays the first true statement after the successive comparison. The next ELSE statement is not evaluated. In another case, while the expression statement returns a false value or in some situation to be NULL for the WHEN clause, it returns the else false statement.
The same while expanding to multiple conditions in a CASE statement which gives out the syntax like:
SELECT (CASE WHEN (condition 1 exp) THEN ( true statement ) WHEN (condition2 exp) THEN ( true statement ) ELSE( false statement ) END) AS "Conditional_ex" FROM table;It evaluates the condition statement and executes first result and the remaining where clause is not executed. If the First when Is false the corresponding condition2 is evaluated. You can also make use of multiple when-then pair within the case expressions.
Examples to Implement Ternary Operator in SQL
Using the following table for the rest of the section to see the examples.
Example #1
Query For Creating a Table to Implement CASE and IF statement.
Code:
CREATE TABLE empdb (
ed_id INT NOT NULL,
ed_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
ed_gender varchar (2),
PRIMARY KEY (ed_id),
UNIQUE (ed_name)
);
INSERT INTO empdb (ed_id, ed_name ,ed_gender) VALUES
(01,'leslia','F'),
(02,'Britan','M'),
(03,'Grim Jen','M'),
(04,'Papus','F');
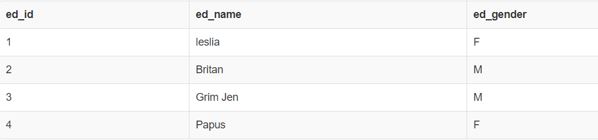
select * from empdb;Query:
SELECT ed_name, (CASE WHEN ed_gender = 'M' THEN 'Prince' ELSE 'Princess' END) AS ed_gender FROM empdbOutput:
Example #2
Considering the new table Airline for the next example.
Code:
CREATE TABLE Airline (
Aid INT NOT NULL,
Airlinename VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
service INT,
City varchar (20),
PRIMARY KEY (Aid),
UNIQUE (Airlinename)
);
INSERT INTO Airline
(Aid, Airlinename , Service ,City)
VALUES
(01,'Indigo', 15,'SriLanka'),
(02,'SpiceJet',12,'Hyderbad'),
(03,'Lufthansa',08,'Doha'),
(04,'AirIndia',21,'Delhi') ,
(05,'Emirates',18,'Norway');
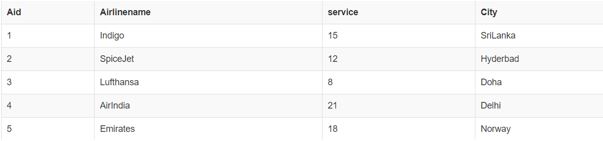
select * from Airline;Query:
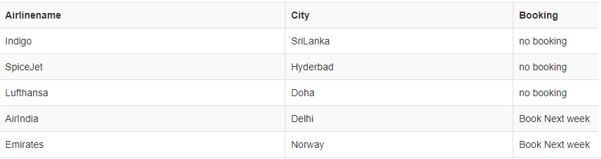
SELECT Airlinename, City,
CASE
WHEN Service> 15 THEN 'Book Next week'
WHEN Service = 21 THEN 'Book Immediately'
ELSE 'no booking'
END AS Booking
FROM Airline;Output:
Example #3
Using IF function:
This Function is treated as an extension of CASE expression and it returns true if the condition is true and it returns false for other value. This IF () function is entirely different from IF Statement of SQL.
IF((condition), <value true statement>, <value false statement>)If the condition expression evaluates to positive then the first expression ‘value true statement is executed provided if it is not null, otherwise, it returns ‘false value’.
In the below section we shall see several scenarios how the if the function is done with various examples. Let’s go.
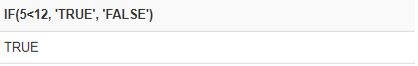
- Checking Numeric Conditions and returning the result as String. checking Numeric values 5 and 10 if 5 is less than Twelve the first statement ‘True’ is executed.
Code:
SELECT IF(5<12, 'TRUE', 'FALSE');Output:
- Checking with numeric values
Code:
SELECT IF(5 != 3,'true','false');…………………. Returns TRUE
SELECT IF(5 = 3,'true','false');………………….. Returns FALSEComparing Two strings with IF ()
SELECT IF(STRCMP('Welcome to the Blog', 'blg')=0, 'TRUE', 'FALSE');Output:
- Checking Numeric Condition and returning numeric value as a result.
Code:
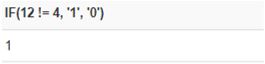
SELECT IF(12 != 4, '1', '0');Output:
Example #4
Let’s see the implementation by taking Airline Database using IF().
Code:
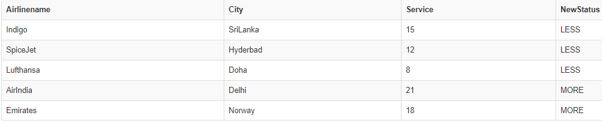
SELECT Airlinename, City, Service, IF(Service>15, "MORE", "LESS") As NewStatus
FROM Airline;Output:
Where Clause: Using Where Clause in IF() to check the condition for true/false.
Code:
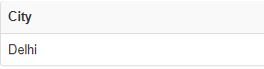
SELECT City
FROM Airline
WHERE IF(`Service` = '21', 1, 0) = 1Output:
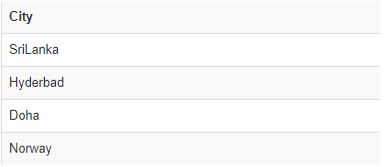
- If we Change the above Query with the where condition = ‘0’ then apart from Delhi other city are displayed with respective to false condition = 0.
Code:
SELECT City
FROM Airline
WHERE IF(`Service` = '21', 1, 0) = 00Output:
Conclusion
Therefore, coming to the end part of the article, we have seen how to use alternate of the ternary operator with CASE statement and IF statement which fulfils the conditional statements completely. And also, we have reviewed some examples where the conditions have been evaluated.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Ternary Operator in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.