What is Technology Enablement?
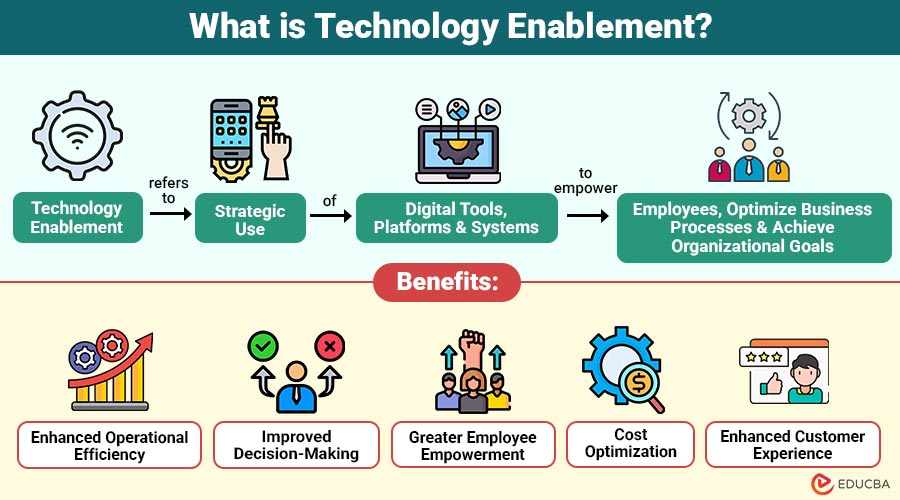
Technology enablement refers to the strategic use of digital tools, platforms, and systems to empower employees, optimize business processes, and achieve organizational goals. It focuses not just on technology adoption but on ensuring that technology is effectively integrated, accessible, and aligned with business objectives.
Unlike simple automation or IT implementation, technology enablement prioritizes user adoption, skill development, process alignment, and measurable value creation. Making technology a performance facilitator rather than a stand-alone investment is the aim.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Technology enablement empowers employees by effectively aligning digital tools with skills, processes, and organizational objectives.
- Streamlined workflows and automation enhance productivity, agility, and innovation while reducing costs and operational inefficiencies.
- Successful enablement requires user-centric adoption, training, change management, and continuous monitoring for measurable business value.
- Technology enablement is an ongoing strategy bridging technology investments with improved performance, customer experience, and competitiveness.
Importance of Technology Enablement
Technology enablement has become essential due to increasing market complexity, customer expectations, and competitive pressure. Its importance can be understood through the following elements:
1. Improved Productivity
Technology streamlines processes by automating repetitive tasks, minimizing human labor, and freeing up employees to concentrate on higher-value work.
2. Enhanced Agility
Organizations respond faster to market changes and evolving customer needs, thereby improving flexibility, decision-making, and overall business adaptability.
3. Innovation Enablement
Technology provides insights, tools, and platforms that empower teams to develop new products, services, and creative business solutions.
4. Employee Empowerment
Employees gain efficiency, collaboration, and job satisfaction through accessible technology, skill development, and streamlined processes supporting their performance.
5. Customer-Centric Operations
Digital tools enable personalized, seamless experiences, improving engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty, and consistently delivering services tailored to customer expectations.
Key Components of Technology Enablement
Here are the key components that collectively drive effective technology enablement within organizations:
1. Digital Tools and Platforms
Organizations leverage tools such as cloud computing, CRM systems, ERP platforms, collaboration software, and analytics tools to streamline operations and improve decision-making.
2. Process Optimization
Technology enablement involves redesigning workflows to maximize the value of technology, eliminating redundancies and manual inefficiencies.
3. People and Skill Development
Employees must be trained and supported to use technology effectively. Change management and digital upskilling play a crucial role.
4. Data and Analytics
Data-driven insights enable organizations to monitor performance, predict trends, and make informed decisions.
5. Governance and Security
Strong governance ensures compliance, data security, and responsible technology usage across the organization.
Benefits of Technology Enablement
When implemented effectively, technology enablement offers numerous benefits:
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Organizations may lower errors, increase productivity, and maximize resource use by automating repetitive processes and optimizing workflows.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Managers can make well-informed decisions that support corporate goals thanks to data-driven insights from advanced analytics and BI technologies.
3. Greater Employee Empowerment
Technology enablement allows employees to focus on strategic initiatives rather than mundane tasks. Tools and training empower teams to collaborate efficiently and innovate continuously.
4. Cost Optimization
5. Enhanced Customer Experience
Technology enablement enables personalized experiences, faster response times, and seamless interactions across multiple channels, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges of Technology Enablement
Despite its advantages, technology enablement presents several challenges:
1. Resistance to Change
Employees may resist adopting new technologies, especially if they feel unfamiliar or complex. To overcome this reluctance, training programs and effective change management are crucial.
2. High Initial Investment
Implementing advanced technologies requires financial investment in hardware, software, and training. Organizations must plan for both upfront and ongoing costs.
3. Integration Complexities
Integrating new systems with the existing infrastructure can be challenging. Preventing data silos and preserving interoperability are essential for success.
4. Cybersecurity Risks
As organizations become more digitally enabled, they face increased exposure to cyber threats. Robust security protocols and continuous monitoring are critical to safeguard data.
5. Skill Gaps
Technology enablement requires skilled personnel. Organizations must address skill gaps through continuous learning, hiring, or outsourcing.
Use Cases Across Industries
Here are use cases of how technology enablement drives value across various sectors:
1. Enterprise IT
Enabling cloud platforms, DevOps tools, and automation frameworks to improve system reliability and scalability.
2. Healthcare
Putting telemedicine platforms, data analytics, and electronic health records (EHRs) into practice to improve patient care and organizational effectiveness.
3. Banking and Financial Services
4. Manufacturing
Adopting IoT, predictive maintenance tools, and smart factory solutions to optimize production and reduce downtime.
5. Retail and E-commerce
Leveraging CRM systems, recommendation engines, and omnichannel platforms to personalize customer journeys.
Real-World Examples
Here are real-world examples demonstrating successful technology enablement in different industries:
1. Global Enterprise Collaboration
A global company used cloud collaboration tools so remote teams could work together easily, cutting project completion time by 30%.
2. Financial Services Automation
A banking institution enabled AI-powered workflow automation, improving compliance accuracy and reducing processing costs.
3. Retail Digital Enablement
A retail brand adopted data analytics and CRM platforms to personalize customer interactions, increasing customer retention rates.
Best Practices for Successful Technology Enablement
Here are best practices organizations follow to ensure effective technology enablement:
1. Align Technology with Business Goals
Make sure every technology effort clearly helps achieve measurable business goals by improving efficiency, boosting productivity, and supporting long-term growth.
2. Adopt a User-Centric Approach
Focus on usability, accessibility, and employee experience to maximize engagement, adoption, and satisfaction with technology solutions.
3. Invest in Training and Change Management
Provide continuous learning, support, and guidance to employees to ensure successful adoption of new technologies.
4. Start Small and Scale Gradually
Pilot initiatives minimize risk, allow testing, and enable scalable technology implementation with higher success rates.
5. Leverage Data for Continuous Improvement
Use analytics to monitor adoption, evaluate performance, and optimize technology investments for sustained business value creation.
Final Thoughts
Technology enablement is no longer optional—it is a strategic necessity in the digital era. By empowering people, optimizing processes, and leveraging the right technologies, organizations can unlock efficiency, innovation, and sustainable growth. When executed thoughtfully, technology enablement bridges the gap between technology investment and business value, ensuring organizations remain agile, competitive, and future-ready.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is technology enablement measured?
Answer: Through KPIs such as adoption rates, productivity improvements, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
Q2. Can small businesses benefit from technology enablement?
Answer: Yes. Scalable cloud tools and digital platforms enable accessibility to organizations of all sizes.
Q3. What role does leadership play in technology enablement?
Answer: Leadership drives vision, adoption, and cultural change essential for success.
Q4. Is technology enablement a one-time initiative?
Answer: No. It is an ongoing process that evolves with business needs and technological advancements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Technology Enablement” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
