Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to T-SQL DATEDIFF
The T-SQL DATEDIFF is defined as a primary function in T-SQL that can be used to find the difference between two date-utilities in which it has been utilized to differentiate between two date values having various date parts. This function occurs in the date function; it can take three parameters: interval, start date, and end date. The interval part is the defined part that can be returned, and it can have the specified values and the dates that have been used to find the variance between them, and it will give back the variance between two identified dates.
Overview T-SQL DATEDIFF
The DATEDIFF is the normal function in the T-SQL that can be used to perform mathematical calculations depending on the dates; it provides the output as integer values as dates, months, years, minutes, and seconds. This function can be helpful when we want to find out the difference between two dates. It is related to the data functions category; it takes three parameters: interval, first date, and the end date, in which we can say it can have the interval part and the date value part.
The date function can be demonstrated with the date and time values as a dispute; the function is necessary when we try to find the variance between the date and timestamps; it has been compatible with some SQL server versions that are, SQL server 2008 plus, Azure SQL database and data warehouse, and also with a parallel data warehouse.
When to use T-SQL DATEDIFF?
The T-SQL DATEDIFF is the function that can be provided in the date function of T-SQL, so when we have to find out the variance in the days, months, and years between the two dates, then this function can be used. Moreover, it is also useful when we have to find out the variance between the expected order delivery date and the actual order delivery; then, in such type of cases, the DATEDIFF() function is workable, and also, when we want to track the time it means that when we want to count how many years we have spent in any project since it has been started and till the present time because this function can give back the count for the specified interval and also it works between the datepart boundaries which have been provided in the start date and the end date.
This function can be helpful if we want to find consecutive dates; the difference between many dates means if we have lots of data and we have to find its difference.
T-SQL DATEDIFF Function
The DATEDIFF() function has been utilized to find the variance between two defined dates, and it can occur in the date function; this function can receive the three parameters in which the first is interval, the second is the start, and the third is the end date.
Syntax:
DATEDIFF (interval/Datepart, start_date, end_date);
Or
DATEDIFF (interval, start_date, end_date) As DateDiff;where,
- Interval: It can be the particular part which we can get back, and the values will be in the following format table list,
- Year, yy, yyyy: This can be the defined Year, Year.
- quarter, qq, q: This can be defined as a quarter.
- month, mm, m: It can also be the specified month.
- dayofyear, dy, y: It is the defined Day of the Year, Year.
- day, dd, d: It is the described Day, Day.
- week, ww, wk: It is the defined Week, Week.
- weekday, dw, w: It is the defined weekday.
- hour, hh: It can be the defined Hour, Hour.
- minute, mi, n: It is the defined Minute, Minute.
- second, ss, s: It is also the defined Second, Second.
- millisecond, ms: It is the defined Millisecond, Millisecond.
- microsecond, mcs: It is the defined Microsecond, Microsecond.
- Start-date and end-date: These are the two defined dates on which we can get the difference between them.
T-SQL DATEDIFF table list Examples
Let us discuss examples of T-SQL DATEDIFF.
Example #1
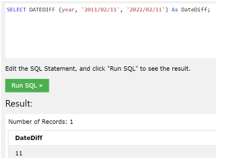
The example of the DATEDIFF() function is where we can get the variance between two date values in a year.
In the above example, we try to get a date value in which we will get the output as 11; as we can see in the query, we have added the ‘As DateDiff’ as it is optional.
Example #2
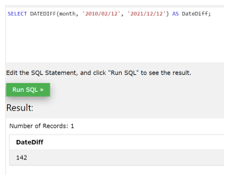
Now see the example of the DATEDIFF () function in which we can get the variance between two date values but in a month.
In the above example, we have provided two different dates for retrieving the date variance, and we get the result in months, as shown in the screenshot.
Example #3
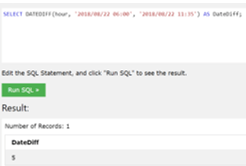
Now we can see the example of the DATEDIFF () function in which we can get the difference between two date values in hours.
In the above example, we need the difference between the hours given in the query, and we get the result shown in the screenshot.
Example #4
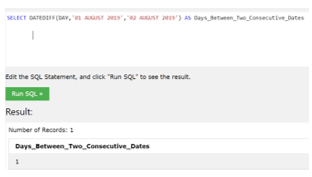
If we try to find the variance between two consecutive dates, we can use the start date and end date, as shown in the screenshot below.
In the above example, we try to find the consecutive dates between the dates provided in the query and get the count of days between them.
Example #5
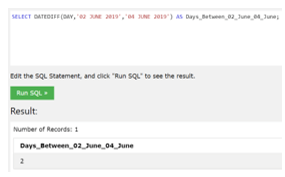
If we try to find the variance between two dates having differences, then by using the below query, we can find it out.
In the above example, we try to find the days count which is present in between the given dates.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that the DATEDIFF is the primary function that can be provided in the date function in which it can give the difference depending on the values; we have also discussed when to use this function, detail of the DATEDIFF function, and list examples of DATEDIFF.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to T-SQL DATEDIFF. Here we discuss When to use T-SQL DATEDIFF, T-SQL DATEDIFF table list, and Examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –