What is Swarm Intelligence?
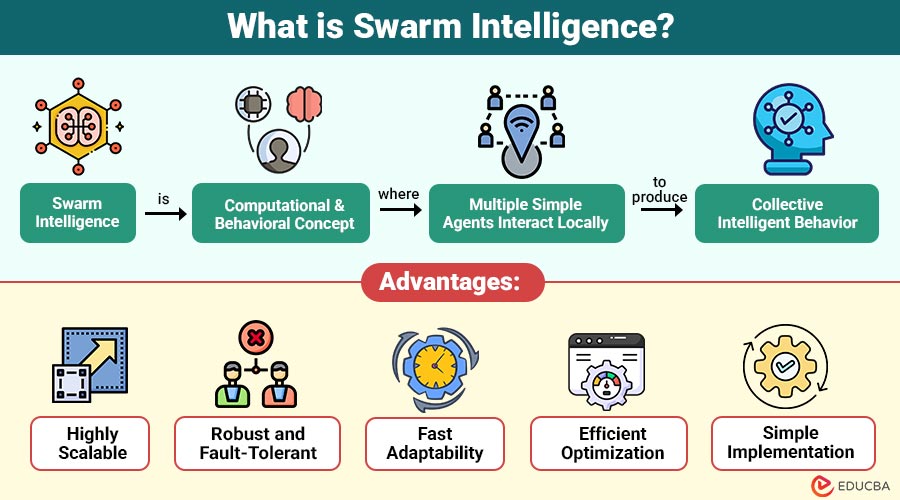
Swarm Intelligence is a computational and behavioral concept where multiple simple agents interact locally to produce collective intelligent behavior. These agents follow simple rules, communicate indirectly, and self-organize to solve problems that would be difficult for a single agent.
Key Characteristics:
- Decentralization – No central authority controls the system.
- Self-organization – Patterns emerge naturally from interactions.
- Flexibility – Swarms adapt quickly to new environments.
- Robustness – The system continues to function even if some agents fail.
- Scalability – Works effectively with small or large populations.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Swarm intelligence leverages interactions among decentralized agents to solve complex problems efficiently and adaptively.
- Natural behaviors of ants, bees, and birds inspire algorithms for optimization and coordination.
- SI systems offer scalability, fault tolerance, and rapid adaptation in dynamic real-world scenarios.
- Swarm intelligence helps groups solve problems without a leader, working together in smart and flexible ways that can be used in many industries.
How does Swarm Intelligence Work?
Swarm intelligence systems rely on three mechanisms:
1. Simple Local Rules
Each agent follows basic rules such as:
- Move toward food
- Avoid collision
- Communicate path
- Share resources
2. Indirect Communication (Stigmergy)
Agents do not communicate directly. Instead, they interact with the environment.
3. Collective Emergence
Individual actions produce global behavior:
- Ants find the shortest path
- Birds produce synchronized flight
- Bees find the best nectar source
These natural phenomena underpin SI algorithms.
Popular Swarm Intelligence Algorithms
Here are some popular swarm intelligence algorithms:
1. Ant Colony Optimization (ACO)
Inspired by ants searching for food, ACO uses pheromone trails to discover optimal paths.
How it works:
- Ant agents explore solutions.
- Better solutions get stronger pheromone updates.
- Over time, the system converges to the best path.
Applications: Routing, scheduling, and network optimization.
2. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
PSO works like a group of birds or fish. Each “particle” moves around, learns from others, and adjusts its direction to find the best solution.
Key concepts:
- Each particle represents a solution.
- Particles follow their own best position and the global best position.
- The system converges to an optimal result.
Applications: Machine learning tuning, engineering design, and neural network training.
3. Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) Optimization
Based on honeybee foraging behavior.
Three types of bees:
- Employed bees search for food (solutions).
- Onlooker bees choose better food sources.
- Scout bees explore new sources.
ABC is well-suited to numeric optimization in large search spaces.
4. Glowworm Swarm Optimization (GSO)
Inspired by glowing behavior in glowworms.
Glowworms emit light → others follow → cluster around optimal results.
Used for multimodal optimization (where multiple solutions exist).
5. Firefly Algorithm (FA)
Fireflies attract each other based on brightness. Fireflies with brighter flashes indicate better solutions. Others move toward them.
Useful for nonlinear optimization problems.
6. Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO)
Based on wolf pack hunting hierarchy:
- Alpha (leader)
- Beta (second leader)
- Delta (assistants)
- Omega (followers)
Agents simulate encircling the prey (the solution) until convergence.
Applications of Swarm Intelligence
Here are some key applications of swarm intelligence across different fields:
1. Robotics
Coordinated multi-robot tasks like exploration, rescue, monitoring, and surveillance without centralized control.
2. Traffic & Transportation
Optimizes traffic flow, vehicle routing, fuel paths, and airline schedules to reduce congestion and delays.
3. Machine Learning Optimization
Efficiently enhances neural networks, feature selection, clustering, and hyperparameter tuning.
4. Telecommunications & Networking
Improves WSN routing, congestion control, resource allocation, and dynamic bandwidth management.
5. Finance & Economics
Aids stock predictions, portfolio management, derivative pricing, and risk assessment using collaborative agents.
Advantages of Swarm Intelligence
Here are the key advantages of swarm intelligence:
1. Highly Scalable
Swarm intelligence enables seamless addition of agents while maintaining system performance without requiring major redesign or restructuring.
2. Robust and Fault-Tolerant
Even if some agents fail, the system continues to operate, delivering consistent, reliable performance under all conditions.
3. Fast Adaptability
Swarm systems rapidly adapt to environmental changes or data variations, maintaining efficiency and effectiveness in real time.
4. Efficient Optimization
SI algorithms can quickly find very good solutions even when problems are big, changing, or complicated.
5. Simple Implementation
Each agent follows straightforward rules, making system development, deployment, and maintenance easier and faster.
Disadvantages of Swarm Intelligence
Here are the main disadvantages of swarm intelligence:
1. Computationally Expensive
Big swarm intelligence systems need a lot of computer power, which makes them take more time and use more energy.
2. Risk of Premature Convergence
Agents can converge too early on local optima, reducing solution quality and overall optimization effectiveness.
3. Difficult to Control
Emergent behaviors from agent interactions can be unpredictable, making precise control and system outcomes challenging.
4. Parameter Sensitivity
Performance depends a lot on choosing the right settings, so you must test and adjust them many times to get the best results.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of swarm intelligence in action:
1. Google Maps Traffic Optimization
2. Drone Swarms in Defense
Autonomous drones coordinate for surveillance, mapping, and target tracking without centralized control or human intervention.
3. Amazon Warehouse Robots
Robots self-organize to pick, move, and sort items efficiently via swarm-intelligence routing algorithms.
4. Robot Fish for Pollution Detection
Schools of robotic fish collaboratively detect oil spills and environmental pollutants in oceans and water bodies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What industries use Swarm Intelligence the most?
Answer: Robotics, telecommunications, logistics, healthcare, finance, and transportation.
Q2. Is Swarm Intelligence used in AI?
Answer: Yes, SI algorithms optimize machine learning, clustering, and neural networks.
Q3. Can Swarm Intelligence replace traditional optimization?
Answer: Not fully, but it complements and often outperforms traditional techniques for complex, dynamic problems.
Q4. How does Swarm Intelligence differ from centralized systems?
Answer: Unlike centralized systems, SI relies on local interactions among agents, leading to emergent, self-organized global behavior without a single controlling entity.
Final Thoughts
Swarm intelligence has transformed how modern systems approach optimization, decision-making, and coordination. Swarm intelligence copies how groups in nature work together, giving powerful, flexible, and reliable solutions for robots, logistics, healthcare, and AI. As industries need smarter and faster coordination, SI will continue to drive future innovations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Swarm Intelligence” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
