Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to Structure Padding in C
Structure padding mainly talks about memory for variables which are aligned based on the size of the variable. Let suppose a “char” of 1 byte memory can be assigned anywhere in between like 0x5000 to 0x5001. Same way if we have an “int” of 4 bytes memory can be assigned anywhere in between like 0x5004 to 0x5008. This structure padding concept is automatic for its member are byte aligned by the compiler.
Pre-requisites: Padding, Structure member alignment and data packing.
How Does Structure Padding Work in C?
- Structure padding is said to be in order to align the data in memory 1 or more un-occupied bytes (empty bytes) are kept between any memory addresses which are actually assigned for other data structure members at the time of memory allocation.
- If we observe the architecture of the computer processor can be read 1 word means bytes in 32 bit processor from memory at a time.
- Utilize this advantage of processor then data is always inserted as 4 bytes package which will becomes insert empty address spaces in between other existing members address.
- After introducing this structure padding concept in we got to know that size of the structure is not always same.
Syntax:
Struct member{
Char character;
Int number;
Double salary;
}Explanation: “Char” data type takes only 1 byte after 3 byte padding(Char, Int and Double) then the number will starts at 4 bytes boundary and rest “Int” and “Double” will takes 4 and 8 bytes respectively.
Examples of Structure Padding in C
Below are the different eamples of Structure Padding in C.
Example #1
Code:
//include basic C library files
#include <stdio.h>
//including string data member in C
#include <string.h>
//creating first structure
struct first_structure
{
int rollNo1, rollNo2;
char firstName;
char character;
float salary;
};
//creating second structure
struct second_structure
{
int rollNo1;
char firstName;
int rollNo2;
char character;
float salary;
};
//main method to run the C application
int main()
{
//taking first structure reference
struct first_structure s1;
//taking second structure reference
struct second_structure s2;
//displaying first_structure and second_structure output
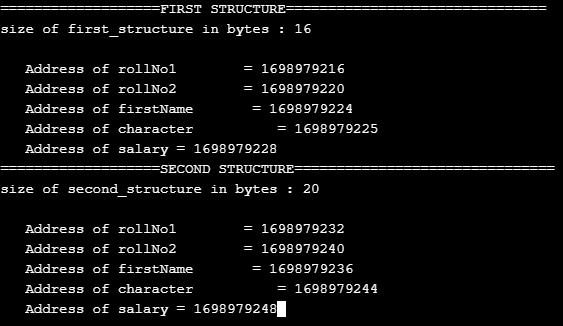
printf("===================FIRST STRUCTURE===============================\n");
printf("size of first_structure in bytes : %d\n",sizeof(s1));
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo1 = %u",&s1.rollNo1 );
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo2 = %u",&s1.rollNo2 );
printf ( "\n Address of firstName = %u",&s1.firstName );
printf ( "\n Address of character = %u",&s1.character);
printf ( "\n Address of salary = %u",&s1.salary);
printf("\n===================SECOND STRUCTURE===============================\n");
printf("size of second_structure in bytes : %d\n",sizeof(s2));
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo1 = %u",&s2.rollNo1 );
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo2 = %u",&s2.rollNo2 );
printf ( "\n Address of firstName = %u",&s2.firstName );
printf ( "\n Address of character = %u",&s2.character);
printf ( "\n Address of salary = %u",&s2.salary);
getchar();
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
Code:
//include basic C library files
#include<stdio.h>
//including string data member in C
#include <string.h>
//creating first structure
struct employee
{
char first_name[40];
char last_name[30];
};
//main method to run the C application
int main()
{
//taking first structure reference
struct employee e;
printf("Enter your first name:");
scanf("%s", &e.first_name);
printf("Enter your last name:");
scanf("%s",&e.last_name);
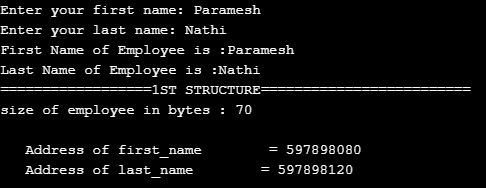
printf("First Name of Employee is :%s\n",e.first_name);
printf("Last Name of Employee is :%s\n", e.last_name);
//displaying output
printf("==================1ST STRUCTURE=========================\n");
printf("size of employee in bytes : %d\n",sizeof(e));
printf ( "\n Address of first_name = %u",&e.first_name);
printf ( "\n Address of last_name = %u",&e.last_name );
return 0;
}Output:
Example #3
Overcome Structure padding problem
Code:
//include basic C library files
#include <stdio.h>
//including string data member in C
#include <string.h>
#pragma pack(1)
//creating first structure
struct first_structure
{
int rollNo1, rollNo2;
char firstName;
char character;
float salary;
};
//creating second structure
struct second_structure
{
int rollNo1;
char firstName;
int rollNo2;
char character;
float salary;
};
//main method to run the C application
int main()
{
//taking first structure reference
struct first_structure s1;
//taking second structure reference
struct second_structure s2;
//displaying first_structure and second_structure output
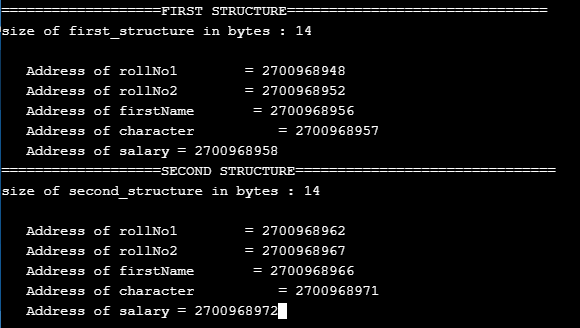
printf("===================FIRST STRUCTURE===============================\n");
printf("size of first_structure in bytes : %d\n",sizeof(s1));
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo1 = %u",&s1.rollNo1 );
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo2 = %u",&s1.rollNo2 );
printf ( "\n Address of firstName = %u",&s1.firstName );
printf ( "\n Address of character = %u",&s1.character);
printf ( "\n Address of salary = %u",&s1.salary);
printf("\n===================SECOND STRUCTURE===============================\n");
printf("size of second_structure in bytes : %d\n",sizeof(s2));
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo1 = %u",&s2.rollNo1 );
printf ( "\n Address of rollNo2 = %u",&s2.rollNo2 );
printf ( "\n Address of firstName = %u",&s2.firstName );
printf ( "\n Address of character = %u",&s2.character);
printf ( "\n Address of salary = %u",&s2.salary);
getchar();
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
Structure padding is said to be in order to align the data in memory 1 or more un-occupied bytes (empty bytes) are kept between any memory addresses which are actually assigned for other data structure members at the time of memory allocation.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Structure Padding in C. Here we discuss the working of Structure Padding in C along with different examples and code implementation. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


