Introduction to SQL WAITFOR
WAITFOR in Standard Query Language (SQL) is a command that is used to block or delay the execution of a batch, transaction or stored procedure for a certain specified amount of time, or till the modification or result of a previously mentioned statement are returned. It’s like making the processor take a small nap before starting the execution of the next query. WAITFOR is used along with DELAY and TIME keywords to delay the execution of a transaction for a certain amount of time.
However, we should note that WAIT FOR works only in SQL SERVER and Azure SQL databases. For other databases, we can use other commands like pg_sleep in POSTGRESQL, DBMS_LOCK.sleep in ORACLE SQL databases.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for using WAIT FOR command in SQL server is as follows :
WAITFOR {DELAY 'time_to_pass' | TIME 'time_to_execute'} [TIMEOUT]The parameters used in the above syntax are as follows:
- DELAY: DELAY keyword is used to specify the time period that must be passed before the execution of the next set of statements or transactions. It can be upto 24 hours at maximum.
- time_to_pass: The amount of time to be passed is mentioned. It can be specified in datetime data format, but just with the time part of the date.
- TIME: The specified time when the next batch or set of statements will start getting executed.
- time_to_execute: It is the time when the WAITFOR statement should stop waiting. Again, similar to time_to_pass, the time can be specified in datetime format but with only time part of the date.
- TIMEOUT: The maximum time for waiting after which the server should come out.
How does the WAITFOR function work in SQL?
The WAITFOR command in the SQL server is generally used with two keywords DELAY and TIME. The former is used to delay the execution of a query or transaction for a specified period whereas the latter is used to execute at a specified time.
Each WAITFOR statement in SQL has a thread associated with it. It is more or less like the process and resources in the operating system. So, if you mention more than one WAITFOR statement on a single server, the WAITFOR statements might not get executed as you have planned for due to starvation and deadlock conditions.
We should note that the WAITFOR command does not make any changes to the semantics of our queries. So, if your first query doesn’t return anything, the WAITFOR will keep waiting for an unprecedented amount of time or till the timeout is reached. Hence, it is a good idea to mention TIMEOUT in such cases. This will prevent the starvation of other WAITFOR statements.
Examples to Implement SQL WAITFOR
Here are a few examples to help us understand the WAIT FOR SQL statement in great detail.
Example #1
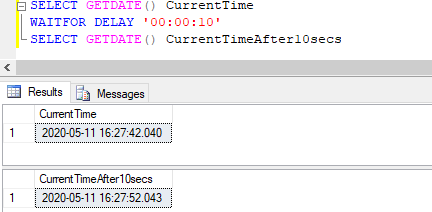
Simple SQL query to illustrate the use of WAITFOR command to delay execution of the next set of statements by 10 seconds.
Code:
SELECT GETDATE() CurrentTime
WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:10'
SELECT GETDATE() CurrentTimeAfter10secsOutput:
Explanation: In the above example, we have used the WAITFOR command to delay the execution of the next statement after a delay of 10 seconds. We can notice that the first GETDATE() function returns the current date and time at 16:27:42.040 and the next GETDATE() function returns the current date and time at 16:27:52.043, that is exactly after DELAY of 10 seconds.
Example #2
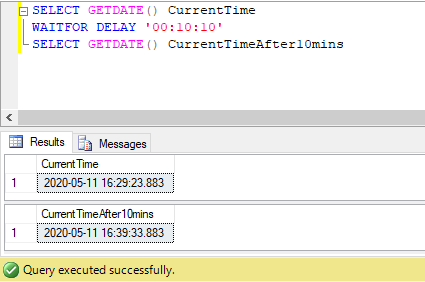
Simple SQL query to illustrate the use of WAITFOR command to delay execution of the next set of statements by 10 minutes and 10 seconds.
Code:
SELECT GETDATE() CurrentTime
WAITFOR DELAY '00:10:10'
SELECT GETDATE() CurrentTimeAfter10minsOutput: The above-mentioned SQL query will keep on executing for 10 minutes and 10 seconds and will return results only after this waiting time is over.
Output: After 10 minutes and 10 seconds, the query gets executed and returns the result as shown in the figure below.
Example #3
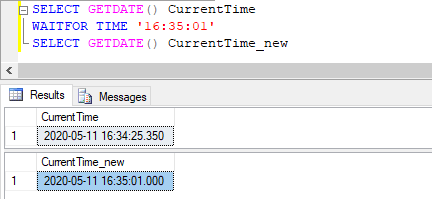
Simple SQL query to illustrate the use of WAITFOR command to execute the next set of statements at a specified time.
Code:
SELECT GETDATE() CurrentTime
WAITFOR TIME '16:35:01'
SELECT GETDATE() CurrentTime_newOutput:
Explanation: Sometimes, we want SQL queries to execute at a specified time. For this purpose, we can use the WAIT FOR command with the TIME keyword.
Example #4
SQL query to schedule a SELECT query after 10 seconds.
Code:
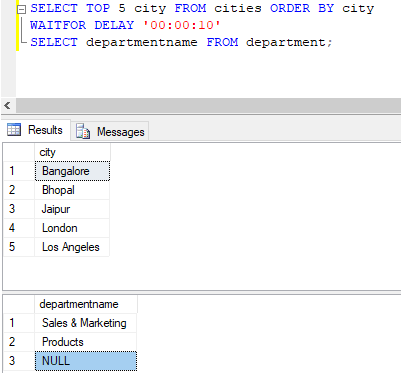
SELECT TOP 5 city FROM cities ORDER BY city
WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:10'
SELECT departmentname FROM department;Output:
Explanation: In this example, we have two queries. The second SELECT query is scheduled to get executed after waiting for 10 seconds after the execution of the first SELECT query, i.e after the return of the first row of the first query.
Example #5
SQL query to schedule a SELECT query at a fixed time.
Code:
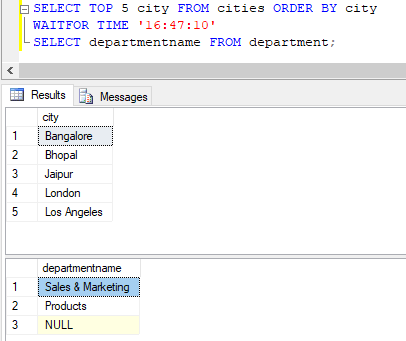
SELECT TOP 5 city FROM cities ORDER BY city
WAITFOR TIME '16:47:10'
SELECT departmentname FROM department;Output:
Explanation: In this example, we have scheduled the execution of the second query at a specified time using the TIME keyword with WAIT FOR command.
Conclusion
WAIT FOR SQL command is used to block or delay the execution of a set of statements, transactions, block, etc. for a specified amount of time. It can also be programmed to schedule query execution at a specified time.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL WAITFOR” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.