Updated June 30, 2023
Introduction to SQL Virtual Table
Virtual tables in SQL, also known as views, are logical structures and entities that assist in adding functionality to simplify the result set of complex queries or a portion of table contents. They act as separate tables that do not physically exist in memory but simulate the working of actual tables. In this article, we will learn about the types of virtual tables that view, their implementation with the help of certain examples, and also the advantages and disadvantages of using them.
What are Virtual Tables?
There are often situations where we only want to allow access to part of table data that satisfies certain constraints to some users. For these security reasons, we can define a view that is a virtual table for that particular table satisfying those particular constraints and granting the privilege of that virtual table to that user instead of the original table. Other than this, virtual tables also prove helpful when retrieving only the summarized data from the table and adding abstraction over the original tables by defining the views that involve group statements. Also, note that if changes are made in any records of the simple views, they do affect the table automatically.
Types of Virtual Tables
The views i.e, virtual tables are categorized into four types that are listed below:
- Simple View
- Complex View
- Inline View
- Materialized View
Let us understand each type of virtual table in detail –
1. Simple View
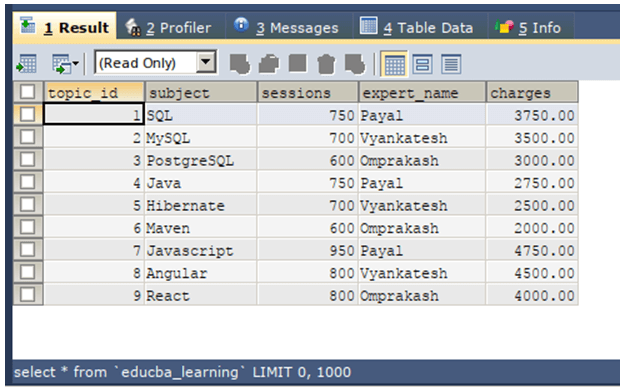
It is the view that is defined based on the contents of a single table, and that does not involve the usage of any complex functions or group by statement. We can perform Data Manipulation Language commands like insert, update, and delete on the records of the simple virtual table, which automatically affects the original table. Consider an example where there is an existing table named educba_articles that has the structure and contents as shown in the output of the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM `educba_learning`;The execution of the above query statement gives an output that is as shown below –
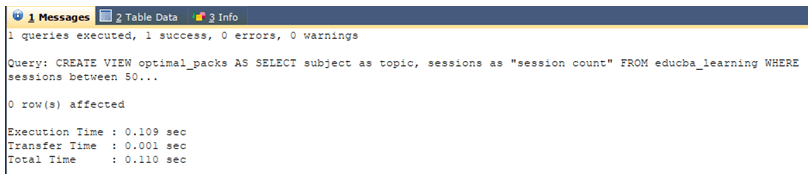
Now, we will create a simple view that has the session value ranging from 500 to 750 and name it optimal_packs and have column values of the only subject as the topic and session count in it using the following query statement –
CREATE VIEW optimal_packs AS
SELECT SUBJECT AS topic, sessions AS "session count"
FROM educba_learning
WHERE sessions BETWEEN 500 AND 750;The execution of the above query statement gives an output that is as shown below –
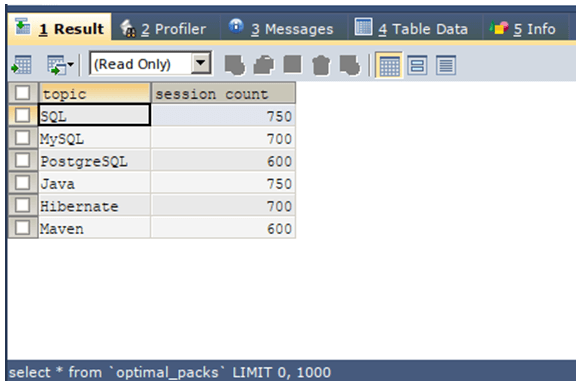
Let us select the records from the virtual table and check its contents –
SELECT * FROM `optimal_packs`;The execution of the above query statement gives an output that is as shown below –
2. Complex Vitual Tables
These are the views that are defined based on more than one table or even on a single table that involves the usage of complex functions such as aggregate functions and group by statement. Note that these types of virtual tables are not allowed for manipulation by Data manipulation Language commands. This is mostly used for abstraction, providing summarized data, and using this in subqueries in multiple queries. Let us consider one example,
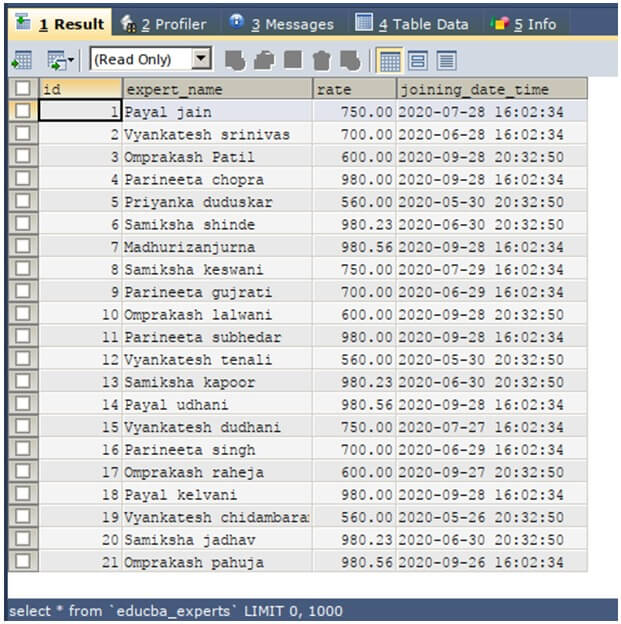
SELECT * FROM `educba_experts`;The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is shown below.
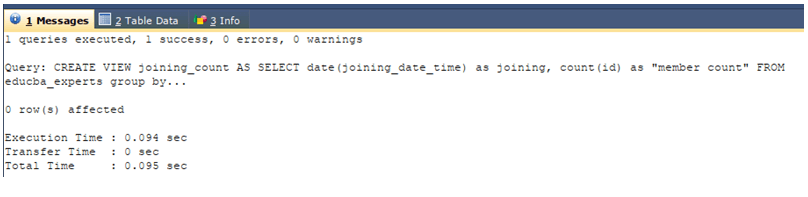
Now, we will create a complex view that has the joining_date and count of members joined on each day and name it as joining_count using the following query statement.
CREATE VIEW joining_count AS
SELECT DATE(joining_date_time) AS joining, COUNT(id) AS "member count"
FROM educba_experts
GROUP BY DATE(joining_date_time);The execution of the above query statement gives an output that is shown below.
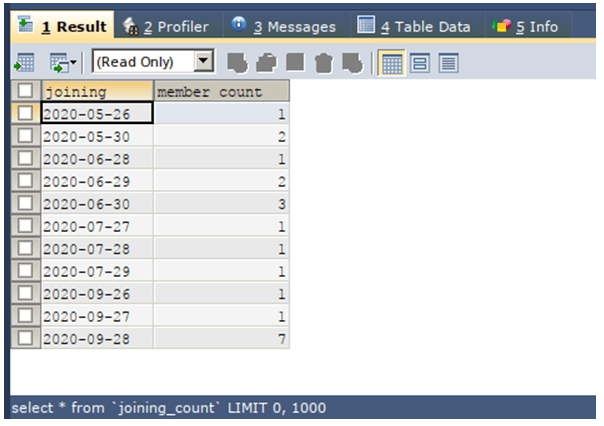
SELECT * FROM `joining_count`;The execution of the above query statement gives an output that is shown below.
3. Inline View
Inline views are virtual tables that are commonly used in subqueries. They are created with the purpose of providing a temporary table that can be referenced and utilized further within a query. Inline views are sometimes referred to as duplicates of the original table because they contain the same data, but the contents of the original table are not actually modified.
4. Materialized Virtual Table
Views in SQL do not store a copy of the original table in memory. Instead, they are logical structures that are defined by queries to retrieve data from underlying tables or views when accessed. This means that views are not physically stored but dynamically generated based on the query definition.
Conclusion
Here we discussed what SQL Virtual Tables are and how we can use virtual tables for various reasons like using them for abstraction purposes, security reasons, summarization, and making queries by using them in subqueries. However, there are some disadvantages associated with views in SQL. One disadvantage is that if the original table structures are modified, the view may need to be updated accordingly. Changes in column names, data types, or table relationships may require modifying the view definition to ensure its accuracy and compatibility with the new table structure.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Virtual Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.