Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to SQL Substring Function
SQL substring function is used to retrieve the part of the string from the original string that begins from the position that we have specified and should contain only that many characters as specified by us in the function parameters. SQL substring function can be used with any string value wrapped in single or double quotes or the string values stored in the variables of type varchar and even on the values of the columns that store string values, binary, text format values, and images. This article will study the syntax of the substring function, it’s working, and implement the function in multiple examples to make the concept clearer.
Syntax
The syntax of the substring function in SQL is as shown below –
SUBSTRING ( expression_value ,start_position , length )where the expression value is the original string which can be a string literal, column value of the table having varchar datatype, binary, text, or even the image. The expression value is considered as the original string whose part is to be retrieved as the substring using the substring function of SQL. Start position is the integer value that helps [s] specify the position and location of the first character from where the substring should be started to consider. The positioning of the characters in the expression always starts at 1.
The length is the positive integer value that stands for the number of the characters that should be added starting from the start position from the original string or expression to retrieve the substring. In case if we specify the negative integer value in the function, then the query will return an error. Also, note that if the value of the start position and the length parameter should not exceed the original string’s actual length, or else the query will generate an error that starts position+ length <= length of expression or value considered as the original string.
Working of substring function
Whenever the substring function is used, all the characters in it are iterated, and then, beginning from the position that is specified in the second parameter, a new string is started to generate. The number of characters up to which all the iterating characters starting from the start position are added depends on the length parameter value specified in the third parameter. As soon as that length is finished, the iterating of characters stops, and then the final newly prepared string is returned as the return value of the substring function. If the start position is specified as the negative integer, the count of position is considered beginning from the end of the index value and having the negative scale increasing till from the ending position of the string to starting position of the string.
Examples
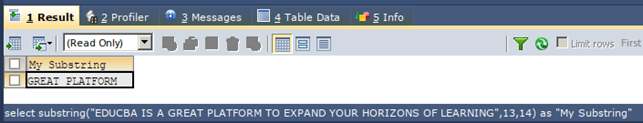
Let us consider our first example of retrieving a substring from the string literal value. In this example, our original string is “EDUCBA IS A GREAT PLATFORM TO EXPAND YOUR HORIZONS OF LEARNING”, and we have to retrieve the substring GREAT PLATFORM from the original string. We can observe that the G character of GREAT is located at the 13th position from the start of the string. Hence, our start position will be 13, and the number of characters in the substring that we have to retrieve “GREAT PLATFORM” is 14; hence the length parameter value will have 14 in it. Our final query statement to retrieve the substring will be as follows –
SELECT SUBSTRING("EDUCBA IS A GREAT PLATFORM TO EXPAND YOUR HORIZONS OF LEARNING",13,14) AS "My Substring";The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
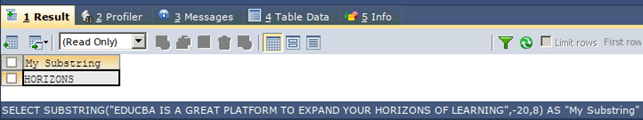
Now, we will try to use a negative start position instead of a positive one. Consider the same original string “EDUCBA IS A GREAT PLATFORM TO EXPAND YOUR HORIZONS OF LEARNING”. Now, we have to retrieve the substring “HORIZONS” from it. If we use the negative positioning, then the character H or the Horizons is located at the 20th position from the end and has 8 characters in it. Hence, our start position will be -20, and the length parameter will have the value 8. Our query statement will be as follows –
SELECT SUBSTRING("EDUCBA IS A GREAT PLATFORM TO EXPAND YOUR HORIZONS OF LEARNING",-20,8) AS "My Substring";The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
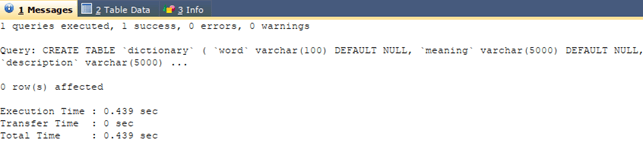
Let us now consider the column values instead of string literals. For this, we will create one table named dictionary that will contain three columns with names, word, description, and meaning. We will use the following query statement to create the table.
CREATE TABLE `dictionary` (
`word` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`meaning` varchar(5000) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(5000) DEFAULT NULL
);that gives the following output after execution –
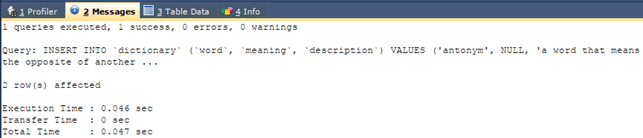
Let us insert a few records in the table –
INSERT INTO `dictionary` (`word`, `meaning`, `description`) VALUES
('antonym', NULL, 'a word that means the opposite of another word'),
('connotation', NULL, 'an additional idea or emotion that a word suggests to you');that gives the following output after execution –
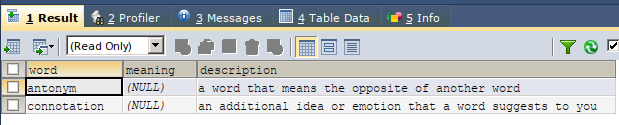
We will check the contents of the table by retrieving them using the following query statement –
SELECT * FROM dictionary;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
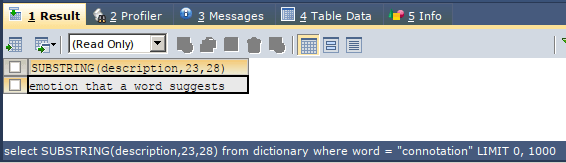
Now, we have to retrieve the substring “emotion that a word suggests” from the description column of the dictionary record whose word is connoted. For this, we will have to find the position of character e of emotion in the original string, which is 23. The substring that we want to retrieve has 28 characters in it. Our query statement will be as shown below –
SELECT SUBSTRING(description,23,28) FROM dictionary WHERE word = "connotation";The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
Conclusion
We can use the substring function to retrieve only the part of the string from the original string, and the characters to be included in the substring can be specified by mentioning the start position and the number of the characters that are to be included in the substring.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Substring Function” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.