Updated July 6, 2023

Introduction to SQL Server Replace
Replace function is used to replace all the occurrences of the substring that you have specified. Normally we specify three arguments in the Replace function.
1) Actual_string
2) Old_substring
3) New_substring.
Here Actual_string resembles the string in which you want to make the changes take place. Old_substring is the substring of Actual_string, which you want to be changed to the New_substring.
We can perform replace operations in the database column as well. We need to specify the required column that needs to replace with the New_substring.
In this session, let us learn a few things like How and Where the “Replace function” is used.
Syntax:
Now let us see the syntax for the replace function:
replace(Actual_string, Old_substring, New_substring)Now let us see the syntax for the replace function if we want to perform the operation on the column of the database table:
replace(column_name, Old_substring, New_substring)How to use Replace in SQL Server?
Now let us see how the replace function works in the SQL server:
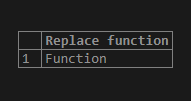
select replace('Sunction','S','F')as "Replace function";Output:
Now let us replace the column with some particular string. The thing to remember is that if u specify a replace function in a column whole column will be replaced with the mentioned string.
Let us create a table with default data in it and perform the replace function in one column.
Table creation:
create table replace_test
(
Serial_no int,
Animal_name varchar(20)
)Insert data into the Table:
insert into replace_test values ( 1,'cst');
insert into replace_test values ( 2,'besr');
insert into replace_test values ( 3,'Elephsnt');
insert into replace_test values ( 4,'rsbbit');
insert into replace_test values ( 5,'girsffe');
insert into replace_test values ( 6,'msmmsl');
insert into replace_test values ( 7,'gost');
insert into replace_test values ( 8,'bst');
insert into replace_test values ( 9,'esgle');
insert into replace_test values ( 10,'gorills');
select * from replace_test;Output:
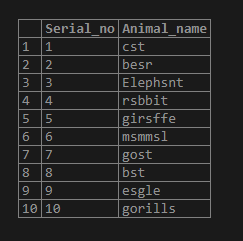
Here in the above table, we have inserted animal names that have an ‘a’ string in them. But we have misplaced the ‘a’ with ‘s.’
Eg:- Cat ->cst
Bear ->besr and so on. Now let us replace the ‘s’ substring with ‘a’ from the column “animal_name.”
select *, Replace(animal_name,'s','a') as "Reformatted animal name" from replace_test;Output:
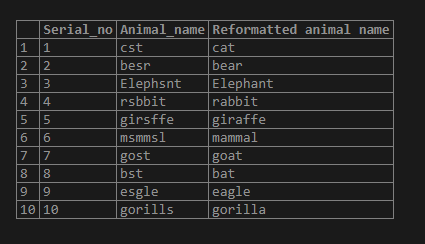
From the above output, we could observe that the ‘s’ is replaced with the ‘a.
To update the column values, we can do the below:
update replace_test
set Animal_name = replace( animal_name,'s','a');
select * from replace_test;Now we have updated the animal replace column with the required replacement. Let us see if the data is updated. Updated data output should be in the below manner: –
Output:
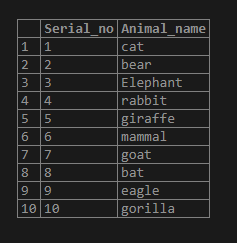
We could see that the data has been updated in the table as well.
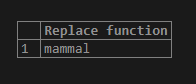
Replace function is not a case- sensitive. Hence ‘s’ and ‘S’ are the same. Let us see an example of the same.
select replace('Sassal','S','m')as "Replace function";Here above example is to replace the ‘s’ with ‘m’. As replace is not case sensitive, all the ‘s’ strings will be replaced with ‘m’.
Output:
Example
Now let us consider a few examples for the replace function and its output as below: –
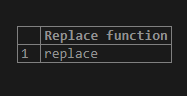
Example #1
select replace('repldce','d','a')as "Replace function";Output:
Example #2
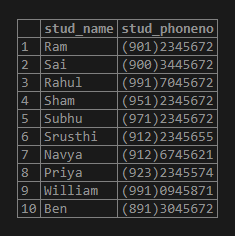
Now let us consider the table of students along with their phone numbers.
Table Creation:
create table replace_test_student
(
stud_name varchar(20),
stud_phoneno varchar(20)
);Insert data into the table:
insert into replace_test_student values ('Ram','(901)2345672');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Sai','(900)3445672');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Rahul','(991)7045672');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Sham','(951)2345672');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Subhu','(971)2345672');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Srusthi','(912)2345655');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Navya','(912)6745621');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Priya','(923)2345574');
insert into replace_test_student values ('William','(991)0945871');
insert into replace_test_student values ('Ben','(891)3045672');
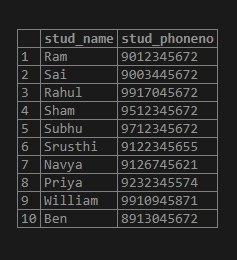
select * from replace_test_student;Output:
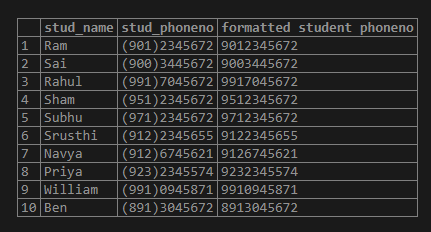
Now let us replace the ‘(‘ and ‘)’ with none.
select *,replace(replace(stud_phoneno,'(',''),')','') as "formatted student phoneno" from replace_test_student;Output:
To update the change in the table:
update replace_test_student
set stud_phoneno = replace(replace(stud_phoneno,'(',''),')','');
select * from replace_test_student;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Server Replace” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

