Updated May 15, 2023

Introduction to SQL Ranking Function
Rank function comes under the windows functions. It usually assigns a rank to each row within a partition set of a result set in SQL. If the partitioned rows have the same values then we receive the same rank for the matching records.
we use the Rank function to get the latest value based on the partition condition.
RANK() OVER ( [PARTITION BY partition_expression, ... ]
ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ... )Here in the above syntax, we can say that based on the partition by expression the row sets are divided for the result set of the partition by expression the function will be applied.
Order by is used to logically sort order of the rows in each partition either in ascending or descending order.
Syntax:
RANK() OVER ( [PARTITION BY partition_expression, ... ]
ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ... )How ranking function work in SQL?
Let us create a table and apply the Rank function to see how it’s working:
create table test_rank_fun
(
Alphabet varchar(10)
);Now let us insert few duplicated values as below and apply rank on it.
insert into test_rank_fun values ('A');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('A');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('A');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('R');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('R');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('S');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('S');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('F');
insert into test_rank_fun values ('M');Now let us select the above table.
SELECT * FROM test_rank_fun;Output:

Above is the output of the table test_rank_fun. Now let us apply the rank function on the “test_rank_fun“ table. Here no need of applying the partition by on “alphabet” column instead we apply order byon “alphabet” column ascending. Let us see what happens applying partition on the table and without applying partition by.
Applying the partition by:
SELECT Alphabet, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY Alphabet ORDERBY Alphabet)as RANK
FROM test_rank_fun;Output:
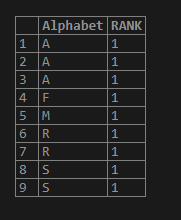
Here when we apply the partition by on the alphabet column all the alphabets are considered in the same partition result resulting into the same rank.
Now let us only apply the order by on the “alphabet” column. The alphabet of same are considered in same logical partition and given same value.
SELECT Alphabet, RANK() OVER (ORDER BY Alphabet)as RANK
FROM test_rank_fun;Output:
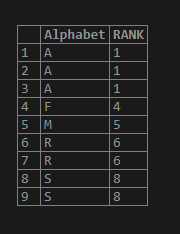
Example
Now let us consider a real-time example and apply the rank function and check for the output: –
Let us create the table “test_rank_customer” with columns cust_id, cust_name, cust_address, cust_phone, cust_salary as below: –
create table test_rank_customer
(
Cust_id int,
cust_name varchar(20),
cust_address varchar(20),
cust_phone varchar(10),
cust_salary int,
dept_id int
);Let us insert few rows in the above table as below and apply the rank function:
insert into test_rank_customer values (1,'Sam','USA','9879876785', 45000,1);
insert into test_rank_customer values (2,'Fred','UK','9872346785', 95000,1);
insert into test_rank_customer values (3,'Will','Germany','9679876785', 85000,2);
insert into test_rank_customer values (4,'Ben','London','8879876785', 45000,2);
insert into test_rank_customer values (5,'William','rome','7879876785', 95000,3);
insert into test_rank_customer values (6,'Bentley','Italy','7877876785', 95000,1);
insert into test_rank_customer values (7,'Suppu','USA','8979873485', 75000,1);
insert into test_rank_customer values (8,'Sian','USA','6579876785', 65000,4);
insert into test_rank_customer values (9,'Shames','London','0979876785', 43000,4);
insert into test_rank_customer values (10,'Harry','USA','9877876785', 56000,5);Now let us see the rows in the table:
select * from test_rank_customer;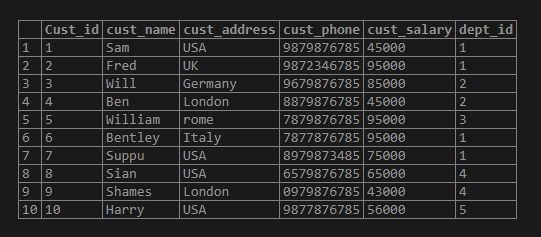
Now let us apply rank function in the table “test_rank_customer”.
select*,RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY dept_id order by cust_salary) AS RANK
from test_rank_customer;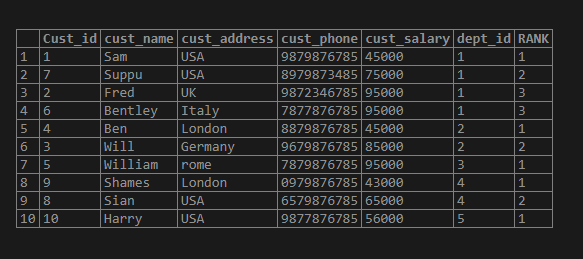
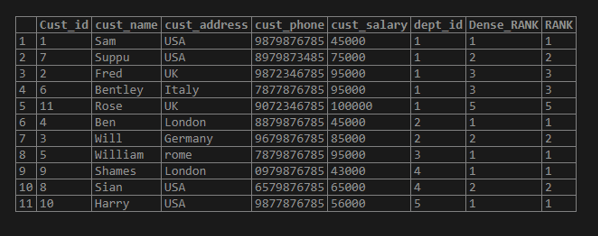
Here if we check the result set the partition is applied based on the “dept_id” column and order by is applied based on the “cust_salary”. So all the same values of “dept_id” will be partitioned together and the order is applied on top of it. Then at last the rank function is applied.
Now let us talk about the highlighted part in the result set. The highlighted part is of the “dept_id” = 1. Here we can see the order by done by “cust_salary”. If you observe the “95000” salary for Fred and Bentley are the same so the rank assigned won’t be different while the rest of the salary are unique and the rank is assigned accordingly.
In above the salary is the same for Fred and Bentley with 95000 rs. So, the rank assigned as 3. If we have a salary greater than 95000 let us say 100000 in the dept_id = 1 then the rank assigned for the salary is 5 and not 4. While in Dense_rank we assign rank as 4 and not 5.
we have inserted another row in the table as below to show the difference with the dense_rank and rank function:
insert into test_rank_customer values (11,'Rose','UK','9072346785', 100000, 1);
select*,RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY dept_id order by cust_salary) AS Dense_RANK, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY dept_id order by cust_salary) AS RANK from test_rank_customer;Output:
Conclusion
Rank function comes under the windows functions. It usually assigns a rank to each row within a partition set of a result set in SQL. If the partitioned rows have the same values, then we receive the same rank for the matching records and the consequent number will be neglected and next number is assigned as the next rank.
Need to know which columns need to be specified in the partition by column
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Ranking Function” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

