Updated March 21, 2023

What is the SQL LIKE Clause?
An SQL can have multiple condition statements, and ‘Like’ is one such condition that can be used along with the ‘Where’ condition clause. ‘Like’ clause can be worked with two operators, namely ‘%’ and ‘_’. In some applications instead of ‘_’, ‘?’ is allowed, and instead of ‘%’, ‘*’ is allowed. Here, ‘%’ is used in place for a one or multiple characters, while ‘_’ is used in place for only one character.
In LIKE clause there are two wildcards used in combination they are
- Percent sign (%)
- Underscore ( _ )
The percent sign symbolizes zero, one or several characters. The underscore symbolizes a distinct number or character. The use of wildcards is to achieve pattern matching in a query. The LIKE condition will be applied in the WHERE clause of INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE or SELECT statement.
Syntax:
The basic syntax of LIKE clause % and _ is as follows
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE 'X%'SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE '%X%'SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE 'X_'SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE '_X'SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE '_X_'By using AND or OR operators we can combine a number of conditions, here X be any string or a numeric value.
How LIKE Clause works in SQL?
The LIKE Clause is a logical operator that concludes a character string matches with a specified pattern. Regular and wildcard characters were included in pattern matching. In SQL Server LIKE operator specifically used in the WHERE clause includes SELECT, DELETE and UPDATE statements, to retrieve data based on row-wise pattern matching.
Examples
1. SQL SERVER LIKE
Let’s see the sample database of Customer_Master,

2. (Percent) % Wildcard
The percent wildcard defines the string of zero or more characters. Let’s see the examples
By using the percent wildcard to find out or retrieve the customers whose first name starts with the letter Z,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_First Name Like 'z%'
Order by Customer_First Name;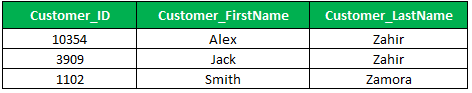
By using the percent wildcard to find out or retrieve the customers whose last name ends with the letterer,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_Last Name Like '%er'
Order by Customer_First Name;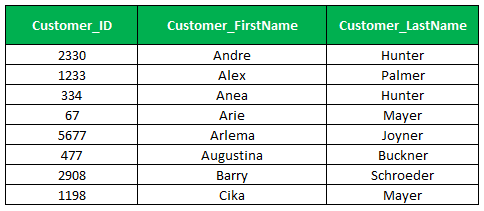
To find out or retrieve the customers whose last name starts with the letter t and ends with letter s,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_Last Name Like 't%s'
Order by Customer_First Name;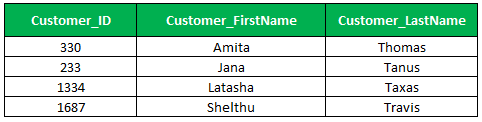
3. (Underscore) _ Wildcard
The underscore defines a single character. Let’s see the examples below,
By using the underscore wildcard to retrieve the customers where the second character is the letter u, the pattern _u% explains that the first underscore character match with a single character, the second letter u match exactly with the letter u and the third character % symbolize the sequence of characters.
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_Last Name Like '_U%'
Order by Customer_First Name;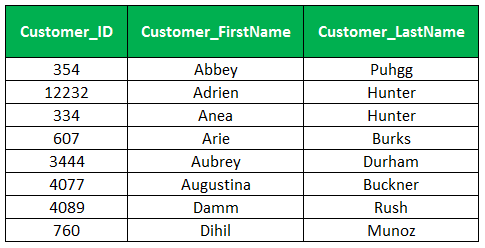
4. [List of Characters] Wildcard
The List of characters specifies that a single character within the particular set, the square brackets with the list of characters, for example [ABC] specifies a character in which one of the characters that occur in the list. Let’s see the example, the statement returns the customers where the customer’s last name starting letter starts with either Y or Z,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_Last Name Like '[YZ]%'
Order by Customer_Last Name;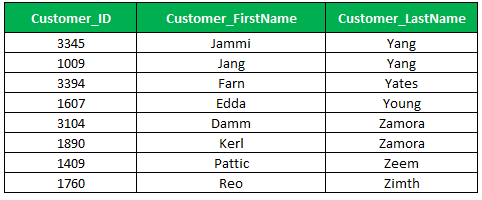
5. [Character-Character] Wildcard
The character-to-character wildcard specifies a character within the specified range. It retrieves the character range only specified within the square brackets, for example [A-C] which displays a character specified within range.
Let’s see the example, the statement returns the customers where the customer’s last name starting letter starts with the range A through C,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_Last Name Like '[A-C]%'
Order by Customer_First Name;
6. [^Character List or Range] Wildcard
The character list or range in the square bracket with ( ^ ) caret sign specifies a character which not within the character list or range. Let’s see the example, the statement returns the customers record where customer’s last name starting letter should not the letter in the range of A through X,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_Last Name Like '[^A-X]%'
Order by Customer_Last Name;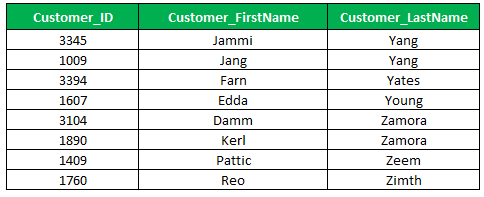
7. Not Like Operator
The NOT LIKE operator returns the result of which not the character, for example, to retrieve the customers’ record where the first name of the customer should not starts with the letter A,
Select Customer_Id, Customer_First Name,customer_Last Name
From Customer_Master
Where Customer_First Name Not Like 'A%'
Order by Customer_First Name;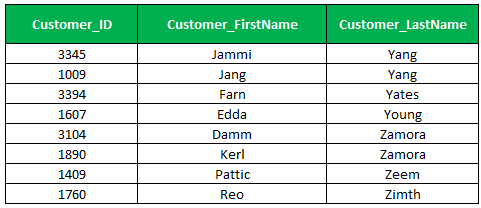
Advantages and Characteristics
- The LIKE clause is useful to retrieve a record to match with a particular pattern.
- Use wildcard character ‘%’ to know the entire value.
- Percent wildcard (%) retrieves the string of zero or more than characters.
- The underscore (_) wildcard retrieves any number of single characters.
- The [list of characters] wildcard retrieves within a specified set of any single character.
- The [character-character] retrieves within a specified range of any single character
- The [^Character List or Range] wildcard retrieves a character which does not within the character-list or within range.
Condition
- The SQL LIKE condition lets you apply wildcards to achieve pattern matching statements. The LIKE condition applied in the WHERE clause of INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE or SELECT statements.
- The LIKE condition returns the result as TRUE where the column matches the particular pattern.
- To reverse the result of the LIKE Condition, use the NOT operator.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL LIKE Clause” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

