Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL LEAD()
LEAD function in standard query language (SQL) is an analytical function that is used to fetch results of the next rows in the result set at a specified physical offset without performing any self joins on the table. The LEAD function is generally used in the SELECT statement of the query for comparing certain values of the current row with the values in the subsequent rows.
LEAD is a window function where the input values are fetched from a virtual “window” of one or more rows from the results of a SELECT statement. It calculates aggregate or final values based on this window of input rows.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for writing LEAD function in SQL is as follows :
LEAD(expression [,offset [,default_value]])
OVER (
[PARTITION BY partition_expression]
ORDER BY order_expression [ASC | DESC]
)The parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are as follows :
- Expression: The column which has to be evaluated is specified here. This the column or expression for which you want values from subsequent rows based on the offset.
- Offset: The number of rows ahead from which the data has to be fetched. It is a positive integer.
- Default_value: The value which will be returned if no data is found in the subsequent row. By default, it is set to NULL.
- Partition_expression: The column based on which the entire dataset has to be divided or grouped.
- Order_expression: The column on the basis of which the rows in the partition set has to be sorted.
Examples
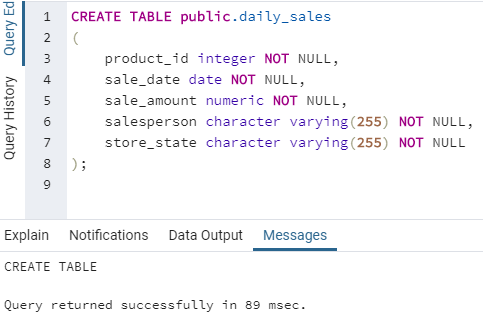
In order to understand SQL LEAD function in detail, let us create a table called “daily_sales” which contains details pertaining to products sold daily by a departmental store. We can use the following code snippet for the same.
Code #1
CREATE TABLE public.daily_sales
(
product_id integer NOT NULL,
sale_date date NOT NULL,
sale_amount numeric NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL
);Output:
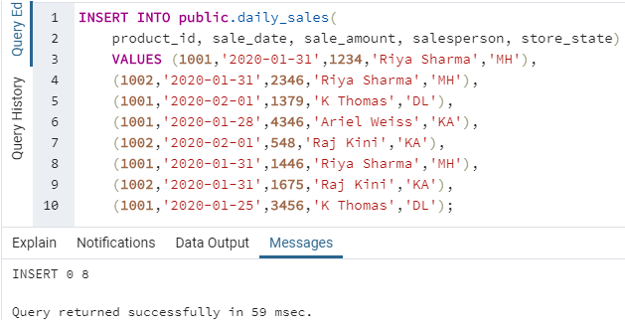
After successfully creating the table, let us insert some random data in it. We can use the following code snippet for this purpose.
Code #2
INSERT INTO public.daily_sales(
product_id, sale_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state)
VALUES (1001,'2020-01-31',1234,'Riya Sharma','MH'),
(1002,'2020-01-31',2346,'Riya Sharma','MH'),
(1001,'2020-02-01',1379,'K Thomas','DL'),
(1001,'2020-01-28',4346,'Ariel Weiss','KA'),
(1002,'2020-02-01',548,'Raj Kini','KA'),
(1001,'2020-01-31',1446,'Riya Sharma','MH'),
(1002,'2020-01-31',1675,'Raj Kini','KA'),
(1001,'2020-01-25',3456,'K Thomas','DL');Output:
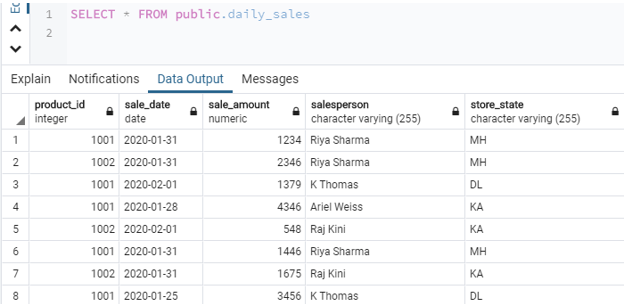
We have successfully inserted the data. Our “daily_sales” table looks something like this now.
Now let us put the above-mentioned table to some use. That is, let us try some examples.
Examples to Implement SQL LEAD()
Below are the examples to Implement SQL LEAD()
Example #1
Find the current amount and the previous amount (i.e amount collected for last sale) for each product in the departmental store.
Code:
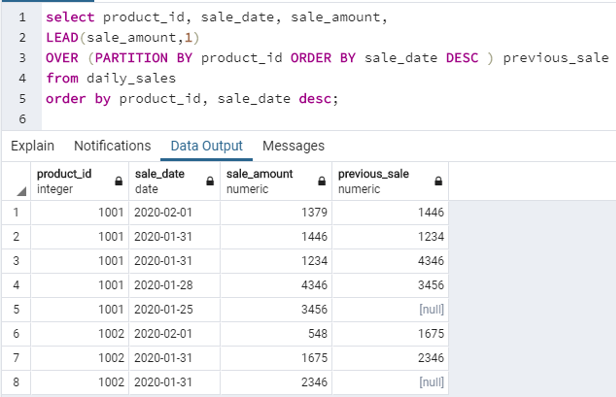
select product_id, sale_date, sale_amount,
LEAD(sale_amount,1)
OVER (PARTITION BY product_id ORDER BY sale_date DESC ) previous_sale
from daily_sales
order by product_id, sale_date desc;Output:
Explanation: We can see that in the previous_sale column, we have got sale_amount values from the previous row since the offset is set to 1 here. The sale_amount for which we do not have any previous value, we have got a default value of NULL. This can be set to some other default value also.
Example #2
Find the current amount and the previous amount (i.e amount collected for last sale) for each salesperson in the departmental store.
Code:
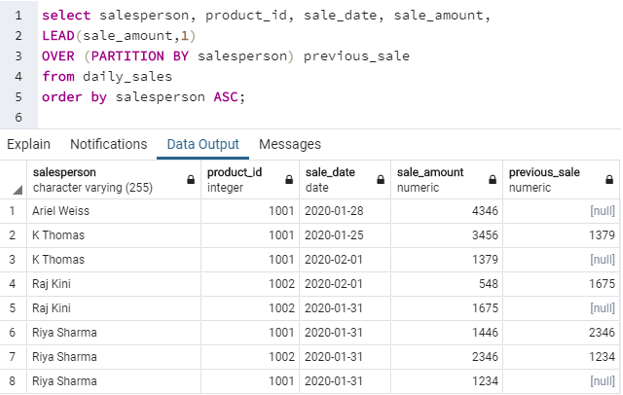
select salesperson, product_id, sale_date, sale_amount,
LEAD(sale_amount,1)
OVER (PARTITION BY salesperson) previous_sale
from daily_sales
order by salesperson ASC;Output:
Example #3
Find the current month sales (sales here means amount sold for ) and previous month sales for each product.
Code:
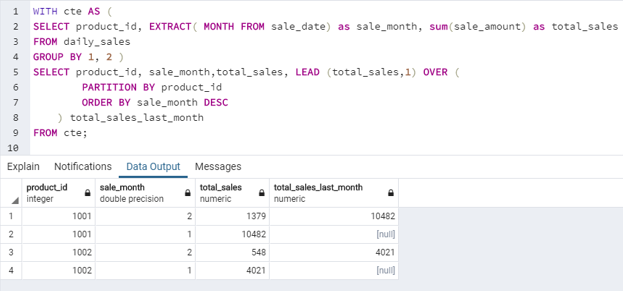
WITH cte AS (
SELECT product_id, EXTRACT( MONTH FROM sale_date) as sale_month, sum(sale_amount) as total_sales
FROM daily_sales
GROUP BY 1, 2 )
SELECT product_id, sale_month,total_sales, LEAD (total_sales,1) OVER (
PARTITION BY product_id
ORDER BY sale_month DESC
) total_sales_last_month
FROM cte;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have first collated everything like sales_month, total sales_amount in a CTE. CTEs are temporary table-like structures that help us in organising data. Then, we have fetched previous month’s sales by partitioning the entire record set by product_id.
Example #4
Find the difference between current month sales and previous month sales for each product.
Code:
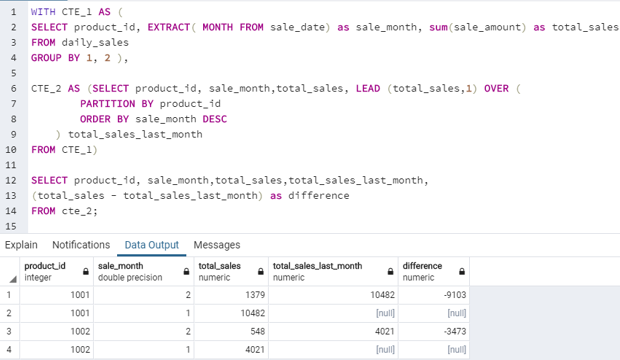
WITH CTE_1 AS (
SELECT product_id, EXTRACT( MONTH FROM sale_date) as sale_month, sum(sale_amount) as total_sales
FROM daily_sales
GROUP BY 1, 2 ),
CTE_2 AS (SELECT product_id, sale_month,total_sales, LEAD (total_sales,1) OVER (
PARTITION BY product_id
ORDER BY sale_month DESC
) total_sales_last_month
FROM CTE_1)
SELECT product_id, sale_month,total_sales,total_sales_last_month,
(total_sales - total_sales_last_month) as difference
FROM cte_2;Output:
Example #5
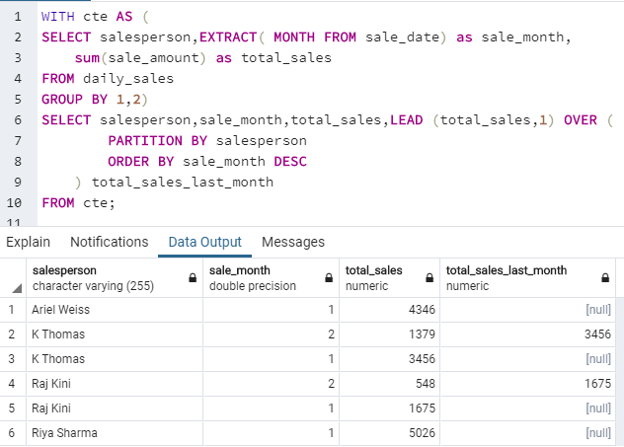
Find the current month sales and previous month sales for each salesperson in the departmental store.
Code:
WITH cte AS (
SELECT salesperson,EXTRACT( MONTH FROM sale_date) as sale_month,
sum(sale_amount) as total_sales
FROM daily_sales
GROUP BY 1,2)
SELECT salesperson,sale_month,total_sales,LEAD (total_sales,1) OVER (
PARTITION BY salesperson
ORDER BY sale_month DESC
) total_sales_last_month
FROM cte;Output:
Example #6
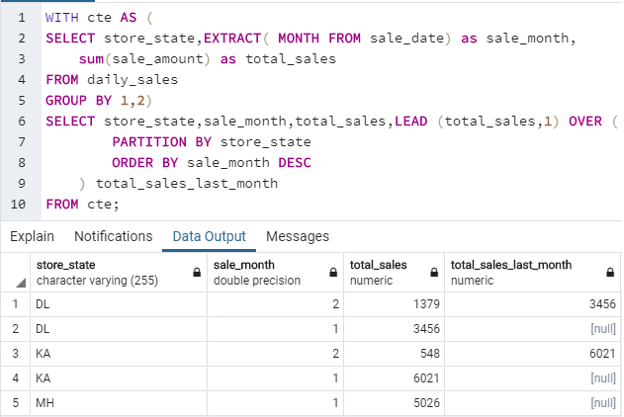
Find the current month sales and previous month sales for each location where the departmental store operates.
Code:
WITH cte AS (
SELECT store_state,EXTRACT( MONTH FROM sale_date) as sale_month,
sum(sale_amount) as total_sales
FROM daily_sales
GROUP BY 1,2)
SELECT store_state,sale_month,total_sales,LEAD (total_sales,1) OVER (
PARTITION BY store_state
ORDER BY sale_month DESC
) total_sales_last_month
FROM cte;Output:
Conclusion
LEAD is a value function in SQL which is used to fetch next subsequent values based on a physical offset. It helps in comparing data present in the same column but in different rows. Hence, it helps us in performing a myriad of analytical functions without performing any self-joins.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL LEAD()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.