Updated March 8, 2023

Introduction to SQL DELETE Trigger
DELETE Trigger is a data manipulation language (DML) trigger in SQL. A stored procedure on a database object gets invoked automatically instead of before or after a DELETE command has been successfully executed on the said database table. DELETE Triggers are usually used in scenarios when we want to track details of data removal from a table in a separate audit table or when we want to perform cascading delete operations, like if we delete a row from table1, then it should be deleted from table2 as well.
Syntax and parameters
The basic syntax used for writing a DELETE Trigger in SQL is as follows :
CREATE TRIGGER [schema_name. ] trigger_name ON table_name
{AFTER| BEFORE | INSTEAD OF } DELETE
AS
{SQL statements}The arguments used in the above-mentioned syntax are as follows :
schema_name: schema_name here corresponds to the name of the schema where the new
A delete trigger will be created. The schema name is optional, but when we do not mention the schema_name, the trigger gets created in the default schema.
trigger_name: trigger_name is the name of the new delete trigger which is being created.
table_name: table_name is the name of the database table on which the new A delete trigger will be created.
AFTER | BEFORE | INSTEAD OF: This argument is to register the time of DELETE trigger invocation concerning the execution of the DELETE statement.
SQL statements: SQL statements are a set of SQL operations that form the body of a DELETE trigger.
Having discussed the syntax and parameters used for creating DELETE triggers in SQL, let us try a few examples to understand it in great detail.
Examples of SQL DELETE Trigger
To illustrate DELETE Triggers’ work in SQL, let us create two dummy tables called students and students_audit, respectively.
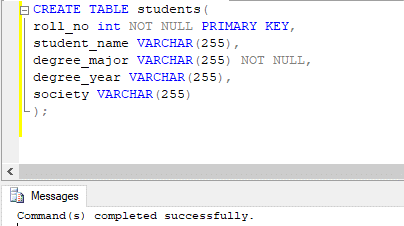
CREATE TABLE students(
roll_no int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
student_name VARCHAR(255),
degree_major VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
degree_year VARCHAR(255),
society VARCHAR(255)
);
Having created the student’s table. Let us insert a few records in it to work with.
INSERT INTO [practice_db].[dbo].[students]
([roll_no]
,[student_name]
,[degree_major]
,[degree_year]
,[society])
VALUES
(1,'Mohith K','Computer Science Engineering','IV','Dramatics'),
(2,'Ayesha Khan','Electrical Engineering','I','Music'),
(3,'Kylie Green','Computer Science Engineering','III','Choreography'),
(4,'Alisha Rojer','Chemical Engineering','III','Music'),
(5,'Andy Bernard','Geosciences','IV','Dramatics')
GO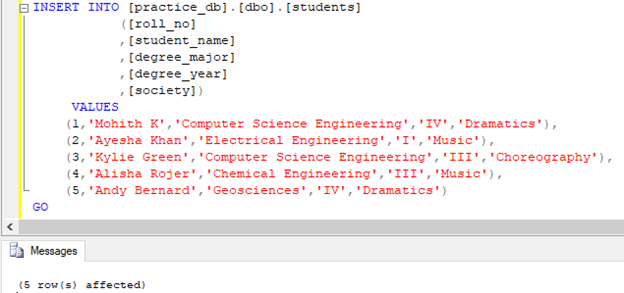
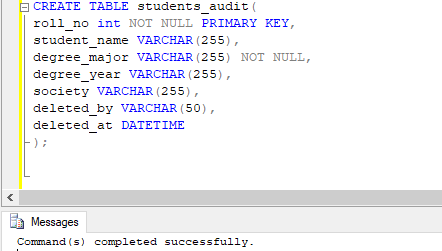
Next, let us create the students_audit table, which is similar to the student’s table but with two additional columns.
CREATE TABLE students_audit(
roll_no int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
student_name VARCHAR(255),
degree_major VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
degree_year VARCHAR(255),
society VARCHAR(255),
deleted_by VARCHAR(50),
deleted_at DATETIME
);
Let’s leave this table empty for the time being.
Example #1
Create a DELETE Trigger on the student’s table that deletes records from the student’s table and insert the deleted records with servername and time of deletion on a separate table called “students_audit”.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER AfterDELETETrigger on students
AFTER DELETE
AS DECLARE
@roll_no INT,
@student_name VARCHAR(255),
@degree_major VARCHAR(255),
@degree_year VARCHAR(255),
@society VARCHAR(255);
SELECT @roll_no = d.roll_no FROM DELETED d;
SELECT @student_name = d.student_name FROM DELETED d;
SELECT @degree_major = d.degree_major FROM DELETED d;
SELECT @degree_year = d.degree_year FROM DELETED d;
SELECT @society = d.society FROM DELETED d;
INSERT INTO students_audit(
[roll_no]
,[student_name]
,[degree_major]
,[degree_year]
,[society]
,[Deleted_by]
,[Deleted_at])
VALUES (@roll_no,
@student_name,
@degree_major,
@degree_year,
@society,
CAST( SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName') AS VARCHAR(50)),
GETDATE());
GO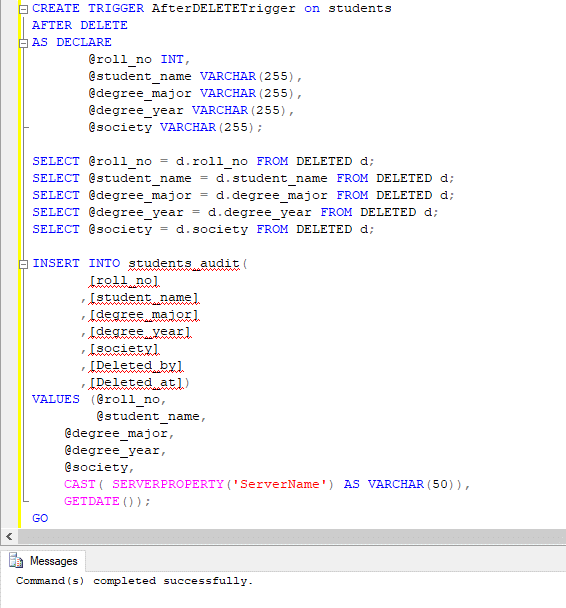
The query was executed successfully. The newly created AfterDELETETrigger has been mentioned under the Triggers head in the object explorer.
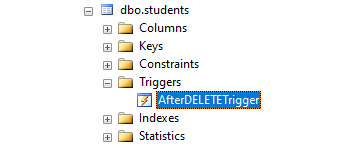
Now let us check if the “AfterDELETETrigger” serves the intended purpose. Here is a DELETE statement on the student’s table that tries to delete a row with roll_no = ‘3’.
DELETE FROM students
WHERE roll_no = '3';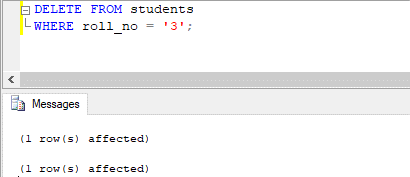
Two rows got affected. That’s true, one row of the student’s table got removed, and one row got inserted in the students_audit table. Let’s check for ourselves using a SELECT statement.
SELECT * FROM students_audit;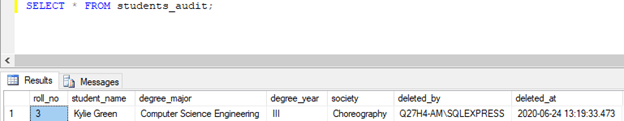
The row with roll_no = ‘3’ has been successfully inserted in the students_audit table.
Let’s try one more DELETE statement. Here, we are deleting one or more rows in the student’s table where the student belongs to ‘Dramatics’ and has a degree_major starting with ‘Geo’.
DELETE FROM students
WHERE society = 'Dramatics' AND degree_major LIKE 'Geo%';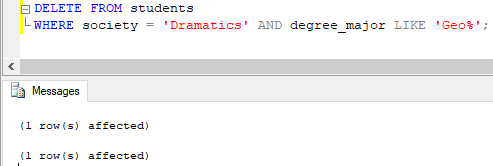
Similar to the previous query, we have successfully deleted and inserted the concerned row from(in) the students and students_audit table respectively.
SELECT * FROM students;
SELECT * FROM students_audit;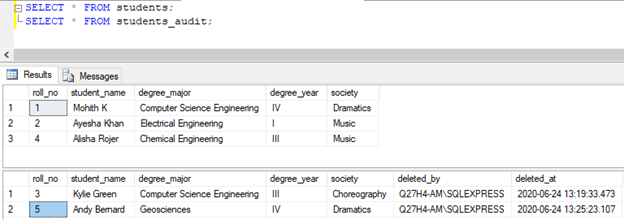
Example #2
Create a delete trigger that, on executing a delete statement on the student’s table, does not delete the row from it but instead deletes it from the students_audit table.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER InsteadDELETETrigger
ON students
INSTEAD OF DELETE
AS
DELETE FROM students_audit
WHERE roll_no IN(SELECT deleted.roll_no FROM deleted)
GO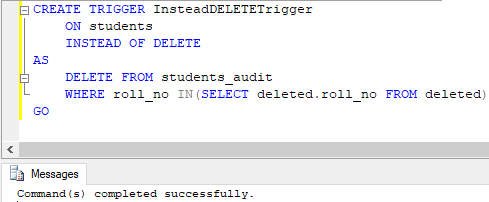
The trigger has been successfully created. It is mentioned under the triggers head of the student’s table in object explorer.
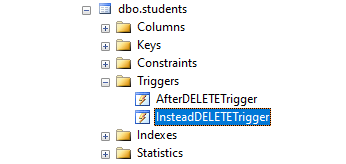
To undo the work of the AfterDELETETrigger, let us insert back the following row in the student’s table (just for the sake of this example).
INSERT INTO [practice_db].[dbo].[students]
([roll_no]
,[student_name]
,[degree_major]
,[degree_year]
,[society])
VALUES
(3,'Kylie Green','Computer Science Engineering','III','Choreography')
GO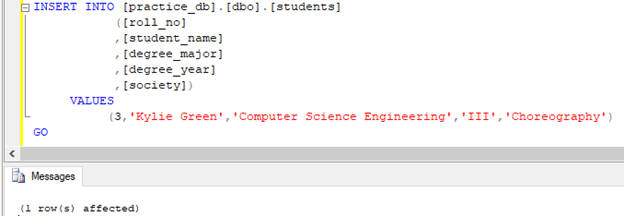
The present status of students and students_audit table is as follows:
SELECT * FROM students;
SELECT * FROM students_audit;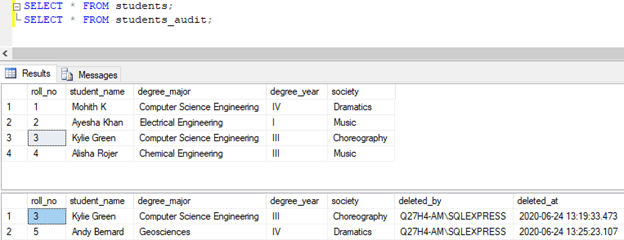
In the previous steps, we have created the ‘InsteadDELETETrigger’. Let’s check its functionality by executing a DELETE statement on the student’s table.
DELETE FROM students
WHERE society = 'Choreography';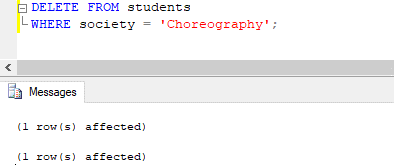
Two rows got affected, but as intended, the row with society = ‘Choreography’ has been successfully deleted from the students_audit table instead of the student’s table.
SELECT * FROM students;
SELECT * FROM students_audit;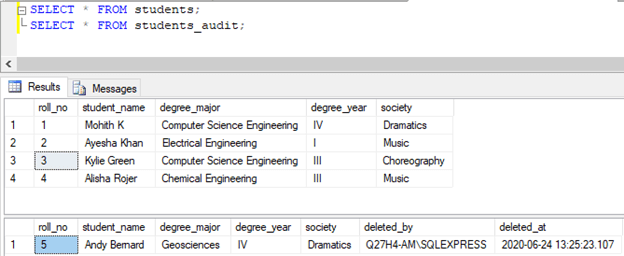
Conclusion
DELETE Trigger is a DDL trigger that gets fired automatically once a DELETE statement has been successfully on a database object.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DELETE Trigger” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

