Updated May 20, 2023

Introduction to SQL AFTER UPDATE Trigger
AFTER UPDATE Trigger in SQL is a stored procedure on a database table that gets invoked or triggered automatically after an UPDATE operation gets successfully executed on the specified table. For the uninitiated, the UPDATE statement is used to modify data in existing rows of a data table. The AFTER UPDATE trigger is helpful in scenarios where we want to record the time of status change or record changes in the rating field based on the modification in values of some other field etc. It helps us in logging, audit, and tracking changes.
Syntax
The basic syntax for writing SQL AFTER UPDATE Trigger in SQL is as follows :
CREATE TRIGGER [schema_name. ] trigger_name ON table_name
AFTER UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
[SET NOCOUNT {ON/OFF}]
{SQL statements}
ENDParameters
The parameters used in the syntax mentioned above are as follows :
schema_name: This is the schema name in which we will create the new trigger. You may ignore it, as a schema name is optional. By default, triggers will be created in the schema you are currently working in.
trigger_name: This is the name of the trigger you want to create.
table_name: This is the table’s name to which the trigger will be applied.
SQL statements: SQL statements form the body of the trigger. These are a set of SQL operations that will be performed once the AFTER UPDATE trigger is invoked.
Examples to Implement SQL AFTER UPDATE Trigger
Let us try a few examples to understand it in detail:
To illustrate the functionality of the AFTER UPDATE trigger, let us create a dummy table called “books_audit_table.” This table contains further information pertaining to books available in a library. We can use the following code snippet to create the said table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE books_audit_table (
book_id INT NOT NULL IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
author_name VARCHAR(100),
genre VARCHAR(100),
updated_at DATETIME,
status VARCHAR(100)
);Output:
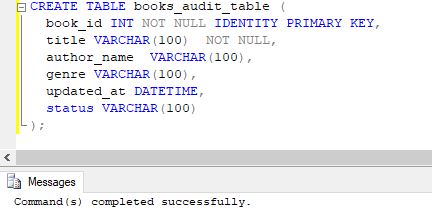
The query returned successfully. Next, using the following INSERT query, insert a few records in the table to work with.
Code:
INSERT INTO [practice_db].[dbo].[books_audit_table]
([title]
,[author_name]
,[genre]
,[updated_at]
,[status])
VALUES
('The Choice','Edith Eva Eger','Memoir',NULL, NULL),
('Deep Work','Carl Newport','Self Help',NULL, NULL),
('A Man Called Ove','Fredrik Backman','Fiction',NULL, NULL),
('When Breath Becomes Air','Paul Kalanithi','Memoir',NULL, NULL),
('Man Search for Meaning','Viktor Frankl','Memoir',NULL, NULL),
('The Third Pillar','Raghuram Rajan','Economics',NULL, NULL)
GOOutput:
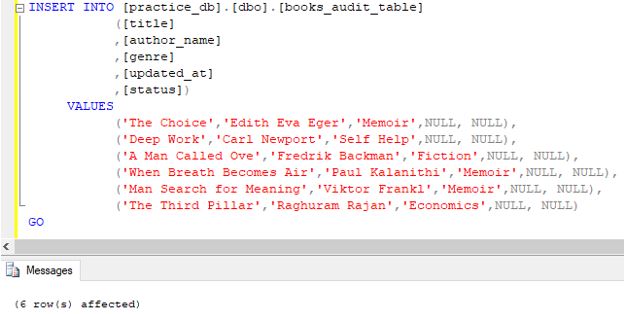
We have successfully created the “books_audit_table.” We will try a few examples based on the AFTER UPDATE trigger.
Example #1
Step 1: Create a trigger in SQL, automatically updating the date and time of borrowing a book from the collection.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER update_trigger ON books_audit_table
AFTER UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
UPDATE books_audit_table set updated_at = GETDATE()
from books_audit_table b
INNER JOIN inserted i on b.book_id=i.book_id
AND i.status = 'Borrowed'
END
GOOutput:
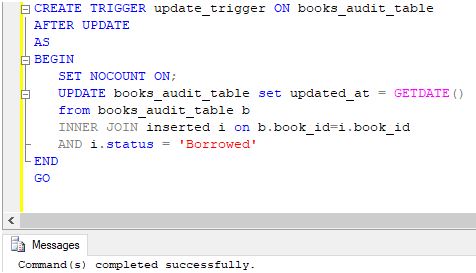
Step 2: The query has successfully created the update_trigger. We can check the newly created trigger in the object explorer.
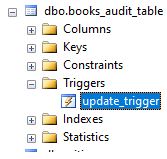
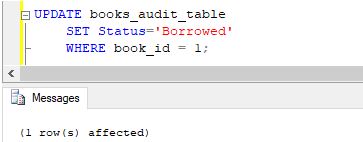
Step 3: Now, let us update the status of the first book to ‘Borrowed’ using the following statement.
Code:
UPDATE books_audit_table
SET Status='Borrowed'
WHERE book_id = 1;Output:
Step 4: Since the update query succeeded, the system must have automatically invoked the update_trigger and populated the ‘updated_at’ column with the current timestamp. The following select query can be used to check the same.
Code:
SELECT * FROM books_audit_table;Output:
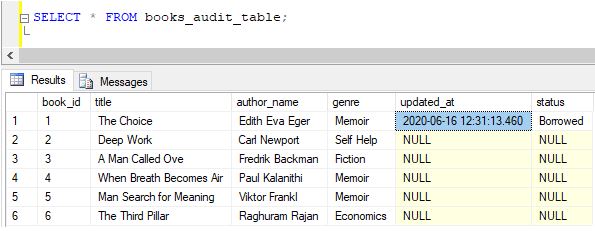
Step 5: We can observe in the image that for book_id = 1, the updated_at column has been populated. Let us try one more example based on the same concept. This time let us do it for book_id = 5.
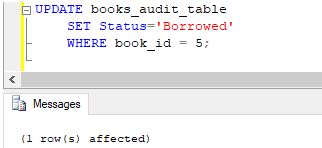
Code:
UPDATE books_audit_table
SET Status='Borrowed'
WHERE book_id = 5;Output:
Step 6:
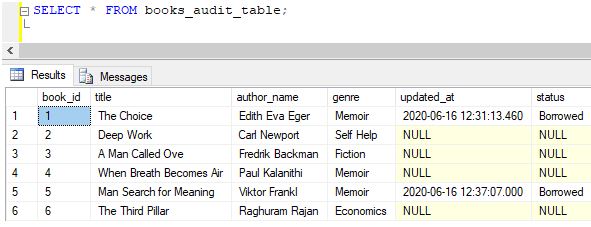
Explanation: Here, the system automatically invoked the update_trigger and updated the ‘updated_at’ column to the current timestamp.
Example #2
Suppose two new columns, such as borrowed_at and returned_at, have been added to the books_audit_table. You must populate these columns with a timestamp when you change the book’s status to ‘Borrowed’ or ‘Returned.'”
Step 1: Modify the table by modifying the following ALTER statements.
Code:
ALTER TABLE books_audit_table
DROP COLUMN updated_at;
ALTER TABLE books_audit_table
ADD borrowed_at DATETIME;
ALTER TABLE books_audit_table
ADD returned_at DATETIME;Output:
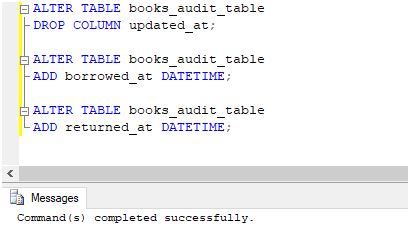
Step 2: The modified table looks something as follows:
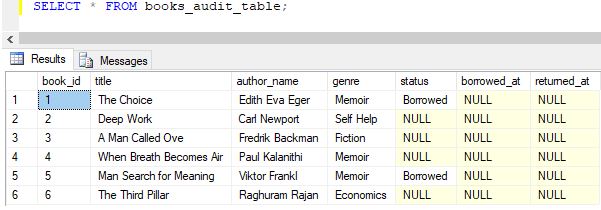
Step 3: Create an after-update trigger called “update_trigger_new” using the following query.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER update_trigger_new ON books_audit_table
AFTER UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
UPDATE books_audit_table set borrowed_at = GETDATE()
FROM books_audit_table b
INNER JOIN inserted i on b.book_id=i.book_id
AND i.status = 'Borrowed'
UPDATE books_audit_table set returned_at = GETDATE()
FROM books_audit_table b
INNER JOIN inserted i on b.book_id=i.book_id
AND i.status = 'Returned'
END
GOOutput:
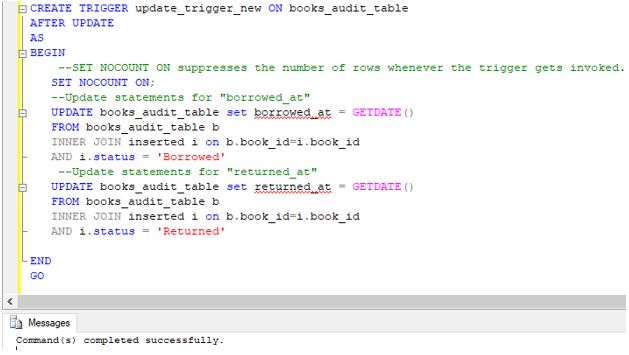
We successfully created the trigger. You can see it in the object explorer.
Step 4: Next, let us update the status of book_id 3 to “Returned.”
Code:
UPDATE books_audit_table
SET Status='Returned'
WHERE book_id = 3;Output:
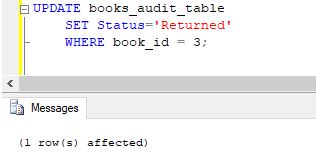
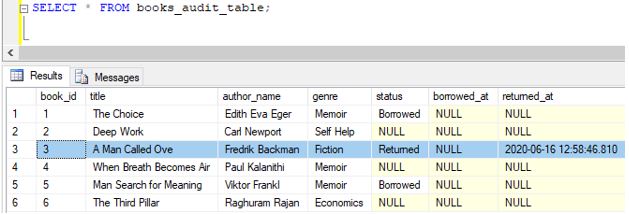
Step 5: The highlighted row shows the changes made by the update query and the trigger. It’s fun, right? Let us try the following update query.
Code:
UPDATE books_audit_table
SET status = 'Returned'
WHERE book_id = 1;Output:
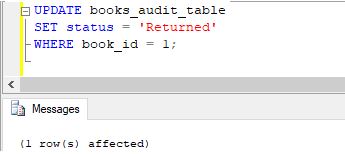
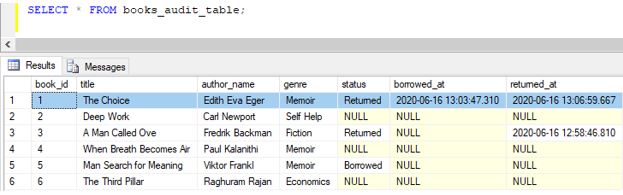
Explanation: Wow, the trigger has made all the necessary changes.
Conclusion
AFTER UPDATE Trigger is a kind of trigger in SQL that will be automatically fired once the specified update statement is executed. It can be used for creating audit and log files which keep details of last update operations on a particular table.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL AFTER UPDATE Trigger” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

