Updated April 1, 2023
Introduction to Spring Boot Service
Spring boot service component is defined as a class file that includes the @Service annotation and allows developers to add business functionalities. The annotation is used with the classes that provide these business functionalities. These classes are auto-detected by the spring context when the annotation-based configuration is used along with class path scanning as it provides a specialization of @Component annotation. The operation performed by the annotated component is offered as an interface and stands alone in the model with no state of encapsulation. This annotation is a general purposed stereotype, and developers may choose to narrow the semantics and make the use of the same as felt appropriate.
Syntax of Spring Boot Service
The spring-boot service component, as mentioned, is a class file for putting in designated areas of adding business functionalities. Here we will see about the spring boot service component from the syntax perspective so that while we see about working of spring boot service component and its features, mapping back to the syntax will enable looking at the complete picture.
1. Decorator needed for working with service component in Spring Boot application.
@Service2. Importing of function that is required for service component working.
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;How does Service Component work in Spring Boot?
- Here we will see the working of the service component in Spring Boot, but before that, we need to know not only the significance of the service component but also the significance of the placement of a @Spring component. It is very important for us to know that typical applications contain distinct layers, for example, access of data, presenting the data, services and business, and in each of these individual layers, there are various beans which enable automatic detection of the layers. @Service annotation helps annotating the classes at the service layer. As we have earlier mentioned, that @Service component provides a specialization of @Component. Now, this makes it even more interesting for us to understand that @Component annotation is used across applications so that the beans are marked as Spring’s managed component, whereas beans marked with @Service happens to house section of the business logic and hence used only in the service layer because of no additional speciality.
- The service component ensures that the class file which incorporates business logic in a different layer and keeps it separated from the @RestController class file. For the functioning of @Service annotation, we need to add the spring core dependency. During the early release of Spring, all beans were declared in an XML file, but with the pointer of scalability in mind, this becomes a herculean task, and hence the @Component annotation provides annotation based injection with the configuration being Java-based. Thus, having the annotation-based injection reduces the declaration of the bean as a <bean> tag. Apart from @Service, which is mainly used in the service layer, @Controller is mainly used for the presentation layer and @Repository for the Data Access Layer or the DAO or Persistence layer.
- Now we will look at the working of the service component using an example. We will declare a service to calculate the interest in case of a deposit made to a bank. At first, we will build the service layer, which will contain the service class that will contain the required function. These functions can be simple interest and/or compound interest functions. The class will be annotated as @Service so that the spring context is able to auto-detect it, and the instance can be instantiated from the context. Now we would define a new class that will contain the instance of the service class. The application context is instantiated. Now the contaxt.scan () function will look for all the annotation, and the required annotation will be registered. Now, as per the @Service annotation, we form the Bean of service class made. This bean will be an instance which will be used for calling any function within the class. Once the required operations are performed, the application context is closed. The instantiation of the bean can also be achieved through explicit casting.
Example of Spring Boot Service
Given below is the example of Spring Boot Service:
Understanding the flow of requests.
Syntax:
InterestCalculator.java:
package com.educba.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.lang.Math;
@Service("ic")
public class InterestCalculator {
public double CI(double P, double R, double T) {
double rate = 1+(R/100);
return P*Math.pow(rate,T)-P;
}
public double SI(double P, double R, double T) {
return P*R*T/100;
}
}DemoserviceApplication.java:
package com.educba.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class DemoserviceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.scan("com.educba.demo");
context.refresh();
InterestCalculator ic = context.getBean(InterestCalculator.class);
double ci = ic.CI(1000, 8, 2);
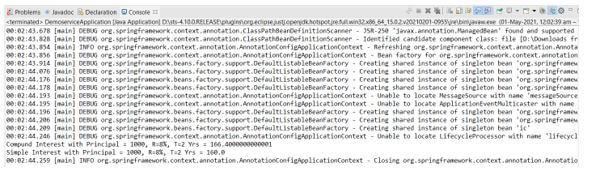
System.out.println("Compound Interest with Principal = 1000, R=8%, T=2 Yrs = " + ci);
double si = ic.SI(1000, 8, 2);
System.out.println("Simple Interest with Principal = 1000, R=8%, T=2 Yrs = " + si);
// Always close the Spring context in order to avoid leakage
context.close();
}
}Pom.xml (add the below dependency to the existing pom.xml):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>Output:
Conclusion
To conclude, this article has provided innumerable insights into how the service component works, along with a short snippet of how it differs from the @Component annotation. In addition, we have gone through a hands-on example to get the idea clearer. One thing to keep in mind for the developers is to always close the application context in order to avoid any leakage.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Spring Boot Service. Here we discuss the introduction, how the service component works in spring boot? And example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –