Updated September 15, 2023
Shrinkflation Meaning
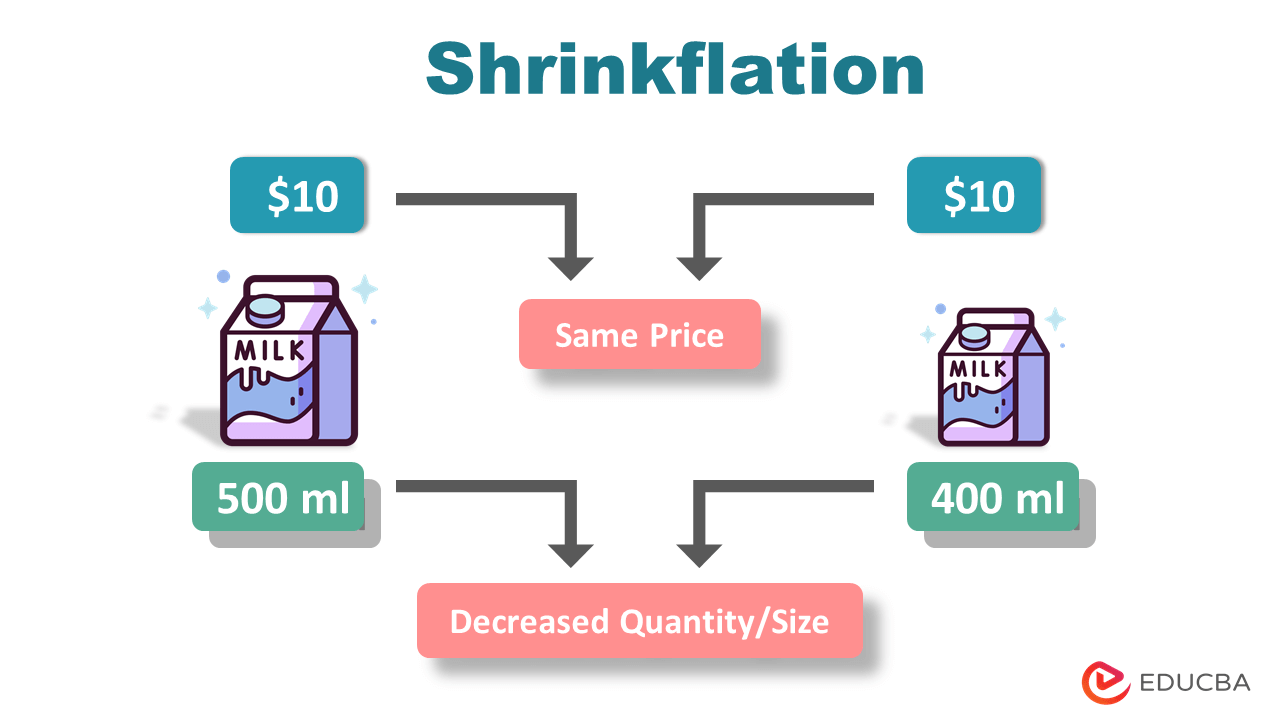
The word “Shrinkflation,” coined by the British economist Pippa Malmgren, is a combination of the words “shrink” and “inflation.” Here, “shrink” refers to the reduction of the size or quantity of the product, and “inflation” refers to the increase in product prices.
Shrinkflation is the concept where businesses reduce the quantity or size of a good instead of increasing its price. It is an extremely common practice in the food and beverage industry. Apart from them, other consumer products like household goods and personal care products also use this practice.
The idea behind this is that as raw material and other input costs increase, manufacturers can no longer afford to sell the product at the same price. However, in price-sensitive industries like food and beverage, consumers can get upset over even a slight rise in prices.
So, instead of increasing the prices, the manufacturers cleverly start reducing the size or quantity of their products instead. This helps them maintain their profits without alarming the public.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- Shrinkflation is a way to make consumers pay more money for less of a product by reducing the quantity of the product rather than increasing the price.
- Rising production costs, changes in demand, and increasing competition are some of its main causes.
- Its advantage is that it helps manufacturers maintain their profits and keep the prices stable.
- Its disadvantage is that consumers might find it unfair and feel cheated by the manufacturers, thus reducing their brand loyalty.
- Skimflation is another clever way of making consumers pay more for less. But instead of reducing the size, the quality of the product is reduced here.
Real Examples
Here are some examples of Shrinkflation in action:
Example 1: Snacks
In 2022, Frito Lay, a popular snack brand, decreased the quantity of its Dorito bags from 9.75 ounces to 9.25 ounces.
Example 2: Toilet Paper
In 2022, the toilet paper brand Charmin reduced the number of toilet paper in its Mega Roll from 264 to 244 sheets. And its Super Mega Roll now contains only 366 sheets compared to the previous 396 sheets. That’s 8.3% less product for the same price.
Example 3: Cereal
Everyone’s favorite cereal brand, Froot Loops, has also been using shrinkflation. Reportedly, they shrunk their $9 Froot Loops box from 500 to 460 grams.
Example 4: Cat Food
In 2021, Royal Canin, a Mars subsidiary, reduced the size of some of its cat food cans from 5.9 to 5.1 ounces without altering the price. The company attributed this reduction in product size to higher demand during the pandemic.
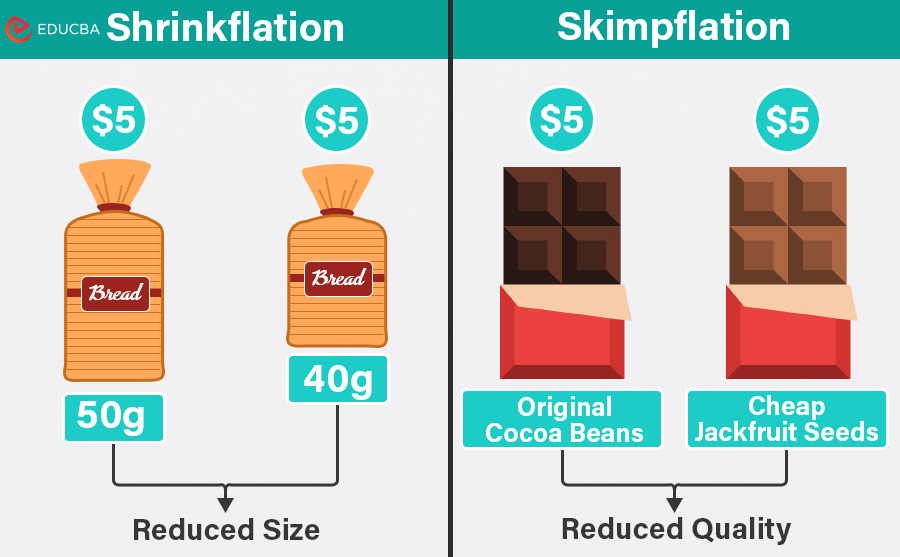
Shrinkflation vs. Skimpflation
Here are the key differences between shrinkflation and skimpflation.
| Aspects | Shrinkflation | Skimpflation |
| Definition | Shrinkflation is the practice of altering the volume or size of the product. | Skimpflation is the practice of decreasing the quality of the product. |
| Cause | Used in response to inflation, increasing competition, and supply chain issues. | Manufacturers use skimpflation to fight rising production costs and labor shortages. |
| Focus | The focus is on maintaining the overall quality and retail price of the product. | In skimpflation, the size, quantity, and price remain the same while the quality decreases. |
| Example | When a 2 liter Coca-Cola bottle becomes a 1.75 liter bottle with no changes in price, it’s shrinkflation. It’s important to note that the ingredients and overall quality remain the same. | Skimpflation is when the ingredients in the Morrisons Guacamole change from 80% avocado and 5% red onion to 77% avocado and an unspecified amount of onion. |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Some of the common advantages and disadvantages of shrinkflation are given below.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Manufacturers can maintain profit margins by reducing the size or quantity of their products, even if the input costs rise. | Consumers have to pay more for a lesser quantity without even noticing the changes. |
| It allows manufacturers to keep consumer prices steady, which can help them avoid adverse reactions to price increases. | This has the potential to erode consumer trust and loyalty. |
| Businesses can transport and store smaller products more easily, resulting in further cost savings for manufacturers. | While technically legal, it is an extremely unfair practice where the burden of inflation is shifted from the manufacturer to the consumer. |
Final Thoughts
Shrinkflation leads to hidden inflation. It means that a typical consumer is often unaware that the per-unit price of their products has increased. On a macroeconomic level, it affects inflation calculations as economics don’t consider this measure while calculating inflation rates.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the risks of shrinkflation?
Answer: Apart from the common risks, such as a decrease in customer loyalty and trust, as well as effects on inflation, here are some risks of shrinkflation.
- Impact on the Economy: If companies worldwide start following this practice, it can lead to a decrease in customer purchasing power and affect economic growth.
- Regulatory Concerns: Some regulatory authorities may find this practice deceptive or unfair, and thus, it can cause the business to be under regulatory scrutiny.
- Backlash from Industry Peers: Companies that use this concept may have fallout industry competitors who maintain product sizes due to the impact on market share.
Q2. What is the opposite of shrinkflation?
Answer: There is no official term for the opposite of shrinkflation. But theoretically speaking, the opposite of this practice would be when companies increase the size or quantity of a product without making any price changes.
Q3. Is shrinkflation a deflation?
Answer: Shrinkflation and deflation are two completely separate concepts. While shrinkflation leads to an increase in the per unit price of a product, deflation means reducing the overall price of goods and services on an economic level.
Q4. What is the difference between shrinkflation and inflation?
Answer: Inflation is a concept where the price of goods and services goes up due to the economic conditions of the region. On the other hand, shrinkflation is a rather sneaky way manufacturers use to shift the burden of inflation onto the final consumers.
Recommended Articles
Thank you for reading the article on Shrinkflation. We hope it’s been informative and useful to you. If you are interested in other economics-related topics, check out these EDUCBA articles: