Updated June 19, 2023
Definition of Scala Synchronized
Synchronization, in general, is the mechanism to control more than one thread on the same shared resource. This is the basic rule for synchronization, which is applicable and true for any programming language. In Scala, they provide support for threads which is based on java only. We can use java classes to implement this in Scala.
Syntax:
In Scala, we can synchronize a code block by using ‘synchronized’ keyword before it. Inside this synchronized block, we can write the logic that we want to synchronize. This will prevent multiple threads from modifying our resource at the same time, thus ensuring the consistency of data.
synchronized {
// we can write our logic here.
}In the above piece of syntax, as we can directly see, we have used the keyword ‘synchronized’ to make our code synchronous. We can also see one practice example to understand the syntax better. See below;
synchronized {
a = b + c ; // some logic
z = a + 10;
}How Synchronized Function Works in Scala?
Now we know that synchronization is important when we have shared resources, and we do not want multiple threads to perform operations on it simultaneously, so we will go for synchronization. It is important because we do not control multiple threads it will result in the data inconsistency issue for us. In Scala, we have the Future trait, which provides us asynchronous mechanism where multiple threads can access the same resource at the same time. This can be a fetching operation where data is not getting manipulated so that we can use that there. Now we will have a closer look at synchronous functions in Scala, how they work, and what is their significance in detail. We will see their advantage, scenarios where we should implement them, and some basic examples for beginners to understand them better. See below;
When to Use: you can use synchronization where we have shared resources, and we do not want them to get modified by multiple or various threads simultaneously. This is very important because we have business logic or some calculations which are dependent on the other data. also, if we do not follow this approach, then the data will be inconsistent, or we can also receive some errors and exceptions as well.
Let’s take one simple real-time example we need synchronization. Without it, data would be inconsistent in the database. Bank transactions can easily understand this. Suppose we have a single account for two members i.e. a joint account, and let’s name them A and B. Overall, they have 2000 rupees in their account, and they both want to withdraw this amount simultaneously. Still, in practice, this is not possible because only one person can get the amount. So we need to lock the resource for the same period of time when the first one, ‘A,’ will be done with their operations; then only, we will release the lock to avoid data inconsistency. So in this critical situation, we have to have synchronization in place to handle those scenarios well. Otherwise, Bank and the customer both have to suffer, and the services we are providing them will be of no use.
Example
Code:
object Main extends App{
synchronized {
println("demo for synchronized")
println("we can put the code here which we want to synchronized")
}
}In the above example, as you can see that we have created one class, here Which is named Main. scala. This class is extending the App class further. After that, we create one synchronized block to print some lines of code there to understand it. So in this way, we can have our shared resource logic placed there, and they will acquire a look at that object until it finishes its work.
Some points need to be remembered while working with synchronization in Scala; see below;
- Synchronization prevents access to multiple threads on the same object simultaneously.
- In this way, this helps us prevent the data inconsistency issue in the future.
- Synchronization makes the execution of the program or process sometimes very slow because it allows only one thread at a time.
- During the synchronization process, it holds a lock on the resource so that no other thread can access it. All the other threads go into the waiting state until the current thread finishes its execution.
- We should try to follow the synchronization approach where we have some kind of dependency on the previous value, which can impact the current value.
How to Use Synchronized in Scala?
In Scala, we can make a synchronized block to place our logic. To use synchronized, we need to use the synchronized’ keyword before our logic acts as the function. We should cover our entire logic inside this block only, creating a lock on the object and preventing simultaneous modifications by other threads.
Example
Code:
synchronized {
// your logic goes here ..
}Example of Scala Synchronized
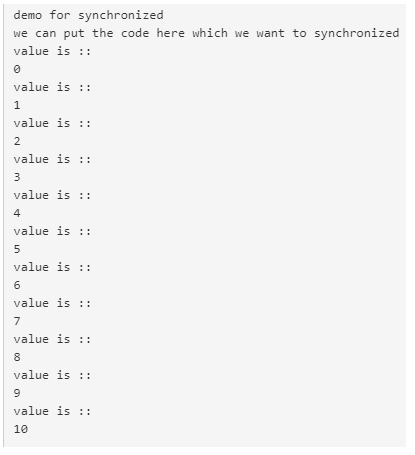
In this example, we are printing the value of the integer from 1 to 10 inside the synchronized block means no other thread can access it at the same time. Simple program for beginners.
Code:
object Main extends App{
// Your code here
synchronized {
println("demo for synchronized")
println("we can put the code here which we want to synchronized")
for (i<- 0 to 10) {
println("value is ::")
println(i)
}
}
}Output:
Conclusion
Synchronization is used to avoid data inconsistency in our application. But sometimes, the performance is slightly slower because only a single thread operates on the object at a time. But in parallel execution, multiple threads can operate the single resource, which makes the process faster, but we cannot use them everywhere. We need some alternative to prevent our data from being malformed.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Scala Synchronized” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


