What is Sales Pipeline Management?
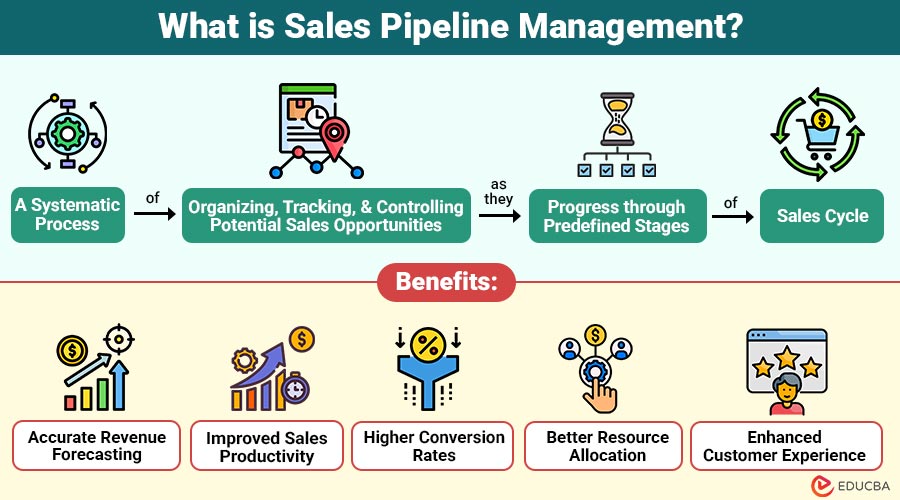
Sales Pipeline Management is systematic process of organizing, tracking, and controlling potential sales opportunities as they progress through predefined stages of the sales cycle. It shows prospects where they are in the purchasing process and what has to be done to get them to convert.
For example, Sales Pipeline Management (Retail Store)
A customer visits a mobile phone store →
The salesperson explains models →
Customer shows interest in one phone →
Price is discussed →
Customer buys the phone.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Sales Pipeline Management provides structured visibility into deals, improving forecasting accuracy and overall revenue predictability.
- Effective pipeline processes increase sales productivity by prioritizing high-value opportunities and reducing time on low-quality leads.
- Tracking pipeline metrics such as conversion rates and deal velocity helps identify bottlenecks and strengthen sales performance strategies.
- Implementing CRM and analytics tools enhances customer engagement, accountability, and long-term relationship management for sustainable growth.
Importance of Sales Pipeline Management
Sales Pipeline Management plays a vital role in improving both sales efficiency and predictability. Its importance includes:
1. Revenue Visibility
Provides clear insight into active opportunities, expected deal values, and upcoming revenue across sales stages.
2. Forecast Accuracy
Uses structured pipeline data to predict revenue outcomes more reliably and support informed business planning decisions.
3. Deal Risk Detection
Highlights slow-moving opportunities early, enabling timely intervention to re-engage prospects and prevent deal loss.
4. Process Alignment
Establishes standardized stages and workflows, ensuring all sales representatives follow uniform methods across opportunities.
5. Data-Driven Decisions
Transforms sales activity data into actionable insights that guide strategy, prioritization, and performance improvements.
6. Sales Accountability
Tracks ownership and progress of deals, encouraging responsibility, transparency, and consistent follow-through from sales teams.
Stages of a Sales Pipeline Management
While pipeline stages may vary across industries, most sales pipelines follow a structured flow. Below are the common stages:
1. Lead Generation
This is the initial stage where potential customers are identified through marketing campaigns, referrals, cold outreach, or inbound inquiries.
2. Lead Qualification
Sales teams evaluate leads based on criteria such as budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT) to determine sales readiness.
3. Initial Contact
Sales representatives engage qualified leads through calls, emails, or meetings to understand requirements and build rapport.
4. Needs Assessment
In this stage, sales teams identify customer pain points and align solutions with business objectives.
5. Proposal or Demo
A tailored proposal, product demo, or pricing discussion is presented to showcase value and differentiation.
6. Negotiation
Terms, pricing, and contract conditions are discussed to address objections and finalize agreements.
7. Closing
The deal is finalized, contracts are signed, and the opportunity is marked as won.
8. Post-Sale Follow-Up
Customer onboarding, support, and relationship nurturing ensure long-term retention and upselling opportunities.
Benefits of Effective Sales Pipeline Management
Here are the key benefits that highlight how structured pipeline management improves sales performance and revenue outcomes:
1. Accurate Revenue Forecasting
Pipeline data predicts future revenue accurately using deal stages and historical conversion performance trends.
2. Improved Sales Productivity
Sales teams prioritize high-value opportunities, reducing time spent on low-quality leads and unqualified prospects.
3. Higher Conversion Rates
Early bottleneck identification helps optimize messaging, accelerate deal progression, and close opportunities more efficiently.
4. Better Resource Allocation
Managers strategically assign resources based on deal value, urgency, probability, and expected revenue impact.
5. Enhanced Customer Experience
Timely engagement and structured follow-ups build trust, improve satisfaction, and strengthen long-term customer relationships.
Key Metrics Used in Sales Pipeline Management
To measure pipeline health, organizations track several metrics:
1. Pipeline Value
Represents total potential revenue from all active deals currently progressing through the sales pipeline.
2. Win Rate
Calculates the proportion of sales prospects that are successfully closed over a given time frame.
3. Sales Cycle Length
Tracks the average time required to move a deal from initial contact to closure.
4. Deal Velocity
Indicates how quickly deals advance through pipeline stages, impacting revenue realization speed.
5. Conversion Rate per Stage
Shows how effectively opportunities progress between stages, identifying strengths and weaknesses in the sales process.
Sales Pipeline Management Tools
Modern businesses rely on CRM and analytics tools to manage pipelines efficiently. Common tools include:
1. Customer Relationship Management Systems
Centralize customer data, track deals, manage interactions, and guide sales teams through pipeline stages.
2. Sales Analytics Platforms
Analyze pipeline performance, identify bottlenecks, forecast revenue, and visualize sales trends using data dashboards.
3. Automation Tools
Automate follow-ups, emails, task reminders, and workflows to improve sales productivity and response times.
Challenges in Sales Pipeline Management
Despite its benefits, pipeline management comes with challenges:
1. Inaccurate or Incomplete Data
Poor data quality leads to unreliable pipeline visibility, misleading insights, and incorrect sales-forecasting decisions.
2. Overloaded Pipelines with Low-quality Leads
Too many unqualified leads waste sales time and reduce focus on high-conversion opportunities.
3. Inconsistent Sales Processes
Different sales approaches create confusion, uneven performance, and difficulty in accurately tracking pipeline progress.
4. Poor CRM Adoption by Sales Teams
Sales reps avoid updating their CRMs, resulting in outdated information and limited visibility into the pipeline.
5. Difficulty Forecasting Complex Deals
Long sales cycles and multiple stakeholders make revenue predictions inaccurate and hard to manage.
Real-World Use Cases of Sales Pipeline Management
These real-world use cases show how different industries use sales pipeline management to streamline sales processes and drive predictable growth:
1. SaaS Companies
Track subscription deals, forecast recurring revenue, prioritize renewals, reduce churn, and improve customer lifetime value.
2. B2B Enterprises
Manage long sales cycles, coordinate multiple stakeholders, track negotiations, and close high-value enterprise contracts.
3. Retail and E-Commerce
Monitor customer buying intent, optimize follow-ups, personalize offers, and increase conversion rates across channels.
4. Financial Services
Track complex customer journeys, ensure regulatory compliance, manage approvals, and forecast revenue accurately for institutions.
Final Thoughts
Sales Pipeline Management is essential to modern sales operations, offering clear visibility into deals, performance, and revenue potential. It enables accurate forecasting, better resource allocation, and improved customer experiences. With the right tools, metrics, and processes, sales pipelines become strategic assets that drive predictable revenue, scalable growth, and long-term business success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main goal of sales pipeline management?
Answer: The main goal is to improve deal visibility, forecasting accuracy, and sales efficiency.
Q2. How often should a sales pipeline be reviewed?
Answer: Ideally, pipelines should be reviewed weekly for accuracy and performance optimization.
Q3. Can small businesses benefit from sales pipeline management?
Answer: Yes, even small teams gain clarity, structure, and predictability using pipelines.
Q4. Is CRM necessary for pipeline management?
Answer: While not mandatory, CRM systems significantly improve tracking, reporting, and scalability.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Sales Pipeline Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

