Updated July 21, 2023
Introduction to Root Cause Analysis
The term ‘Root Cause Analysis’ is a technique to identify the root where the fault or problem occurs in an activity; in other words, when during an activity an occur has occurred which causes a problem while completing a training, then in such a situation this technique called root cause analysis is used to identify the root where such problem occurs and then to take such corrective measures which needs to be taken to solve such issue.
Explanation
The explanation of Root Cause Analysis is as follows:
- It is a situation where an issue or problem occurs due to technical issues.
- The said issue needs to be plugged or fixed by analyzing such a situation at the earliest.
- Then in such a situation, a team effort will make such a problem plugged, and the objective will be achieved.
Root Cause Analysis Process
The process of root cause analysis is as follows:
- The problem that occurred will be identified.
- The data and such relevant information need to be gathered, which helps to understand the issue more accurately.
- The team will analyze why such a problem has occurred.
- Then after analyzing the above two steps, the next step is to analyze that if it happens, then how does it happen?
- Then after understanding all the problems, take remedial steps to resolve the issue.
- Then, take corrective measures to prevent such a problem from happening again.
- Then take such suggestions from the root cause analysis team, which needs to be implemented so that the issue will not occur in the future, and implement such suggestions to the maximum possible level at the earliest.
Examples of Root Cause Analysis
There is a guy who has been suffering from ankle pain for the last few hours after he slipped on stairs; as a remedy, the person takes a painkiller which relieves him for some hours, but the issue still pertains; the pain will automatically happen as and when the effect of such pain killer ends. In this example, the issue is ankle pain, which can only be cured by a professional. Similarly, any issue may occur in a business that is a combination of various areas, and if such an issue arises, what will be the solution to such problems? Two methods could resolve every problem one is to resolve the issue temporarily and finish the task working upon, and the other is to analyze in-depth the issue and resolve the issue in such a manner so that the issue will not occur until the situation or circumstances change.
The issue is analyzed at such deep levels, which will also provide for the situation which is more difficult and major as compared to the issue which already has occurred. Therefore, the concept of root cause analysis comes under play which gives the meaning, i.e., identifying the root or the origin from where the cause or issue has occurred or why such an issue has occurred.
Need for Root Cause Analysis
- In an environment where there is a continuous change in the atmosphere in which an entity operates as nowadays, technology plays a vital role in every business, and timely adoption and up-gradation of such technology help to achieve organizational goals more fluently and easily which itself gives a major reason to perform root cause analysis.
- If any problem arises or takes place, then analyzing and resolving such issues will result in loss of money and resources as well then; by keeping track regularly, one could easily focus on the area where there are chances of such issues.
- It also provides the benefit of problem resolution at the earliest as we have already tried to encounter and resolve such issues during the testing phase.
- Each and every organization understands that it involves time, money, and manpower to be deployed to get the results for a situation that might not occur, i.e., extra precautions may sometimes result in the wastage of resources.
Methods Used in Root Cause Analysis
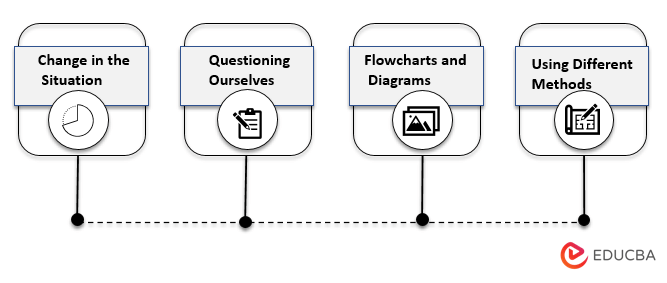
Some of the most used analysis methods are as follows:
- Analysis of change in the situation.
- Questioning ourselves, if yes, then how and why?
- Preparing flowcharts and diagrams of all the possibilities.
- By taking the worst situation and impacts thereof.
- Using a method different from the method generally accepted as the method of operations in an organization and then understanding the impact thereof.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The benefits and disadvantages are given below.
Advantages
- The problem resolved will be permanent or for a longer period.
- The issues encountered are from practical life or the real world, which results in helping others who may face the same issue in the future.
- Regularly assessing such issues or issues that might be issued will also improve the internal control systems of the company.
Disadvantages
- The process defined is time-consuming as analysis needs to be done in-depth.
- The process is very castile as well.
- The method also blocks manpower as in-depth analyses will also need manpower to analyze.
Conclusion
To conclude, the term ‘Root Cause Analysis is used to analyze and grab loopholes that create a problem in an activity to complete the objective to be served through such activity. This technique is mainly used in the industry where the data volume is too high such as telecommunications, IT, data center, etc., which needs to process the heavy volume of data through a defined process; therefore, timely analysis through such process will become more necessary to be done for such type of industries.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Root Cause Analysis. Here we discuss an introduction to Root Cause Analysis along with the explanation, examples, process, methods, advantages, and disadvantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


