What is Robotics Engineering?
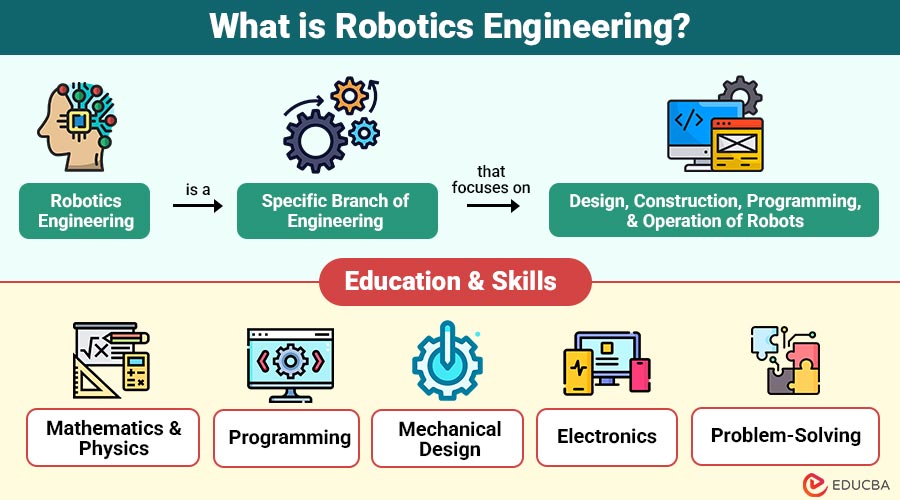
Robotics engineering is a specific branch of engineering that focuses on design, construction, programming, and operation of robots. A robot is characterized as a programmable machine that can carry out a task automatically, either under direct supervision or autonomously, based on pre-programmed instructions and artificial intelligence.
Robotics engineers work on:
- Mechanical structure (the body and parts of the robot).
- Electronics (sensors, circuits, and power systems).
- Software (algorithms and coding to control the robot).
The objective is to build machines that are more capable than humans at complicated, hazardous, or repetitive jobs.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Robotics engineering integrates mechanics, electronics, and programming to design intelligent machines for diverse applications.
- It advances industries like manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and defense by improving efficiency, safety, and reliability.
- Careers range from robotics engineers to AI specialists, offering exciting opportunities in innovation and technology development.
- Despite challenges like high costs and ethical debates, robotics continues to shape the future of automation worldwide.
Education and Skills Needed in Robotics Engineering
To become a robotics engineer, a person usually studies a degree in robotics engineering, mechatronics, electrical engineering, or computer engineering. Some essential skills include:
1. Mathematics and Physics
Provide the foundation for understanding forces, motion, energy, and electronic principles, essential for designing precise mechanical structures, efficient motors, and reliable electronic systems in robotics.
2. Programming
Involves coding with languages such as Python, C++, or Java, enabling robots to process data, follow instructions, and perform tasks through algorithms and control logic.
3. Mechanical Design
Requires knowledge of gears, actuators, motors, and materials, allowing engineers to build strong, efficient, and reliable robot bodies capable of handling real-world applications and environments.
4. Electronics
Focuses on circuits, sensors, wiring, and microcontrollers, ensuring robots receive power, process signals, and interact smoothly with hardware components for proper functionality and efficiency.
5. Problem-Solving
Involves analyzing challenges, applying creativity, and developing innovative engineering solutions, enabling robots to operate effectively, adapt to situations, and perform tasks in dynamic environments.
Applications of Robotics Engineering
Robotics engineering has wide applications across industries:
1. Manufacturing
By accurately, swiftly, and safely assembling electronics, cars, and heavy machinery, robots boost production, reduce costs, and enhance product quality in sectors all over the world.
2. Healthcare
Robots support surgeons in complex procedures, aid patient rehabilitation, manage hospital logistics, and create advanced prosthetics, improving medical accuracy, safety, and overall healthcare delivery.
3. Agriculture
Robots automate planting, harvesting, irrigation, and crop monitoring, increasing yield, reducing labor, and using AI to optimize farming practices for sustainable food production globally.
4. Space Exploration
Robots explore planets, moons, and distant space environments, conducting experiments, gathering samples, and performing tasks dangerous for humans, enabling groundbreaking astronomical and scientific discoveries.
5. Military and Defense
Robots conduct surveillance, defuse bombs, and strengthen security, reducing risks for soldiers while ensuring missions are carried out safely in hostile or hazardous environments.
6. Daily Life
Household robots assist with cleaning, cooking, and simple tasks, offering convenience, saving time, and improving everyday living comfort through smart automation and user-friendly technology.
Advantages of Robotics Engineering
Robotics engineering provides several benefits to society:
1. Efficiency
Robots complete tasks much faster than humans, without fatigue or distraction, significantly boosting productivity, reducing delays, and ensuring smooth operations in industries and daily life.
2. Accuracy
Robots perform with exceptional precision, minimizing errors in manufacturing, healthcare, and research, resulting in higher product quality, reliable outcomes, and consistent performance across applications.
3. Safety
Robots handle hazardous tasks in industries, construction, and war zones, reducing risks to human workers, preventing injuries, and ensuring operations in dangerous or inaccessible environments.
4. 24/7 Operation
Unlike humans, robots function continuously without breaks, holidays, or sleep, ensuring uninterrupted workflows, maximizing efficiency, and maintaining productivity around the clock in critical sectors.
5. Innovation
Robotics drives innovation in medicine, space exploration, manufacturing, and service industries, creating new possibilities, advancing technologies, and shaping future societies with groundbreaking solutions and discoveries.
Challenges in Robotics Engineering
While robotics engineering has many benefits, it also faces challenges:
1. High Cost
Designing, developing, and manufacturing robots involves advanced materials, sensors, and software, making robotics projects expensive, often limiting access for smaller businesses or developing regions.
2. Job Concerns
Many fear robots replacing human workers in industries, leading to unemployment concerns, requiring careful workforce planning, retraining, and balancing automation with human contributions.
3. Complex Technology
Robotics demands expertise in mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and AI, making development difficult, requiring interdisciplinary knowledge and collaboration for building functional and intelligent systems.
4. Ethical Questions
Debates continue about decision-making power, autonomy, and accountability of robots, raising concerns over safety, privacy, fairness, and responsibility in critical areas like healthcare and defense.
5. Maintenance
Robots require regular updates, software patches, and technical servicing to remain reliable, safe, and efficient, which adds ongoing costs and challenges to long-term robotic system operations.
Career Opportunities in Robotics Engineering
Robotics engineers are in high demand. Career options include:
1. Robotics Engineer
Focuses on designing, developing, and building robots, integrating mechanical, electrical, and software systems to create functional machines that perform tasks efficiently in various industries.
2. Automation Engineer
Works with automated manufacturing systems, programming and maintaining robots and machinery to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and streamline production in industrial and commercial environments.
3. AI Specialist
Develops intelligent software and algorithms that enable robots to learn, adapt, and make decisions, enhancing autonomy, problem-solving, and advanced human-like interaction capabilities.
4. Mechatronics Engineer
Combines computer, electrical, and mechanical engineering concepts to create robotic systems, guaranteeing smooth hardware and software integration for effective movement, control, and overall functionality.
5. Robotics Technician
Specializes in maintaining, troubleshooting, and repairing robots, ensuring smooth operation, minimizing downtime, and keeping robotic systems functional, reliable, and safe for industrial or service use.
Final Thoughts
Robotics engineering is a powerful field that mixes science and technology to make machines able to transform human life. From manufacturing and medicine to space and defense, robots are becoming essential in every sector. While challenges exist, the opportunities in robotics engineering are limitless. For students and professionals interested in innovation, robotics offers one of the most exciting career paths of the 21st century.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What does a robotics engineer do?
Answer: A robotics engineer designs, builds, and programs robots to perform specific tasks.
Q2. Is robotics engineering difficult?
Answer: It can be challenging because it combines mechanical, electrical, and software skills, but it is rewarding.
Q3. Which programming language is most used in robotics?
Answer: Python and C++ are the most popular in robotics engineering.
Q4. What is the future scope of robotics engineering?
Answer: Robotics engineering has vast scope in automation, AI, healthcare, space exploration, and everyday life.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Robotics Engineering” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.