Updated July 21, 2023

Definition of Risk/Reward Ratio
The Risk/Reward Ratio is measured by the trader/investor for the level of risk taken on investment against the level of income and growth achieved on investment. The ratio measures probability and level of profit against probability and level of loss taken by the investor.
Every trader/investor, according to his /her risk appetite, generally decides the Risk/Reward ratio. In general high-risk results in high rewards, but there is an investment option where this statement is not true. This ratio helps the investor to make the decision of investment from investment options depending on the level of returns against the level of risk involved in case investment does not move in the expected direction.
Formula
In general, the lower ratio is better than the investment.
Example of Risk/Reward Ratio (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
A decision to invest $400,000. He is willing to take 10-15% of the risk on a short-term investment. He shortlisted two stocks one of which he prefers to invest. They are either Microsoft Corporation at the current price of $172 per share or Apple Inc. at the current price of $320 per share. Mr. A study and analyzed both stock trends and realized that Microsoft Corp. share price can go up to $225 per share and Apple Inc. share price can go up to $400 per share in a period of 3 months. Since it is a stock market investment it involves the risk of share price goes down instead of up. He is ready to take risks up to $48000.
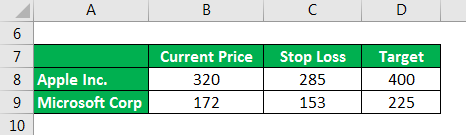
Solution:
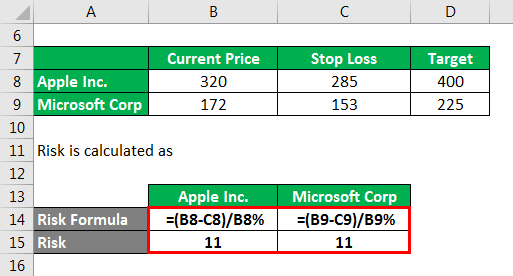
Risk is calculated as
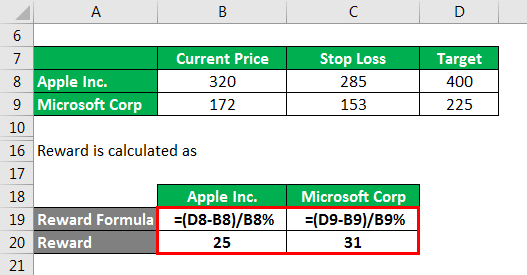
Reward is calculated as
Risk/Reward Ratio is calculated using the formula given below
Risk to Reward Ratio = Risk / Reward
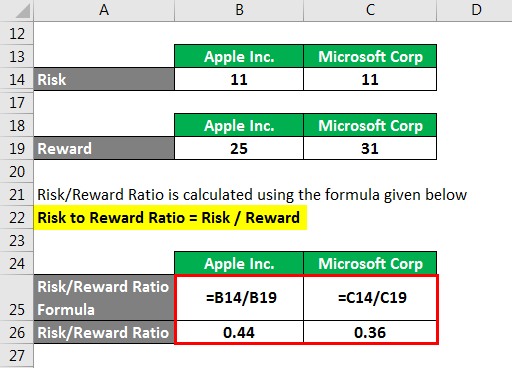
For Apple Inc.
- Risk/Reward Ratio =$35 / $ 80
- Risk/Reward Ratio = 0.44
For Microsoft Corporation
- Risk/Reward Ratio = $19 / $53
- Risk/Reward Ratio = 0.36
Above, calculation, suggests Microsoft is the better investment as per the Risk/Reward ratio. However, it is up to Mr. A to decide which investment he prefers or he may choose to invest in both companies by dividing his investment.
Difference Between Risk and Reward
| Basis of Comparison | Risk | Reward |
| Definition | Risk is the probability and level of loss of investment taken by the investor. | The reward is returns or growth earned on investment by the investor during period |
| Source | Risk is a result of the category of asset, investment and trading strategy, Economic conditions affecting investment. | The reward is a result of Interest, dividend, increase in the underlying value of the investment. |
| Types |
|
|
| Managing | There are 4 way to handle risk
|
Rewards are managed by
|
| Example | Mr. Rock decides to invest in stock A at the current price of $100 he expects the price of the stock can rise up to $120 in 1 month while he decides he should not make the loss of more than $10 in this stock. $10 is a risk taken by Mr. Rock in this investment in case stock moves down. | Mr. Rock decides to invest in stock A at the current price of $100 he expects the price of a stock can rise up to $120 in 1 month while he decides he should not make the loss of more than $10 in this stock. Stock price moves up to $120 in a month this earning of $20 on $100 investment is the reward. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Risk/Reward Ratio
Below we will learn about the benefits and limitation for the same:
Advantages
Below are the advantages:
- Risk appetite: Every individual has a different risk level of risk capacity. Risk/Reward ratio helps them to make selection and decision from various investment option according to capacity and expected returns.
- Investment Decision: Risk/reward ratio help investor to make investment decision from various investment options like mutual funds, stocks, hedge funds, etc.
- Risk-returns estimates: Even if investment provides returns it is important to calculate whether returns earned on investment are worth in comparison with the risk taken. If returns are not as expected compare to risk, an investor can decide whether an investment is worth or not. For e.g. Investor can decide to make an investment in bonds, debentures, fixed deposits that have less risk but will also generate less return on investment, or other options likes the stock, mutual funds which can generate high returns but includes the risk of loss. Investment decision depends on an investor’s expectation and risk capacity.
- Risk Management: Risk can be managed by four ways i.e. avoid, reduce, transfer and accept. With the help of risk to reward ratio investors can manage their portfolio to maximize returns and minimize risk level through various options. Trader trading in various financial instruments can limit his loss with stop-loss by using risk to reward ratio.
Disadvantages
Below are the disadvantages:
- Not completely accurate: Risk/Reward ratio is not always accurate; the investor has to make the decision based on risk capacity and on certain assumptions on price movement. Technical and fundamental analysis help in making better analysis of stock understand risk/reward ratio but they are not completely accurate, and still include assumptions.
- Not Certainty of movement: Risk to reward ratio based on an assumption of certain movement but in reality in the market financial instrument does not necessarily move in expected or opposite direction. Many time if the stock remains stagnant, which will turn the investment into a dead investment without either profit or loss.
Conclusions – Risk/Reward Ratio
Risk/Reward ratio is an important tool for trader/investor to understand the level of risk involved in investment decisions compared to returns. Lower the risk/reward ratio i.e. below 1 is considered as good ratio since the return on investment outweighs the risk. In general, short-term investors and traders use this ratio to select from a variety of categories of investments. In case the price does not move in the expected direction this ratio, helps them to limit their losses.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Risk/Reward Ratio. Here we discuss differences, advantages & disadvantages along with practical example. We also provide a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


