What is Revenue Operations (RevOps)?
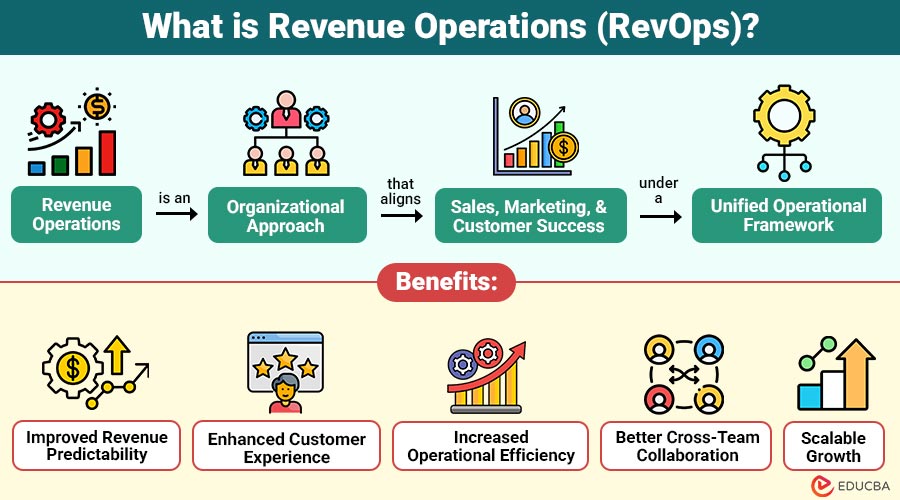
Revenue operations is an organizational approach that aligns sales, marketing, and customer success under a unified operational framework. Its primary goal is to optimize entire revenue lifecycle—from lead generation to customer retention and expansion—by integrating people, processes, and technology.
Unlike traditional models in which departments operate independently with their own metrics and tools, RevOps fosters collaboration and ensures that every team contributes to shared revenue objectives.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why Revenue Operations Matters?
- Core Pillars
- Working
- Difference
- Key Responsibilities
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Real-World Example
- Revenue Operations Metrics to Track
Key Takeaways:
- Revenue operations aligns marketing, sales, and customer success for unified revenue growth.
- Centralized data and analytics improve forecasting accuracy, decision-making, and operational efficiency.
- Standardized processes enhance customer experience, retention, and long-term satisfaction across lifecycle stages.
- Implementing RevOps reduces silos, increases collaboration, and supports scalable, predictable business growth.
Why Revenue Operations Matters?
Here are the key reasons why revenue operations play a important role in driving business growth:
1. Eliminating Operational Silos
Revenue operations aligns marketing, sales, and customer success teams, breaking silos that hinder collaboration and revenue efficiency.
2. Creating a Unified Customer Journey
RevOps ensures consistent messaging, seamless handoffs, and cohesive experiences across all customer lifecycle stages.
3. Improving Decision-making Through Shared Data
Centralized data enables leadership to make accurate, timely, and insight-driven revenue decisions across teams.
4. Increasing Revenue Predictability
Standardized processes and forecasting models improve visibility, stability, and confidence in future revenue outcomes.
Core Pillars of Revenue Operations
Here are the core pillars that drive effective revenue operations:
1. People
RevOps aligns cross-functional teams with clear roles, accountability, and shared objectives. This includes operations professionals, analysts, and leadership working collaboratively.
2. Process
Standardized workflows govern lead management, pipeline progression, customer onboarding, renewals, and upsells.
3. Technology
RevOps integrates tools such as CRM, marketing automation, customer success platforms, analytics, and billing systems.
4. Data & Analytics
Centralized data ensures consistent reporting, accurate forecasting, and actionable insights across the revenue funnel.
How Revenue Operations Works?
Revenue Operations manages the entire revenue lifecycle, ensuring continuity across stages:
1. Lead Generation
Marketing attracts, scores, and qualifies leads using consistent criteria aligned with the overall revenue objectives and companywide goals.
2. Sales Execution
Sales teams execute opportunities through standardized pipelines, defined deal stages, and shared performance accountability metrics tracking.
3. Customer Onboarding
Structured onboarding enables seamless handoff from sales to customer success, accelerating value realization for new customers.
4. Retention & Expansion
Proactive customer engagement reduces churn, identifies expansion opportunities, and sustainably maximizes long-term customer lifetime value growth.
5. Revenue Intelligence
Continuous revenue analysis delivers actionable insights, improves forecasting accuracy, and drives ongoing performance optimization across teams.
Difference Between Revenue Operations and Traditional Operations
The table below highlights how revenue operations differ from traditional operations:
| Aspect | Revenue Operations | Traditional Operations |
| Scope | Full revenue lifecycle | Sales-focused |
| Teams Involved | Marketing, Sales, Customer Success | Sales only |
| Metrics | ARR, CLV, churn, pipeline velocity | Quotas, deals closed |
| Data | Unified and centralized | Fragmented |
| Customer View | Lifecycle-driven | Transactional |
Key Responsibilities of a Revenue Operations Team
Here are the main responsibilities that ensure smooth and efficient revenue operations:
1. Pipeline and Funnel Management
Manage lead-to-revenue pipelines, monitor funnel health, identify bottlenecks, and consistently improve conversion rates.
2. Revenue Forecasting and Reporting
Deliver accurate revenue forecasts and standardized reports supporting leadership decisions and predictable business planning.
3. CRM and Tool Optimization
Optimize CRM systems and revenue tools to ensure adoption, data accuracy, automation, and operational efficiency.
4. Performance Analytics
Analyze revenue performance metrics to identify trends, risks, opportunities, and actionable insights to improve performance.
5. Cross-team Alignment and Enablement
Align customer success, marketing, and sales teams with the same objectives, procedures, and frameworks for enablement.
6. Pricing and Monetization Insights
Provide pricing analysis and monetization insights to maximize profitability, competitiveness, and long-term revenue growth.
Benefits of Revenue Operations
Here are the benefits organizations gain by implementing revenue operations:
1. Improved Revenue Predictability
Unified data and standardized processes enable accurate forecasting while reducing revenue volatility across business operations.
2. Enhanced Customer Experience
Consistent messaging and smooth handoffs enhance customer satisfaction, trust, retention, long-term loyalty, and overall growth.
3. Increased Operational Efficiency
Automation and process alignment reduce manual effort, errors, costs, and inefficiencies across revenue operations teams.
4. Better Cross-Team Collaboration
Shared KPIs, transparent reporting, and unified visibility align teams toward common revenue goals and strategic outcomes.
5. Scalable Growth
RevOps frameworks support scalable growth by adapting processes, systems, and teams as organizations expand efficiently.
Challenges of Implementing Revenue Operations
Here are the key challenges organizations may face when adopting revenue operations:
1. Organizational Resistance
Teams often resist changes in ownership, metrics, processes, or workflows, slowing RevOps implementation and adoption.
2. Data Integration Complexity
Integrating multiple systems into one unified data source requires advanced technical expertise and careful planning.
3. Tool Overload
Excessive or poorly integrated tools can reduce adoption rates, create confusion, and limit overall effectiveness.
4. Skill Gaps
RevOps requires a combination of analytical, technical, and strategic skills, which may be lacking initially.
Real-World Example
Here is an example showing how revenue operations drive measurable business results:
B2B Manufacturing
A mid-sized industrial equipment company faced slow sales cycles and missed upsell opportunities due to disconnected teams.
RevOps Solution: Centralized CRM, standardized pipelines, and shared dashboards across marketing, sales, and customer success.
Result: 20% faster pipeline efficiency, 15% more renewals and upsells, and improved customer satisfaction.
Revenue Operations Metrics to Track
Here are the key metrics that organizations should monitor to optimize revenue operations:
1. Annual Recurring Revenue
Measures total predictable revenue generated annually from subscriptions, helping forecast growth and assess financial stability.
2. Customer Lifetime Value
Estimates total revenue expected from a customer during their relationship, guiding retention and upsell strategies.
3. Customer Acquisition Cost
Ensures that marketing and sales investments continue to be effective and profitable by calculating the average cost to acquire a customer.
4. Churn Rate
Percentage of customers lost over time, indicating retention effectiveness and overall customer satisfaction levels.
5. Pipeline Velocity
Measures the speed and efficiency of deals moving through the sales pipeline, improving forecasting and revenue predictability.
Final Thoughts
Revenue operations is no longer optional—it is a strategic necessity for modern businesses. By aligning teams, data, and technology, RevOps enables predictable revenue growth, better customer experiences, and long-term scalability. Organizations that invest in RevOps gain clarity, control, and confidence in their revenue engine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is Revenue Operations only for SaaS companies?
Answer: No. While popular in SaaS, RevOps applies to any organization with complex revenue processes.
Q2. Who should own revenue operations?
Answer: RevOps typically reports to the CRO, COO, or CEO, depending on organizational structure.
Q3. How is RevOps different from Sales Operations?
Answer: Sales Ops focuses only on sales efficiency, while RevOps covers the entire revenue lifecycle.
Q4. When should a company implement RevOps?
Answer: Ideally, during early growth stages or when revenue complexity increases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Revenue Operations” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
