What is Release Engineering?
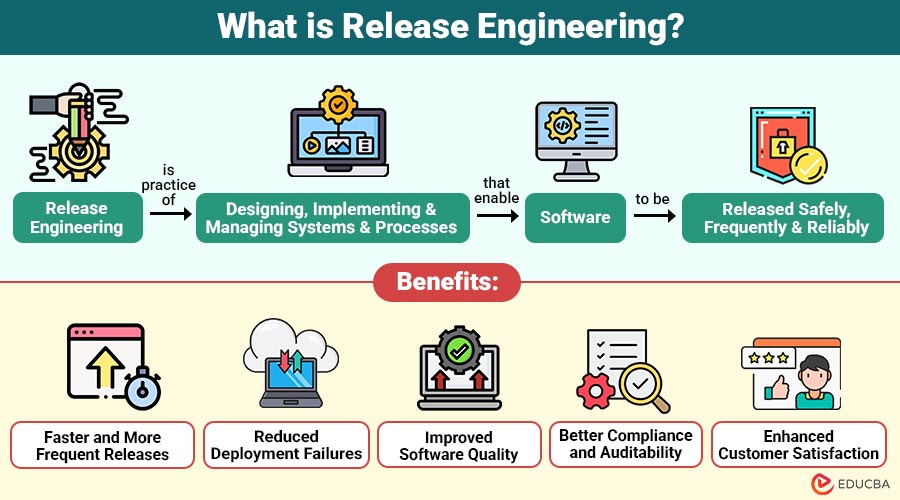
Release Engineering is the practice of designing, implementing, and managing systems and processes that enable software to be released safely, frequently, and reliably. It combines elements of software engineering, automation, infrastructure management, and quality assurance.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Release engineering enables safe, frequent software delivery by automating processes, standardizing pipelines, and implementing controlled deployment strategies globally.
- It reduces deployment failures, improves reliability, and enables rapid rollbacks through monitoring, testing, and versioned artifacts.
- Scalable release processes align development, QA, and operations teams, enabling collaboration, transparency, and consistent delivery outcomes.
- Using release engineering helps companies deliver software faster, follow rules, improve quality, and make customers happier consistently.
Importance of Release Engineering
Here are the key reasons that highlight why release engineering is important for modern software development organizations:
1. Faster Time-to-Market
Streamlined release processes enable rapid delivery of features, fixes, and updates, allowing organizations to respond to market demands.
2. Improved Reliability
Automated and carefully tested release processes reduce the need for people to do tasks manually, which helps prevent mistakes, system crashes, and downtime when updates are made.
3. Scalability
Release engineering supports frequent deployments across multiple environments, platforms, and teams without sacrificing stability or performance at scale.
4. Risk Reduction
Controlled release strategies like canary deployments, monitoring, and rollbacks limit failure impact and ensure faster recovery during incidents.
5. Better Collaboration
Having a standard way to release software helps developers, testers, and operations work together better. It makes everything clear and ensures everyone is responsible for their part of the project.
Key Components of Release Engineering
Here are the key components that collectively ensure software releases are automated, reliable, scalable, and easy to manage:
1. Build Automation
Automated build systems put together code, handle required libraries, run tests, and create reliable files ready for deployment using tools like Maven or Gradle.
2. Continuous Integration
Continuous integration automatically checks and tests every code change when it’s added to the main project, helping find problems early and keeping the shared code reliable.
3. Release Pipelines
Release pipelines are a step-by-step process that includes testing, staging, approvals, and final deployment, making sure updates are delivered in a controlled, consistent, and reliable way.
4. Environment Management
Environment management maintains consistency across development, testing, staging, and production systems, reducing configuration drift and deployment-related failures during software releases.
5. Versioning and Artifact Management
Versioning and artifact management help track changes, reproduce builds, and safely store them using version control and release repositories.
6. Monitoring and Rollback
Monitoring and rollback mechanisms track post-release performance, detect failures early, and restore stable versions quickly when issues arise in production.
Release Strategies Used in Release Engineering
Here are commonly adopted release strategies that help organizations deploy software safely, reliably, and with minimal disruption:
1. Blue-Green Deployment
Two identical environments run in parallel, enabling instant traffic switching between old and new versions with minimal downtime.
2. Canary Releases
New versions are deployed to a small user subset first, allowing monitoring, validation, and risk reduction before full rollout.
3. Rolling Deployments
Updates are gradually deployed across servers in batches, ensuring service availability and preventing downtime during application updates.
4. Feature Toggles
Feature toggles enable teams to dynamically enable or disable functionality without redeploying code, supporting controlled releases and testing.
Tools Used in Release Engineering
Here are the essential tools that support efficient, automated, and reliable release engineering practices:
1. Version Control
Version control systems manage source code changes, enable collaboration, track history, and support branching and merging across development teams.
2. CI/CD Tools
CI/CD tools automate build, test, and deployment workflows, ensuring faster, reliable, and repeatable software releases with minimal manual effort.
3. Configuration Management
Configuration management tools automate system setup, enforce consistency, manage infrastructure changes, and reduce configuration drift across environments.
4. Containerization
Containerization packages applications with dependencies, enabling consistent deployments, scalability, isolation, and efficient orchestration using Docker and Kubernetes.
5. Artifact Repositories
Artifact repositories securely store versioned build outputs, enabling traceability, reuse, dependency management, and reproducible deployments across environments.
6. Monitoring
Monitoring tools collect metrics, visualize system health, detect anomalies, and support proactive issue resolution after deployments in production environments.
Use Cases of Release Engineering
Here are common use cases where release engineering plays important role in delivering reliable and scalable software:
1. Enterprise Software Development
Release engineering helps large enterprises coordinate complex, multi-team releases while maintaining quality, compliance, and predictable delivery schedules.
2. SaaS Platforms
SaaS platforms depend on release engineering to deliver frequent updates, maintain uptime, and ensure consistent customer experiences globally.
3. Mobile Application Releases
Structured release engineering manages app store approvals, version control, staged rollouts, and quick rollbacks for mobile applications.
4. Cloud-Native Applications
Release engineering helps deliver microservices, containers, and cloud systems reliably, making it easier to scale and update them continuously.
Benefits of Release Engineering
Here are the benefits organizations gain by adopting strong release engineering practices:
1. Faster and More Frequent Releases
Streamlined automation enables teams to deliver features and updates rapidly without sacrificing stability or control.
2. Reduced Deployment Failures
Standardized pipelines and automated testing significantly minimize human errors, configuration issues, and production deployment risks.
3. Improved Software Quality
Continuous integration and validation ensure consistent code quality, reliability, and performance across all release cycles.
4. Better Compliance and Auditability
Having clear workflows you can track, keeping versions of work, and getting approvals makes it easier to check and review processes. It also helps make sure rules and regulations are being followed properly.
5. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Reliable, timely releases improve user experience, reduce downtime, and build long-term customer trust and confidence.
Challenges in Release Engineering
Here are common challenges organizations face when implementing and scaling release engineering practices:
1. Tool Complexity
Managing numerous release tools and integrations increases operational overhead, learning curves, and maintenance challenges for teams.
2. Legacy Systems
Old systems (legacy platforms) usually don’t work well with new automation tools, which makes it hard to release updates quickly and reliably.
3. Cultural Resistance
Teams may resist adopting new release practices due to habits, skill gaps, or fear of disruption.
4. Security and Compliance
To release software fast and safely, you need automation, clear guidelines, and organized workflows.
Real-World Example
Here is an example that demonstrates how release engineering delivers measurable business and operational impact in real-world scenarios:
A financial company used automated release processes and gradual updates, which cut deployment failures by 45%, changed releases from monthly to weekly, improved system uptime to 99.9%, and made audits 30% faster.
Final Thoughts
Release engineering is essential for delivering software safely, reliably, and efficiently. Using automation, clear processes, and smart release plans helps companies deliver software faster, make fewer mistakes, and work better as a team. Whether small or large, following structured release practices improves software quality, keeps customers happy, and helps the company adapt to fast-changing technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is release engineering only for large organizations?
Answer: No. Startups and small teams also benefit from structured and automated release processes.
Q2. How is release engineering different from deployment?
Answer: Deployment is one step in the release lifecycle, while release engineering covers the entire process.
Q3. Does release engineering require DevOps?
Answer: Release engineering complements DevOps but can exist independently.
Q4. How does release engineering support continuous delivery?
Answer: Release engineering enables continuous delivery by automating build, test, and deployment processes, ensuring software is always in a releasable state with minimal risk.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Release Engineering” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
