Updated March 28, 2023
Introduction to Queue in C
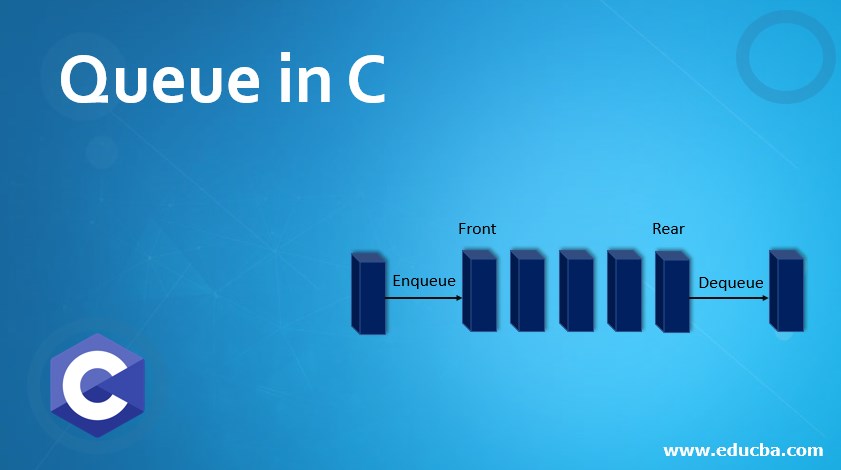
Queue in C is a data structure that is not like stack and one can relate the behavior of queue in real -life. Unlike stack which is opened from one end and closed at the other end which means one can enter the elements from one end only. Therefore, to overcome the scenario where we need to insert elements from both ends is needed and this flexibility is being provided by the data structure Queue in C. These data structures play a very pivotal role in our day to day life in a way that efficiency and implementation become more flexible and versatile.
Syntax:
Basically, there is no specific syntax for Queue its just that we have certain operations to perform on queue as it works on FIFO order [First In First Out]. This data structure like the stack is used for the removal of items in the FIFO order itself.
Common Syntax will include all these operations to be performed with data structures which are as follows:
- Enqueue()
- Dequeue()
- Front()
- Rear()
Struct Queue {
// will create a queue
// allocation of memory to the queue
// empty queue or full queue
// Perform function with the operations such as enqueue, dequeue, Front and Rear ()
}How does queue work in C?
As mentioned above Queue already has these operations to be performed but on the other hand, it has some more operations to be performed simultaneously that will imply whether or not we need the desired element to be inserted or deleted and whether the queue has the capacity to insert or delete which means whether it is overflow or underflow situation.
One classic example of the queue which we can relate to the real-world scenario is people standing in the queue of a ticket counter. One person comes and joins the queue whereas other people who is collecting the ticket once collects gets out of the queue. Exactly this way a queue functions in FIFO order. The person who is coming first will be served first.
A Queue can be implemented in many ways using arrays, linked lists, Pointers and Structures. But for some simplicity’s sake, we should implement it using the single-dimensional or one-dimensional array.
Before going into detail, we should have prior knowledge of when to use the current data structure and Why to use it?
The queue never gets used if we are in a need of quick and urgent processing of a set of input and output. Processing using queue takes place using FIFO and especially while using Breadth-First Search. This provides and lets queue to become a versatile and flexible data structure.
Scenarios can be as follows:
- When multiple consumers make use of or in need of a single resource makes use of queue as a data structure. Example: Disk Scheduling, CPU Scheduling.
- When data sent and received is not at the same pace or rate while transfer from one pipe to another or node to another or files and Buffers.
Now, therefore, we land in a situation of using queue and now we will go through the proper working:
For implementing queue, we need to get two pointers which will continuously keep a track on both the ends and will get incremented when we need to enqueue an element from the front and when we need to dequeue an item from the rear end again depends on the requirement.
Even if we continuously keep on moving a pointer and let it increment then also a problem will come where the front pointer may reach to the end or cross the rear end. Therefore, to avoid this problem it is needed to move both the pointer in a circular manner.
Queue Member Types in C
There are three types namely:
- Priority Queue
- Circular Queue
- Deque
1. Priority Queue
As its name suggests a priority queue is a kind of queue that will be assigned a priority to the elements needed to be inserted or deleted.
Assignment of rules are as follows:
- An element inserted with higher priority will be processed first and then with the lower priority.
- Two elements being added simultaneously will get the priority in an order in which they are added simultaneously.
Further this priority queue can be divided into two types depending on the scenario:
- Ascending Priority Queue
- Descending Priority Queue
All time-sharing systems make use of the Ascending or descending priority queue depending upon the scenarios.
2. Circular Queue
Circular Queue Is a kind of queue which Is used to select the item from the queue which is the very first index or a location inserted within the queue till the last location when the queue is full. Any new element will be inserted if and only if the last location is empty.
Rules following that are:
- When the front is pointing to the first element.
- If front=rear and then the queue becomes empty.
- Whenever a new element is inserted an increment is made to the rear end saying one rear[index] gets incremented by rear+1.
3. Deque
Deque stands for the double-ended queue which will be let the elements get entered in both ways that is the front end and rear end both.
Further, these are of two types:
- Input Restricted Dequeues.
- Output Restricted Dequeues.
Queue Functions in C
Basic Functions involves:
1. Enqueue(): This function will help in the insertion of elements from either of the ends whether front end or rear end.
2. Dequeue(): This function will help in the deletion of elements from either of the ends whether front end or rear end.
3. Peek(): It will help in getting the element in front of the queue without eliminating it from the pipe.
4. isFull(): This function will ensure that the queue is full, and no more element can be inserted as it is in overflowing condition.
5. isEmpty(): This function will help to determine whether the queue is empty I.e. in underflow condition.
Conclusion
Queue in C is a versatile and data structure in C which overcomes the problems of insertion and deletion of elements whether from the front end or rear end. Moreover, it has the capability of determining the operations in a way that they can be enqueued and dequeued in any way. Unlike stack, it is being used in First in First Out [FIFO] order.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Queue in C. Here we discuss How queue works in C along with the three types of members and basic functions. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


