What is Quantitative Finance?
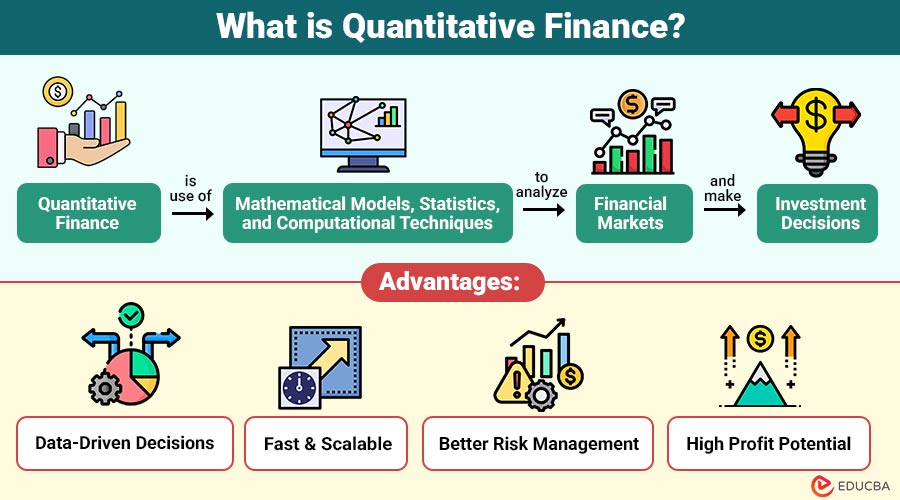
Quantitative finance is use of mathematical models, statistics, and computational techniques to analyze financial markets and make investment decisions.
It focuses on building numerical models to:
- Price derivatives
- Measure and manage financial risk
- Predict asset returns
- Optimize portfolios
- Build automated and algorithmic trading systems
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why does Quantitative Finance Matter?
- Core Concepts
- Tools and Technologies
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Skills Required
- Real-World Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Quantitative finance combines mathematics, statistics, and programming to analyze markets, price assets, and manage risk effectively.
- Algorithmic trading and quantitative models enable faster, data-driven decision-making, reducing human bias and significantly improving investment accuracy.
- Mastering quantitative finance skills unlocks high-demand careers in trading, risk management, portfolio optimization, and financial technology sectors.
- Tools, frameworks, and financial databases empower analysts to build predictive models, forecast markets, and evaluate portfolios efficiently.
Why does Quantitative Finance Matter?
Financial markets generate massive amounts of data every second. Human decision-making alone cannot keep up. Quantitative models help:
1. Process Large Datasets Quickly
Quantitative finance uses advanced algorithms and computational models to analyze enormous financial datasets efficiently and accurately.
2. Reduce Biases from Human Emotions
Automated models remove human emotional influence, ensuring investment decisions are objective, consistent, and data-driven.
3. Improve Accuracy in Pricing and Forecasting
Mathematical models provide precise asset pricing and reliable market forecasts, reducing errors in investment strategies.
4. Automate Trading at Millisecond Speeds
High-frequency trading algorithms execute trades instantly, capturing small opportunities and minimizing market reaction delays effectively.
5. Evaluate Portfolio Risk Under Different Scenarios
Quantitative tools simulate multiple market scenarios, assess potential losses, and optimize risk management strategies comprehensively.
Core Concepts in Quantitative Finance
Here are the core concepts used in quantitative finance:
1. Stochastic Processes
Financial markets behave unpredictably. Stochastic models help represent random price movements.
Common tools include:
- Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) for stock prices
- Poisson processes for rare events
- Mean-reversion models for interest rates
2. Time Series Analysis
Used to predict future asset prices using historical data.
Techniques include:
- ARIMA
- GARCH (volatility modeling)
- Exponential smoothing
- Kalman filters
3. Derivatives Pricing
Quantitative finance heavily focuses on pricing:
- Options
- Futures
- Swaps
- Exotic derivatives
Popular models:
- Black–Scholes Model
- Binomial Tree Model
- Monte Carlo Simulation
4. Portfolio Optimization
Allocating capital to maximize return and minimize risk.
Key frameworks:
- Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT)
- Markowitz Efficient Frontier
- CAPM model
- Multi-factor models
5. Risk Management
Quantitative finance helps firms calculate:
- Value at Risk (VaR)
- Conditional VaR
- Credit risk (PD, LGD)
- Market risk
- Liquidity risk
6. Algorithmic & High-Frequency Trading
Quants build automated systems that:
- Analyze real-time market data
- Detect patterns
- Execute trades within milliseconds
Tools and Technologies Used in Quantitative Finance
Quantitative finance uses a mix of programming, data analysis, and mathematical modeling tools.
1. Programming Languages
- Python – Widely used for building models, prototyping algorithms, data analysis, and financial simulations efficiently.
- R – Excellent for advanced statistical analysis, visualizations, and quantitative research in finance applications.
- C++ – Preferred for high-frequency trading and low-latency systems due to speed and computational efficiency.
- MATLAB – Powerful for quantitative modeling, numerical computation, and financial engineering calculations in research environments.
2. Libraries & Frameworks
- NumPy & Pandas – Essential Python libraries for data manipulation, processing, and numerical operations efficiently in finance.
- SciPy – Provides advanced mathematical and scientific functions used in modeling financial and statistical problems.
- Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch – Machine learning libraries to develop predictive models, algorithmic trading, and risk analysis tools.
- QuantLib – Industry-standard open-source library for pricing derivatives, managing risk, and modeling complex financial instruments.
3. Financial Databases
- Bloomberg Terminal – A Professional tool providing real-time market data, analytics, news, and financial information globally.
- Thomson Reuters Eikon – Financial database offering pricing, news, analytics, and research tools for investment professionals.
- Quandl – Data platform providing structured historical and real-time financial, economic, and alternative datasets.
- Yahoo Finance – A free platform offering stock quotes, historical data, financial news, and investment research tools online.
Advantages of Quantitative Finance
Here are some key advantages of using quantitative approaches in finance:
1. Data-Driven Decisions
Quantitative models eliminate human biases and emotions, enabling consistent, objective, and highly accurate financial decision-making processes.
2. Fast and Scalable
Computers process millions of financial data points instantly, enabling large-scale analysis and rapid decision-making.
3. Better Risk Management
Advanced quantitative models evaluate market, credit, and portfolio risks under varying conditions, enhancing financial stability.
4. High Profit Potential
Algorithmic trading and arbitrage strategies leverage market inefficiencies to generate significant profits with minimal manual intervention.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Finance
Despite its benefits, quantitative finance also comes with certain disadvantages:
1. Model Risk
Incorrect assumptions in quantitative models can lead to misleading results, resulting in significant financial losses and poor decisions.
2. Overfitting
Predictive accuracy can be greatly decreased by models that perform well on historical data but fail in actual market situations.
3. High Complexity
Quantitative finance requires advanced skills in mathematics, statistics, programming, and modeling, making it challenging for beginners.
4. Black Swan Events
Rare extreme events, such as financial crises or market shocks, can render models ineffective unexpectedly.
Skills Required for Career in Quantitative Finance
A successful career in quantitative finance demands a mix of technical, programming, and financial expertise.
1. Technical Skills
- Probability and Statistics – Understanding probability theory and statistics is essential for modeling financial data accurately.
- Calculus and Linear Algebra – Required for modeling complex financial systems effectively.
- Stochastic Calculus – Crucial for precisely modeling random processes in financial markets.
- Numerical Methods – Numerical methods allow solving complex mathematical problems that cannot be solved analytically.
2. Programming Skills
- Python – Python is widely used for data analysis, modeling, and algorithmic trading in quantitative finance.
- R – R is popular for statistical analysis, data visualization, and research in finance applications.
- C++ – C++ provides speed and efficiency, ideal for high-frequency trading and performance-critical systems.
- MATLAB – MATLAB is used for financial modeling, simulations, and quantitative research in professional environments.
3. Financial Knowledge
- Derivatives – Understanding options, futures, and swaps is essential to pricing them successfully and trading them.
- Trading Strategies – Knowledge of trading strategies enables the effective design of profitable, risk-managed market approaches.
- Portfolio Theory – Portfolio theory helps optimize asset allocation and balance risk-return trade-offs in investments.
- Market Microstructure – Understanding it is critical for accurately analyzing liquidity, pricing, and trading behavior.
Real-World Examples
Quantitative finance is widely applied in real markets to improve decision-making, trading, and risk management.
1. Options Trading Desk Using Black–Scholes
A trading desk uses the Black–Scholes model to price call and put options and dynamically hedge them using delta hedging.
2. Hedge Fund Using Algorithmic Trading
A quant hedge fund builds algorithms that detect small price inefficiencies and execute trades at millisecond speed.
3. Banks Measuring Value at Risk
Banks use VaR to estimate how much they might lose under market volatility, helping them meet regulatory requirements.
Final Thoughts
Quantitative finance revolutionizes global markets by integrating mathematics, data analysis, and computational techniques. It empowers institutions to make informed decisions, automate trading, optimize portfolios, and manage risk efficiently. As data grows and markets evolve, mastering quantitative finance equips students, analysts, and professionals with high-impact skills, unlocking rewarding, in-demand, and lucrative careers in finance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is quantitative finance hard?
Answer: Yes, it requires strong skills in math, statistics, and programming, but it becomes easier with consistent practice.
Q2. Do I need to know coding?
Answer: Yes. Python, C++, and R are widely used in quant finance roles.
Q3. Is quantitative finance only for banks?
Answer: No. Hedge funds, fintech companies, insurers, and investment firms use quant models.
Q4. Can AI replace quantitative finance?
Answer: AI enhances models but cannot replace the need for financial theory, risk expertise, and human judgment.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Quantitative Finance” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.