Updated June 20, 2023

Introduction to Python Ternary Operator
Python, one of the most user-friendly programming languages with very few syntactic hassles, is becoming one of the fastest-growing programming languages worldwide. A strong community of Python users and developers contributes to the betterment and growth of the language. Since its inception in 1991, Python has always been very dynamic in nature, and it is still evolving with time, with new features being added and old features getting depreciated.
The Ternary Operator came as an enhancement in the Python 2.5 version. It helps us to write conditional statements in Python in a single line. It can be considered a single-line representation of an if-else code block. Let us look into the Ternary Operator’s syntax and application in more detail.
Syntax:
var = true_val if condition else false_valThere are three operands in a Ternary Operator
- condition: It is a Boolean expression that evaluates to either true or false.
- true_val: It is the value to be assigned if the expression is evaluated to be true.
- false_val: It is the value to be assigned if the expression is evaluated as false.
The following figure will help to show the point:
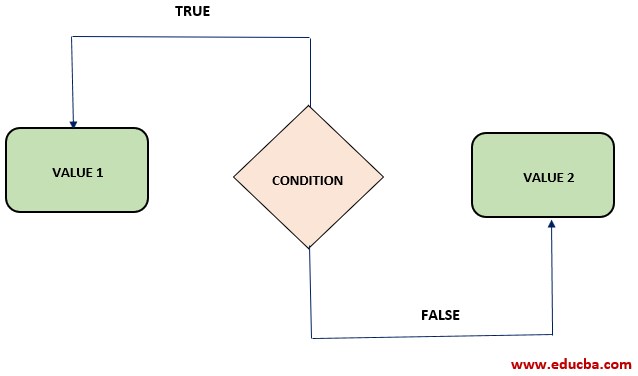
Examples of Python Ternary Operator
Let us see a simple program of determining a number to be odd or even. We would first write using a normal if-else statement, and then we would use Ternary Operator to appreciate its usage best.
1. Using If-Else Block of Code
Code:
num=int(input("Enter number to check :"))
if(num%2==0):
msg=str(num)+"is an even number"
else:
msg=str(num)+"is an odd number"
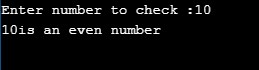
print(msg)Output:
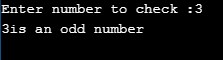
Below is for the odd number,
2. Using Ternary Operator
Code:
num=int(input("Enter number to check :"))
msg=str(num)+"is an even number" if num%2==0 else str(num)+"is an odd number"
print(msg)Output:

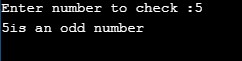
Below is for the odd number,
The above examples demonstrate that achieving the same functionality is possible in both if-else blocks and by using a Ternary Operator. Using the if-else block takes 6 lines of code, while Ternary Operator takes only 3 lines of code. It takes half the time and effort to achieve the same functionality. Thus for complex programs, the usage of a Ternary Operator should be a must.
Usages of Ternary Operator
Here are the other usages of Python Ternary Operators given below:
1. Using Python Tuples
Code:
a=3
print(("Odd","Even") [a%2==0])Output:
![]()
Below is the other example to check it,
Code:
a=24
print(("Odd","Even") [a%2==0])Output:
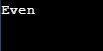
In the above example, we are using Ternary Operator using Python Tuples. The condition for determining odd or even is provided within square brackets, i.e. [a%2==0], and the values based on the condition are to be passed within the tuple; the first value, i.e., “Odd” in this case, is for the negative scenario and the second value, i.e., “Even” in this case for the positive scenario.
2. Using Python Dictionary
Code:
a=40
print({True:"Even", False: "Odd"} [a%2==0])Output:

Below is the other example to check it,
Code:
a=15
print({True:"Even", False: "Odd"} [a%2==0])Output:

In the above example, we are using Ternary Operator using Python Dictionary. The condition for determining odd or even is provided within square brackets, i.e. [a%2==0], and the values based on the condition are to be passed within a Dictionary. The keys would be True and False, respectively, and the values for the respective keys are to mention.
Here when the condition a%2==0 is true, then a is an Even number, so the value for the key “True” is “Even,” and conversely, the value for the key “False” is “Odd.”
3. Using Python Lambda Function
Code:
a=3
print((lambda:"Odd", lambda: "Even") [a%2==0]())Output:

Below is the other example to check it,
Code:
a=20
print((lambda:"Odd", lambda: "Even") [a%2==0]())Output:
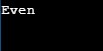
In the above example, we are using Ternary Operator using the Python lambda function. The condition for determining odd or even, [a%2==0], appears within square brackets. Pass the values based on the condition as illustrated above. The first value is for the negative scenario, and the second value is for the positive scenario.
When a%2==0 evaluates to true, assign ‘Even’ as the second value and ‘Odd’ as the first value.
Limitation of Ternary Operators
Here are some of the limitations of the ternary operator explained below:
- Ternary Operators can replace if-else statements, but a single if-else statement can only use them.
- Multiple if-else statements typically do not utilize Ternary Operators.
- You can use a Ternary Operator as a nested if-else statement for a condition with three possible values.
Ternary Operator as Nested If-Else
Code:
num1, num2=5,3
print("Both num1 and num2 are equal" if num1==num2 else "num1 is greater than num2" if num1>num2 else "num2 is greater than num1")Output:
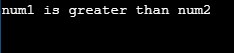
This is a simple example of comparing two numbers to determine which is greater than the other. It might look like an example with only two values as output. “num1 greater than num2” and “num2 greater than num1”. But for better programming practice, we must consider the scenario when both the numbers would be equal; thus, there is a total of 3 scenarios. We must use Ternary Operator as a nested if-else to accommodate all three scenarios.
Conclusion
In the following article, we have discussed Ternary Operator, one of Python’s most essential tools, which has reduced code size, replacing conventional if-else statements, thus resulting in better code readability. The different usages of Ternary operators and their syntax and examples have also been discussed in detail.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python Ternary Operator. Here we discuss the syntax and example of Python Ternary Operator, its usage, and limitations. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


