
Introduction to Python NameError
The following article provides an outline for Python NameError. NameError is a kind of error in Python that occurs when executing a function, variable, library, or string without quotes that have been typed in the code without any previous Declaration. When the interpreter, upon execution, cannot identify the global or local name throws a NameError. You can view the NameError in the last line of the error message to understand which function, variable, package, or string has not been declared.
Syntax of Python NameError
When writing a function with a name, we often miss calling the exact function name in the future, which will lead to a NameError.
Example:
Code:
## Functions which return values
def calc_sum(x,y):
op = x + y
return(op)
ss = calc_sum(5,10)
print(ss)
Output:
![]()
For the same function, let’s see the NameError.
Code:
## Functions which return values
def calc_sum(x,y):
op = x + y
return(op)
ss = calc_su(5,10)
print(ss)
Output:
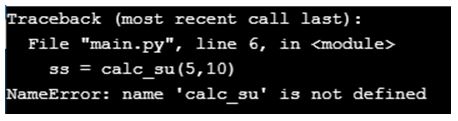
It was initially built to conduct some operation between two numbers and named calc_sum, but when we called it, we used the name calc_su, therefore, it had not previously been defined, and it would throw us a NameError.
How NameError Works?
When working with user-defined variables in coding, the NameError often occurs due to the difficulty in identifying the local/global values for the interpreter.
Example:
Code:
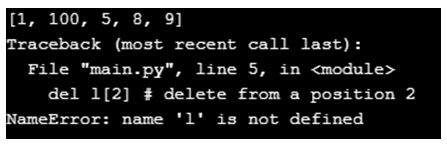
l1 = [1,2,5,8,9]
l2 = [1,5.6,"hello"] # mix of data types
l1[1] = 100 # muting the 1st position of l1 to 100
print(l1)
del l1[2] # delete from a position 2
print(l1)Output:

Code:
l1 = [1,2,5,8,9]
l2 = [1,5.6,"hello"] # mix of data types
l1[1] = 100 # muting the 1st position of l1 to 100
print(l1)
del l[2] # delete from a position 2Here we are performing a delete operation on a variable l that is not defined.
Only l1 & l2 have been defined, and the interpreter can only identify l1 & l2 variables. So if we operate on l, which is not defined, it will throw us a NameError.
Output:
There are cases of NameError that also occurs during operations done with a Python library or a package. Where if we miss importing the package or library or if we haven’t defined the name of that package or library and upon executing an operation using that library, we will get a NameError
Example:
Code:
l10 = [1,2,6,7,4,5,7,8,6,3]
l11 = [1,2,6,7,4,5,7,8,6,3,1000]
## numpy operations
np.mean(l11)
np.median(l11)
np.std(l11)Output:
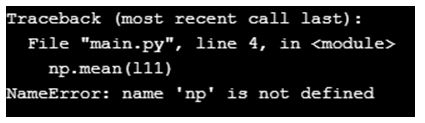
We haven’t imported the numpy library as np, and upon executing the operation, we will see the NameError.
Code:
import numpy as np
l10 = [1,2,6,7,4,5,7,8,6,3]
l11 = [1,2,6,7,4,5,7,8,6,3,1000]
## numpy operations
print(np.mean(l11))
print(np.median(l11))
print(np.std(l11))Output:

Another kind of NameError occurs when we fail to insert a string value inside the quotes, and the interpreter identifies it as a variable and throws a NameError.
Example:
Code:
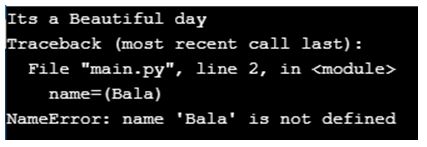
print('Its a Beautiful day')
name=('Bala')
print(name,'Its a Beautiful day')Output:

Code:
Error,
print('Its a Beautiful day')
name=(Bala)
print(name,'Its a Beautiful day')Here we fail to put the string inside the quotes, so the console will throw us the NameError.
Output:
Avoiding NameErrors in Python
The NameError can be avoided easily by using the Python Error handling technique or exception handling, which denotes the user about the NameError that is occurring in the block of code without actually throwing an error.
The most common errors that occur in Python are the SyntaxError & NameError. When we write our code, and if the programming language does not accept it, then the SyntaxError arises.
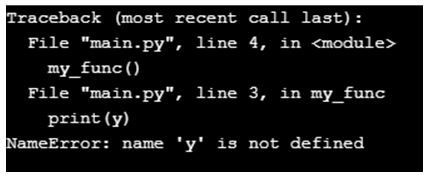
Code:
def my_func():
x="Name Error Exception"
print(y)
my_func()
Output:
Even if we write code without any SyntaxError, the program can result in runtime errors. These are called Exceptions. There are numerous built-in exceptions available in Python, and One such exception is NameError Exception.
In Python, the NameError exception comes into the picture when we try to use or refer to a name that is not defined locally or globally.
Example:
For NameError Exception handling.
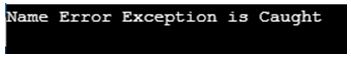
Code:
try:
x="Name Error Exception"
print(y)
except NameError:
print("Name Error Exception is Caught")
Output:
The try block allows us to check and see whether our code will throw an error or not. We can use this block to trail our code to see if there may be a potential for errors to occur.
The Except Block will allow us to write the part where we want to handle the error. We can use this block to denote the use of want went wrong without the console throwing errors.
We can also use a Finally block along with try and except to continuously run the code without termination by indicating only the exception message.
Example:
Finally, block.
Code:
name='Smith'
try:
print("Hello" " "+ name)
except NameError:
print("Name is not denoted")
finally:
print("Have a nice day")
Output:

Below we have deleted the name denoted; we can see the exception message thrown.
Code:
name='Smith'
try:
print("Hello" " "+ name)
except NameError:
print("Name is not denoted")
finally:
print("Have a nice day")
del name
try:
print("Hello " + name)
except NameError:
print("Name is not denoted")
Output:

The code can be run without stopping since the assigned name is removed by including a final block. Furthermore, even if the try block throws an exception, the final block will be executed. We can use this technique to overcome the NameError.
Conclusion
The main takeaway to remember in Python NameError is the failure of the interpreter to identify the name or text we have used in our code. We have seen in detail about the NameError that occurs in the Python programming language and the techniques to overcome the NameError.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python NameError” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


