Updated April 10, 2023

Introduction to Python Input String
In Python, to read the string or sentence from the user through an input device keyboard and return it to the output screen or console, we use the input() function. There are also some built-in methods or functions to read the string on the console and return it in other languages. In Python, as we know that we don’t specify any data types while declaring any variable, and also there are two different functions to display and handle input data obtained from the user, they are input() and print(). In Python, the print() function is used to display the input obtained or the value it wants to display, which is specified, whereas to accept the input line from the user, there are two functions such as input() and raw_input().
Working of Python Input String
Python has two functions for taking in the input from the user or reads the data that is entered through the console, and the result of this can be a string, list, tuple or int, etc., which is stored into a variable. Two input functions of Python are:
1. raw_input()
This Python method reads the input line or string and can read commands from users or data entered using the console. The return value of this method will be only of the string data type. In Python, this method is used only when the user wants to read the data by entering through the console, and the return value is a string.
Syntax:
raw_input([prompt])
Parameter:prompt: This is optional; it can be any string or command which you want to display on the output console.
Example:
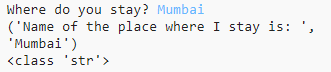
place = raw_input("Where do you stay?")
print ("Name of the place where I stay is: ", place)
print(type(place))
Output:
2. input()
This is also a Python method for reading the input string from the user through an input device like a keyboard and display the return value of this function on the output screen or console. The return value of this method can be string or number or list or tuple, etc. In Python, we do not declare any data type while initializing or declaring the variable. As in the raw_input() function, it can return an only a string value, but in this input() function, we can get the return value of any data type; Python decides as to what data type to be returned based on the variable value. If you have asked the user to enter the age, it will automatically take an int as the data type for the variable age.
Syntax:
input([prompt])
Parameter:prompt: This is optional again; it can be any string or commands that the user wants to display. In this function, whatever the user enters, the input() function converts it into a string, and this function stops the execution of the further program until the user enters the value that is asked through this function.
Example:
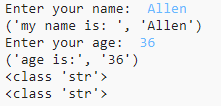
name = input("Enter your name: ")
print("my name is: ", name)
age = input("Enter your age: ")
print("age is:", age)
print(type(name))
print(type(age))
Output:
From the above program, as the first variable “name” has input() function that asks the user to enter the name input() function always converts the value taken by into string as “name” variable is already of string type there is no such problem, but in the second variable it’s “age” which is of data type int, still the input() function converts it into a string. Sometimes you can be more perfect by declaring input value as integer type explicitly.
Examples
Lets us discuss the Examples of Python Input String.
Example #1
Let us take to display the multiplication of two numbers.
Code:
n1 = int( input("Enter the first number for multiplication: "))
n2 = int( input("Enter the second number for multiplication: "))
product = n1 * n2
print( "Multiplication of two numbers is: ", product)
Output:

Example #2
The input() function can also accept the float value similarly to integer value by explicitly declaring float as we did in the above program as int.
Code:
fn1 = float(input("Enter float number: "))
print("The float number is: ", fn1)
Output:
![]()
Example #3
This input() function can also be used to read the list as input from users. We could accept int and float in the same way we can accept list and array also through this function().
Code:
lst = input ("Enter the list of numbers you want to display: ")
out_list = lst.split()
print(" The list you entered is: ", lst)
Output:
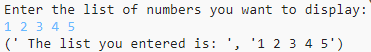
Example #4
From the above example, we are using the split() function to split the string by space and append those numbers to the list.
Lastly, you can use the input() function to even read multiple values from users of different data types in one sentence. This can be shown in the below example:
Let us consider we want to ask the profile of the user as below code:
Code:
name, height, weight, age = input(" Enter the profile data as your name, height, weight, age\n using space to differentiate the values: ") .split()
print(" The profile data of the user is as follows: ", name, height, weight, age)
Output:

Conclusion
In Python also you can ask the user to enter the values or string or list of tuples, etc., through an input device and display it on the output screen or console. As in C language, we do this by using the scanf() function similarly in Python, it can be done using raw_input and input(), and to display these values obtained by these functions, we use the print() function. As we saw in this article raw_input() function is very rarely used as it can return only the values of the string data type. But the input() function is mostly used as it can accept the input of any data type and if we want to be surer, then we can even explicitly convert the value of the variable to the respective data type as input() function always converts any data type of the variable to string.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python Input String” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

