Introduction to Python Event Loop
- Python Event Loop is the centre of each asyncio application. Occasion circles, run offbeat assignments and callbacks, perform arrange IO activities, and run subprocesses.
- Python Event Loop is useful to deal with all the occasions in a computational code. It acts round the route during the entire program’s execution and monitors the approaching and execution of occasions. The Asyncio module permits a solitary occasion circle for every procedure.
- Asyncio module gives base classes that you can subclass to execute your system conventions. Those classes are utilized related to transports; the convention parses approaching information and requests the composition of active information, while the vehicle is answerable for the real I/O and buffering.
Syntax:
Get_event_loop(loop)
Set_event_loop(loop)How does the Event loop work in Python?
Now we see various examples of how to implement different functions using get_event_loop. There are some important functions that we need to know while implementing get_event_loop. The get_event_loop sets up a callback function or time delay function, which helps it to schedule the functions in a specific manner. The callback function returns back to the get_event_loop as soon as it is called at the earliest, and it helps in rescheduling the time delays as it shows the current time in the get_event_loop clock. Thus, the asyncio functions help the get_event_loop function in other subclasses of the main class by setting it and finally implementing it and returning to implement another get_event_loop. Hence, the get_event_loop schedules itself around a loop. Stop function, which helps it run the code or command whenever it wants to run and finally implement the user’s command.
Examples to Implement Python Event Loop
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Implementing a simple operation using get_event_loop.
Code:
import time
import asyncio
def hi_everyone(loop):
print('Hi Everyone')
loop.stop()
loop.call_soon(hi_everyone, loop)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_forever()
loop.close()
Output:
![]()
Explanation: In the above example, we first import the asyncio module in python, which is a built-in module. Here, we use the get_event_loop to give the occasion loop to the present setting. We initially define the statement that we have to print and assign it to the loop. Later, we use the get_event_loop to callback this defined context and finally produce the output.
Example #2
Using get_event_loop to implement the future class in Python
Code:
import time
import ayncio
def async Mygoal(future_class):
await asyncio.sleep(3)
future.set_result('Future Class Implemented')
future = asyncio.Future()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
asyncio.result_future(Mygoal(future_class))
try:
loop.run_until_complete(future_class)
print(future.get_result())
finally:
loop.close()
Output:
![]()
Explanation: In the above program, we first import the asyncio module. Then we define the future class and implement the result by the set_result function. Then we use the try and finally loops along with the get_event_loop to implement the future class in Python.
Example #3
Using get_event_loop, we implement coroutines.
Code:
import time
import asyncio
def async Mygoal():
print("Coroutines Implemented")
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
try:
loop.run_until_complete(Mygoal())
finally:
loop.close()
Output:
![]()
Explanation: Here, we first understand what coroutine means. The idea of coroutines in Asyncio is like the idea of a standard Thread object under the stringing module. This is the speculation of the subroutine idea. A coroutine can be suspended during the execution, so it sits tight for the outside handling and comes back from where it had halted when the outer preparation was finished. We first initialize the async def() function here to print the coroutines and finally add the get_event_loop to implement these coroutines.
Example #4
Using get_event_loop to implement different tasks
Code:
import time
import asyncio
def async Task_ex(x):
time.sleep(4)
print("Task {}".format(x))
def async Produce_task():
for n in range(10):
asyncio.set_future(Task_ex(n))
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_forever(Produce_task())
loop.close()
Output:
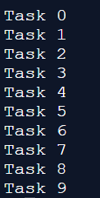
Explanation: In the above program, the Asyncio module’s subclass is answerable for the execution of coroutines inside an event loop in an equal way. Here, we import time and asyncio modules and later assign time. Sleep function to implement all the tasks from 1 to 10. Hence, the program obeys the command, and the python module considers all the tasks or processes in the range “i” and print all the tasks from 0 to 9 and then return to the callback function. These tasks are processed and implemented by the get_event_loop.
Conclusion
Application engineers ought to regularly utilize the elevated level asyncio capacities, such as asyncio.run(), and should seldom need to reference the loop article or call its techniques. This area is proposed generally for creators of lower-level code, libraries, and systems, who need better power over the occasion loop conduct.
On the off chance that there is no recent development loop set in the present OS string, the OS string is primary, and set_event_loop() has not yet been called, asyncio will make another occasion circle and set it as the present one.
Since this capacity has rather complex conduct (particularly when custom occasion circle strategies are being used), utilizing the get_running_loop(,) work is liked to get_event_loop() in coroutines and callbacks. Consider additionally utilizing the asyncio.run() work as opposed to utilizing lower level capacities to physically make and close an event loop.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python Event Loop” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


