Updated April 13, 2023

Definition of Python Constants
Python Constants are basically those variables whose values do not change during the program implementation.
- Python is basically a programming language that makes complex programs easier to understand and implement also; it is used in commercial applications.
- These constants are basically assigned to a document.
- The document consists of variables and functions, which are therefore recorded in the main file.
- The constants are thus written inside this main file in capital letters and underscores by isolating the words.
Assigning and Declaring Python Constants
- The first and foremost thing to remember while declaring Python Constants is that the constant values should always be declared in capital letters/uppercase.
- The values declared should not be abbreviations of the names, and it has to be declared completely.
Example:
- The first step is to create a new python file called constant.py and enter the values. We should always remember that the constant values should be fixed and not changeable. Also, as seen in the snapshot, both the constants have been named in capital letters/uppercase.
PI = 3.14
GRAVITY = 9.8- The next step is to create another file named mainzz.py and add the code, which means to say that we will import the constant values to the main file and later print the constants.
import constant
print(constant.PI)
print (constant. GRAVITY)- Finally, when we run the code, it will show us the values of these constants, which are non-interchangeable.

Python Constants and Literals with Examples
Literals are also constant values in Python, which are fixed. Hence, python mainly supports 2 types of literals which are,
- Numeric literals
- String Literals
1. Numeric Literals
These are numeric values that remain constant. There are 3 types of Numeric Literals which are,
- Integer
- Float
- Complex
When we speak of these 3 classes of built-in literals, we assume that we can use any numerical value, which is not the case. We need to select fixed values for each literal.
Example:
lit_1 = 0b1100
lit_2 = 202
lit_3 = 0o320
lit_4 = 0x13c
fllit_1 = 12.4
fllit_2 = 13.5e2
a = 4.16j
print(lit_1,lit_2,lit_3,lit_4)
print(fllit_1,fllit_2)
print(a,a.imag,a.real)
Output:

- Here we create a new file called lit.py to represent the literals. So, lit_1 represents binary literals, lit_2 represents decimal literals, lit_3 represents octal literals, and lit_4 represents hexadecimal literals.
- Once we print these values, we get the output as shown in the above code’s first line.
- Similarly, we create values to the floating-point literals, which are decimal values, and when we represent 13.5e2, it means 13.5*10^2, and thus we get the desired output as shown in line 2 of the above code.
- Finally, we add a complex literal. When the complex literal is assigned to a variable a and printed out, the operation which Python performs is a.real and a.imaginary, and it gives both the values as shown in the above code.
2. String Literals
String literals are a series of keywords that are enclosed by a pair of quotations.
- Concatenating the string literals – Concatenation is a combination of more than one statement together. We use concatenation with escape characters.
Example:
message = "Hello World"
print((message+"\n")*10)
Output:

Here, \n is used to produce the message is a new line.
Multiline Strings
The string literals which can be added in multiple lines. The representation of a multiline string literal should always be enclosed in three double quotations (“).
Example:
print("""Python helps me learn. Python helps me learn.
Python helps me learn. Python helps me learn.
""")
Output:

Boolean Literals
These are the literals having only two values that are “True“ and “False“.
Example:
bool_1 = (1 == True)
bool_2 = (1 == False)
bool_3 = True + 8
bool_4 = False + 7
print("value is:",bool_1)
print("value is:",bool_2)
print("value is:",bool_3)
print("value is:",bool_4)
Output:

In Boolean constants/literals, the numeral 1 always represents True, and the numeral 0 always represents False. Hence, in the above program, since 1=true, it adds up 8 and 1 to produce the output as 9, and since the numeral 1 is not equal to false, the program does not recognize and add up 7 with 1, and hence it remains constant.
Other Literals
There are various other types of literals such as Lists and tuple.
- Lists are basically adding values in square parenthesis and assigning them to a variable. These lists can be strings or integers, and they can be fixed; that is, they are constant.
Example:
veggies = ["tomato","potato","onion"]
nums = [3,4,5,6]
print(veggies)
print(nums)
Output:
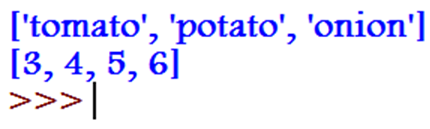
Conclusion
Thus, we discussed various python constants and the built-in python constants, which will help us design and programming on different games, websites, software development, and many more. It also helps us enhance our programming skills. These Python basics help us get a good grip of the language used to perform various mathematical operations and implement these Python constants and variables in the commands. The syntax is very much different and easier compared to other programming languages.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Python Constants” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


