Updated July 4, 2023
Introduction to Print Array in Java
An Array is a data structure where we can store similar types of elements. For example, an array of integers stores multiple integers, an array of strings stores multiple strings, etc. So if you have an Array with a large amount of data, you might need to print those to view them at your convenience with Print Array in Java. We can follow several ways to print an array in java. You can follow any of those methods to print an array. Here, I will discuss each method of printing an array in Java; I have given examples of code for better understanding and hands-on purposes. I have also added comments inside the codes for better readability.
Moreover, I have given screenshots of the output of each code. Go through the codes line by line and understand those. Then write and run those codes on yourself in java compilers and match those outputs with the given one.
Techniques to Print Array in Java
Below are the Techniques to Print Array in Java:
Method 1: Using for loop
As we know, a loop executes a set of statements repeatedly until a particular condition is fulfilled. We will use this functionality of for loop to print the array here.
Example: 1
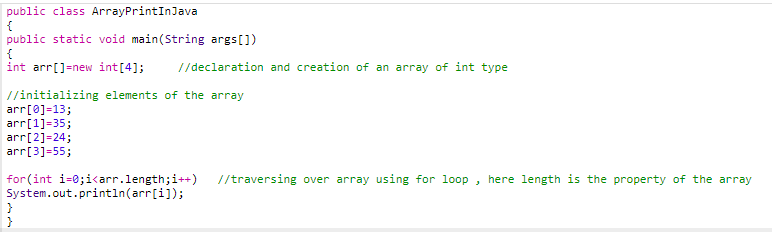
Here we will create an array of four elements and will use for loop to fetch the values from the array and print them.
Code:
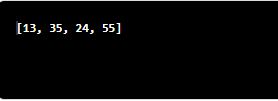
Output:

The above example is for the one-dimensional array.
Example: 2
For a two-dimensional array, you will have rows and columns that must be printed out. So you will need to run two for loops in a nested fashion. One for rows and inside it, the other for columns.
Code:
for ( k = 0; k< rows; k++)
for ( m = 0; m< columns; m++)
For print: System.out.print(arr[k][m] + " " )Try it yourself and see the magic.
Method 2: Using the for-each loop
A for-each loop is also used to traverse over an array. As output, it will return elements individually in the defined variable.
Example
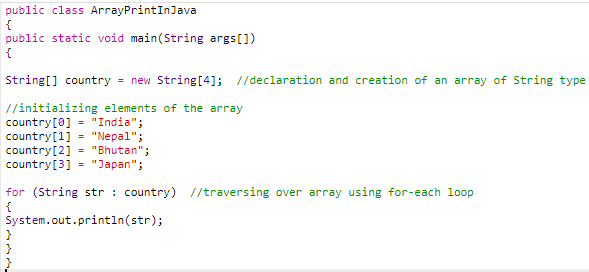
We will create an array of four strings and iterate and print those using a for-each loop.
Code:
Output:

So far, we have used for and for-each loops to print array. But from the next methods onwards, we will use classes related to the array under java. util packages which are specifically provided in java for the handling of arrays. We will use various static methods of those classes to deal with arrays. This will make our coding simple and hassle-free.
Let’s have a look at those ones by one.
Method 3: Using Java Arrays.toString()
The java.util.Arrays package has a static method, Arrays.toString(). Hence, we need to import that package to use this static method. Arrays.toString() accepts an array of any primitive type (for example, int, string) as its argument and returns the output as a string type.
Example: 1
This string-type representation is a one-dimensional array. Hence, you can represent data in either rows or columns.
Code

Output:
Note the square brackets on the output. Square brackets denote the level of dimension. Thus, one pair (opening and closing pair) of the square bracket here denotes that the array is one-dimensional.
- Limitation of Arrays.toString()
Example: 2
For arrays with dimensions two or larger, we cannot use Arrays.toString() method. Below is one example code:
Code:
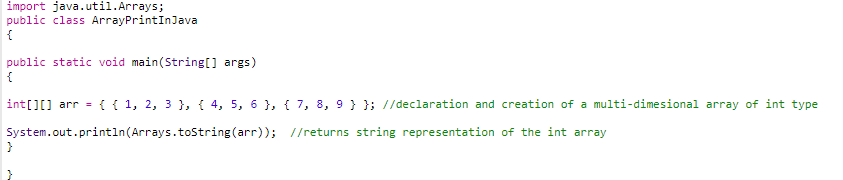
Output:
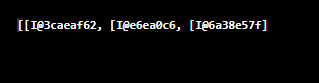
This is happening as the method does not do a deep conversion. It will only iterate on the first dimension and call each item’s toString() method. Hence we are getting undesired results. What is the solution, then? Let’s have a look at our next method.
Method 4: Using the Arrays.deep string() method
For arrays of dimension two or more, we will use the static method Arrays.deepToString(), which belongs to java.util.Arrays package. This method will do a deep conversion into a string of an array. Here also, the dimension of the array will be represented as a representation of square brackets.
Example
Three-dimensional arrays
Code:
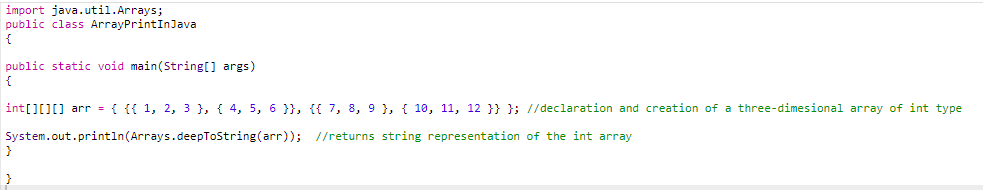
Output:
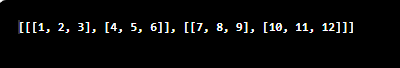
Note the square brackets representation. The square brackets are also 3 levels deep, confirming the array’s dimension as three.
Method 5: Using the Arrays.asList() method
The java.util.Arrays package has a static method Arrays.asList(). Hence, we need to import the package to use this static method.
Example
Arrays.asList() accepts an array as its argument and returns the output as a list of an array.
Code:
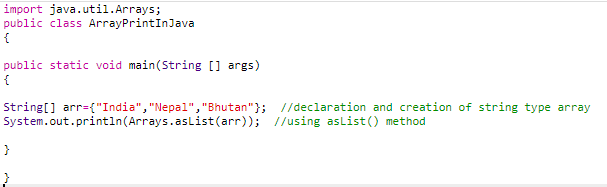
Output:

Method 6: Using the Iterator interface
The java.util.The iterator package has an interface Iterator. Hence, we must import the package to use this interface for array printing. We will create an Iterator object by calling the iterator() method. We will first convert the array into the list and then invoke the iterator() method to create the collection. Then we will traverse the collection using a while loop and print the values.
Example
As we need to convert the array into the list, we also need to use Arrays.asList() method and hence, also need to import java.util.Arrays.
Code:
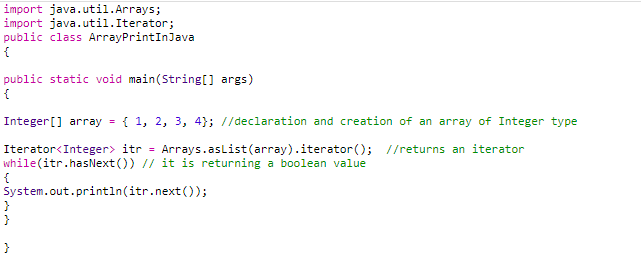
Output:

Method 7: Using ArrayList( ) method
A normal array in java is a static data structure because the initial size of the array is fixed. An ArrayList is a dynamic data structure where items can be added and removed from the list. So if you are unsure how many elements will be in your array, this dynamic data structure will save you. You need to import java.util.ArrayList package to use ArrayList() method to create an ArrayList object. Once you have a new ArrayList object, you can add/remove elements to it with the add() /remove() method:
Example
Similar to Method 6. Here also, we will convert the array into the list and invoke the iterator() method to create the collection. Then we will traverse the collection using a while loop and print the values.
Code:
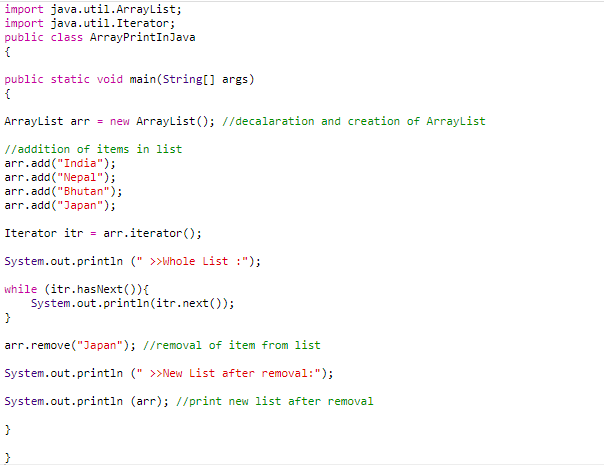
Output:

Method 8: Using Java Stream API
Example
We also can convert an array to a stream using the Arrays.stream() method. Then we iterate through the stream using foreach() and print them.
Code:
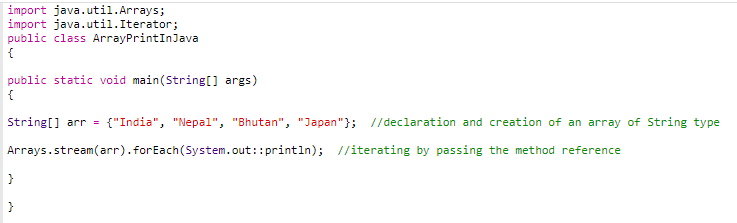
Output:

This concludes our learning for the topic “Print Array in Java.” Practice the examples by writing the codes mentioned in the above examples. Learning codes will be incomplete if you will not do hands-on by yourself. Happy coding!!
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Print Array in Java. Here we have discussed the basic concept, Techniques to Print Array in Java with different methods, codes, and outputs. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


