Updated April 13, 2023
Introduction to Preprocessor in C
The preprocessor is a processor which allows you to define abbreviations for longer constructs that can be used in the program instead of many numbers of lines of codes to less number of lines of codes. In C, the preprocessor is not a part of the compiler instead which is used to transform the code before its compiled. This is also called a macro processor because it helps you to define the code in short names called as a macro. In C, preprocessors provide few commands which begin with # (hash symbol). These preprocessor directives contain a set of statements as single macros that are used at the beginning of the program so that we can use it any number of times in the entire program.
How does Preprocessor works in C?
In C programming language, the preprocessor directives are defined using the # hash symbol. In general, when the C programs are written and then saved using .c and such files are then processed by the preprocessor, this expanded file is then compiled and the object file with .obj which are linked with linker which links these object file to generate an executable file with .exe files. So these preprocessor directives are having a set of codes that can be defined with a single name called as a macro that can be used any number of times in the entire program that is defined and declared at the beginning of the program.
Types of Preprocessor in C
There different types of preprocessor directive are as follows:
1. Macros
As discussed above, macros are a piece of code in which it contains set of statements that do a particular work or contains logic that needs to be used any number of times in the program, then we can just declare this defined macro in the program whenever needed to execute this logic in the program. This is done by the compiler whenever the compiler encounters this macro name in the program then the compiler replaces this macro name with a set of code that is defined at the beginning of the program. This is done using the #define directive to define the macro name.
Let us consider an example of how macro is defined and used in the program.
#define macro_name macro_valueCode:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 8
int main()
{
printf("To print the numbers using macro definition:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
{
printf("%d \n",i);
}
return 0;
}Output:
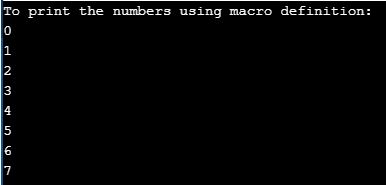
Explanation: In the above program, we can see that we have defined macro with name as “MAX” which has value as 8. This means that the program takes a macro name in the program to print the numbers until the macro value defined in the beginning.
In C, macros are classified into two different types they are Object- like and function-like macros. In object-like macros are symbolic constants that are used to define identifiers.
For example #define PI 3.14
In function-like macros are expressions that are used to perform some particular operation.
#define SQUARE (s) s*sCode:
#include<stdio.h>
#define SQUARE(s)s*s
int main()
{
printf("Welcome to Educba tutorials!\n\n");
int side = 3;
int area = SQUARE(side);
printf("The area is: %d\n", area);
return 0;
}Output:
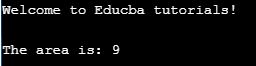
Explanation: In the above program, we are defining the macro name “SQUARE” with an argument which is known as function-like macro and the above program uses the macro known as “MAX” where the value is assigned as 8 this type of the macro is known as an object-like macro.
2. Predefined macros in C
In the C programming language, ANSI C provides predefined macros that can be used in the programs. There is a list of predefined macros and are as follows:
- _DATE_ This macro defines the current date in the program and it will be displayed in the format “MMM DD YY”.
- _FILE_ this predefined macro gives the name of the current file that the program will display.
- _TIME_ this macro also defined the current time where it is displayed in the format as “HH: MM: SS”.
- _LINE_ this macro defines the current line number of the program.
- _STDC_ this macro has ANSI standard value as 1 when compiler compiles this ANSI standard.
Let us implement all the above-predefined macros in a single program to see how they display the output.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Below are few predefined macros that are used in C:\n");
printf("This will print the current File name :%s\n", __FILE__ );
printf("This will print the current Date :%s\n", __DATE__ );
printf("This will print the current Time :%s\n", __TIME__ );
printf("This prints the current Line number :%d\n", __LINE__ );
printf("This prints the ANSI standard STDC :%d\n", __STDC__ );
return 0;
}Output:

Explanation: In the above program, we have used all 5 predefined macros of ANSI C standard and we can see the different outputs.
Conclusion
In this article, we conclude that preprocessor in C programming language, is nothing but a small piece of code which is used as a single name that is defined at the beginning of the program known as macro and this macro can be used in the entire program any number of times whenever the value of the macro is needed to use you can simply specify the macro name in the program. There two types of macros they are object-like and function-like macros. There are also few predefined macros provided by the ANSI C standards.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Preprocessor in C. Here we discuss introduction to Preprocessor in C, how does it work , types with respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


