Updated March 18, 2023
Introduction to Preprocessor Directives in C
Most often it is made as a misconception that Preprocessors or macros are part of the compilation of the program, but it is totally wrong. Preprocessor directives are the type of macros and a phase before compilation takes place. It can be said that these are some set of instructions given to compiler to perform actual compilation. They are also known as longer construct abbreviations for macros which means the value in macros gets replaced with the segment of codes. Macro is defined by a special symbol and has a symbol starting with “#” Therefore these # define is a kind of special preprocessor followed by the actual compiler. In this topic, we are going to learn about Preprocessor Directives in C.
The preprocessor has a special type of representation for its identification like any preprocessor directive initiates itself by a special symbol of “#” followed by an identifier and then the directive name. Whitespace is also allowed before and after the #. For example, # include.
There are certain fits or facilities which a C Preprocessor can provide:
- Header files: Inclusion of header files are a way in which declarations can get substituted by program syntax and program body.
- Expanding Macro: Defining macros are like abbreviating a piece of code which a C preprocessor replaces the macros with their respective definition throughout.
- Compilation by Conditions: According to various scenarios or various conditions inclusion of certain parts of the program is possible by conditional compilation.
- Line Control: If you use a program to combine or rearrange someone or more source files into an intermediate file for compilation, you can use line control to inform the compiler of where each source line originated from.
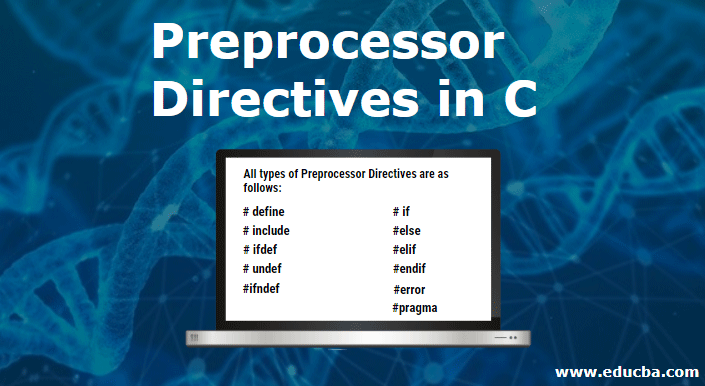
Types of Preprocessor Directives
All types of Preprocessor Directives are as follows:
- # define
- # include
- # ifdef
- # undef
- #ifndef
- # if
- #else
- #elif
- #endif
- #error
- #pragma
1. #define (Macros)
A macro is a code snippet that is replaced by some value of the code of macro. Any macro is mostly described and defined by its #define directive.
Syntax:
#define token valueThere are two types of macros:
- Function – like macros
- Object – like macros
Function – like macros
The function like-macro works almost like a function call.
For example:
#define MAX(a,b) ((a)>(b) ? (a): (b))MAX here is the Macro name.
Example:
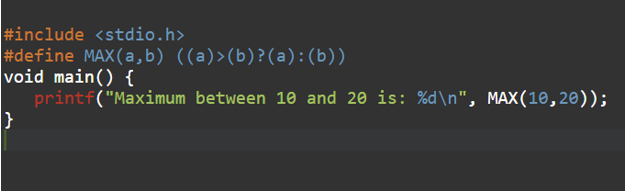
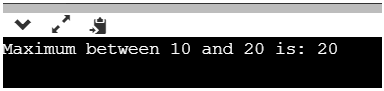
Output:
Object – like macros
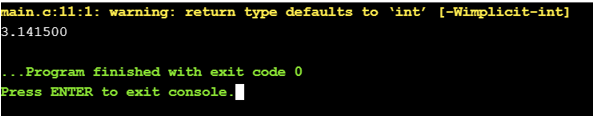
Object-like macros are the type of identifier replaced by value. It is mostly used to represent numeric constants.
#define PI 3.1415Here the value of PI will get substituted by the macro.

Output:
2. #include
There is some other functionality for the include preprocessor directive. It has its own three variants which replace the code with the current source files code.
Three variants are as follows:
- #include<file>
- #include”file”
- Include anything else
#include<file>
Searches for a file in the defined list of the system or directories as specified then searches for a standard list of system libraries.
#include”file”
This type is used for your own customized header files of the program. A search is made for a file named file first in the current directory followed by system header files and current directories of directory current file.
#include anything
This type of include preprocessor directive is used when none of the other remaining two types of the directive and its arguments don’t fit and satisfy the computation structure.
3. #Ifdef
Checks whether the macro is defined by # define or not. If yes, it will execute the code otherwise it will not.
Syntax:
#ifdef MACRO
{
Code body
}
#endif
#undef:To cancel the definition of a macro means it is undefined and is preceded with #undef directive.
Syntax:
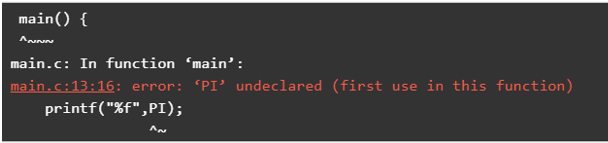
#undef token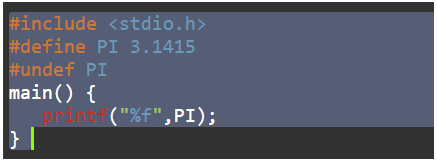
Output:
4. Ifndef
This processor checks whether #define is defined or not by #define. If yes, it executes the code.
Syntax:
#Ifndef MACRO
//code
#endif
#IfThis processor works like an if loop only, it evaluates the expression or condition. If condition id true It will execute the code otherwise not.
Syntax:
#if expression
//code
#endif
#elseThe #else preprocessor directive is used to evaluate the expression or condition if the condition of #if is false. It can be used with #if, #elif, #ifdef and #ifndef directives.
Syntax:
#if expression
//if body
#else
//else body
#endifExample:
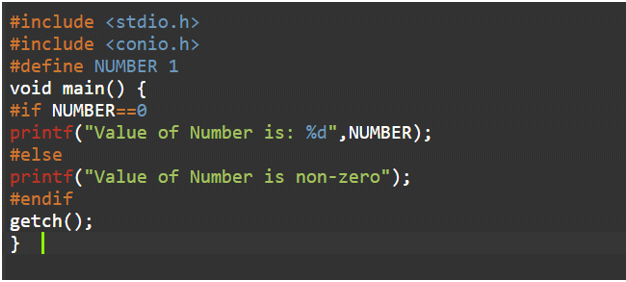
Output:

5. #Error
As its name suggests Error preprocessor directive is used to indicate an error and then the compiler gives a fatal error if error directive is found and skips the next compilation steps.
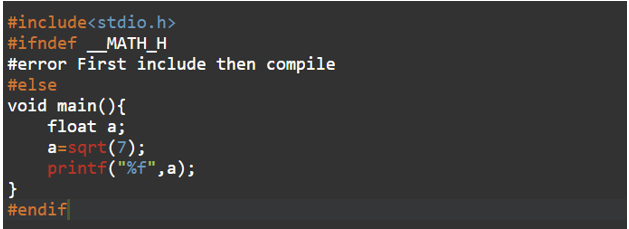
Output:

6. #pragma
It depends on the compiler as different OS and different machines provide all types of operating system feature which is used by the compiler to offer additional information to the compiler.
Syntax:
#pragma tokenExample:

Output:

Every Preprocessor has its own significance like conditional directive is used to check whether a part of the program is to be taken into consideration based on scenarios or not.
Suppose a program wants to get compiled in a specified environment with the specific config of Operating system but as soon as it goes to that phase of compilation it throws an error or it may give an invalid code merely giving its program the possibility of a big no to link the program and run it while executing. There can be another possibility also where the same source file with two different programs can make a time-consuming consistency check or its immediate data, or prints the values of data with debugging.
Also, these scenarios to be created with computation can also be used to run on one machine by using preprocessing directives.
Conclusion
The output from the C Preprocessor looks a lot like the input, except that all preprocessing directives have been replaced with blank lines or whitespaces. Different files and formats have different syntaxes saying that the start of a new file has been made or indicating a return to a file or processing should be done before compilation.
All the scenarios are used to let others know the power of C preprocessor and how it is evolving with different versions of compiler started with GCC and ANSI standards.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Preprocessor Directives in C. Here we discuss the types of Preprocessor Directives with syntax and examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more-


