Updated March 6, 2023
Definition of PowerShell Write to Console
PowerShell Write to console commands purpose are to write the Information, data, outputs, progress, verbose, variables, warnings on the console where we can use the different colors to decorate the displayed output on the console, ask for the user input, write the error messages on the console when something goes wrong with script or command, write the verbose to display the command process running the background and write information for the user attention.
Syntax:
There are various commands are used for the console display and they are as below.
Write-Host
[[-Object] <Object>]
[-NoNewline]
[-Separator <Object>]
[-ForegroundColor <ConsoleColor>]
[-BackgroundColor <ConsoleColor>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Write-Output
[-InputObject] <PSObject[]>
[-NoEnumerate]
[<CommonParameters>]
Write-Warning
[-Message] <String>
[<CommonParameters>]
Write-Verbose
[-Message] <String>
[<CommonParameters>]
Write-Information
[-MessageData] <Object>
[[-Tags] <String[]>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Read-Host
[[-Prompt] <Object>]
[-MaskInput]
[<CommonParameters>]
Read-Host
[[-Prompt] <Object>]
[-AsSecureString]
[<CommonParameters>]
How Write to console works in PowerShell?
PowerShell has various methods to write the output or the customized output on the display console. When we write the line directly on the PowerShell console it displays that string. For example,
"This is a display output"
Output:
When we concatenate the strings,
"This is a display output" + " This is a string"
Output:
So basically when we don’t use any command to display the output, it automatically pipelines the output to the Out-Host command. So the first input is similar to,
“This is a display output” | Out-Host
Output:
Again, when we use any cmdlet which displays the output on the console, it by default uses the hidden cmdlet Out-Host to display the output on the console. The Command output is pipelined to the Out-Host for the display but this process is hidden.
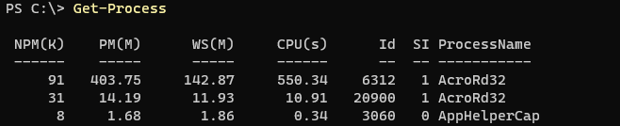
Get-Process
Output:
The above command is similar to the,
Get-Process | Out-Host
And there are other commands like Write-Host, Write-Output, Write-Error, Write-Verbose, etc shown in the syntax which can customize the output like Foreground or background color specific, user inputs, writing verbose to display on the console.
Examples
More explanation is given in the examples below.
Example #1: Using Write-Output to write the output on the console.
Write-Output command is used to write the output on the PowerShell console.
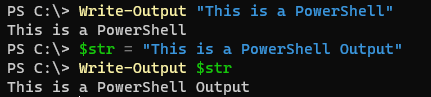
Write-Output "This is a PowerShell"
Output:
We can also store the string inside the variable and write the output.
$str = "This is a PowerShell Output"
Write-Output $str
Output:
It also takes the pipeline input.
"This is a PowerShell" | Write-Output
Output:
If you store the output of the Write-Output command to the file, it won’t display the output on the console.
Write-Output "This is a PowerShell" | Out-File C:\Temp\output.txt
Output:
This command is useful for writing on the console where we can’t use the Write-Host like, PowerShell workflows and Azure PowerShell runbooks.
Example #2: Using Write-Host to write output on the console.
The Write-Host command is to display the output on the console with the decorative background and the foreground colors.
Write-Host "This is a PowerShell"
Output:
With the different background and the foreground color.
Write-Host "This is a PowerShell" -BackgroundColor Blue -ForegroundColor White
Output:
We can also pipeline the output.
"This is a PowerShell" | Write-Host -BackgroundColor DarkGray -ForegroundColor DarkGreen
Output:
If we try to store the output to the file, this command won’t let you that but it will still display the output on the console.
Write-Host "This is a PowerShell" -BackgroundColor Blue -ForegroundColor White | Out-File C:\Temp\Hostout.txt
Output:
The above output does not store anything in the Hostout.txt file. It will be blank.
Example #3: Write-Verbose to write the output on the console.
Verbose is the message stream used to write the command processing information on the display but it needs the special parameter -Verbose to display the message. For example,
The below line will not display anything because we are not using the -Verbose parameter.
Write-Verbose "This is the PowerShell"
Output:
But once we add the -verbose parameter,
Write-Verbose "This is the PowerShell" -Verbose
Output:
Almost all the cmdlets in PowerShell use the -Verbose parameter so that we don’t need to write every information.
$services = "Spooler", "wuauserv"
Get-service $services | Stop-Service -Force -Verbose
Output:
Example #4: Write-Error to display the error on the console.
Write-Error message is useful for writing error messages on the console.
$service = 'Spooler1'
if(Get-Service -Name $service -EA Ignore){
Write-Output "$service is exist"
}
else{
Write-Error "$service doesn't exist"
}
Output:
You can also use the different parameters associated with the Write-Error command, like Category, ErrorID, Exception, etc.
Write-Error -Message "Error: Too many input values." -Category InvalidArgument -ErrorId B1
Output:
Example #5: Read-Host command to write on the console.
The Read-Host command takes the input from the user and it passes to another cmdlet. We can also use this command to display the message on the console after it is stored. For example,
Read-Host "Enter Message"
Enter Message: This is a PowerShell input
Output:
Example #6: Using System.Console class to write on the console.
We can use the .Net class System. Console to write the output on the console and for that, it uses the methods like
Write() and WriteLine().
[System.Console]::Write('This is a PowerShell')
Output:
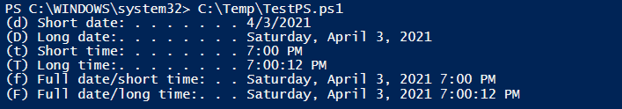
Using WriteLine() method.
[System.Console]::WriteLine( "(d) Short date: . . . . . . . {0:d}`n" +
"(D) Long date:. . . . . . . . {0:D}`n" +
"(t) Short time: . . . . . . . {0:t}`n" +
"(T) Long time:. . . . . . . . {0:T}`n" +
"(f) Full date/short time: . . {0:f}`n" +
"(F) Full date/long time:. . . {0:F}`n"
, (Get-Date))
Output:
Conclusion
PowerShell has introduced many useful commands for writing on the console and that depends on the nature of the work. For example, let say if we want to display the error message, we can set either the background color of the text to Red or use the Write-Error command. If you want to write a script that can display verbose then use the Write-Verbose command and so on.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Write to Console. Here we discuss definition, syntax, and How Write to console works in PowerShell?. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –